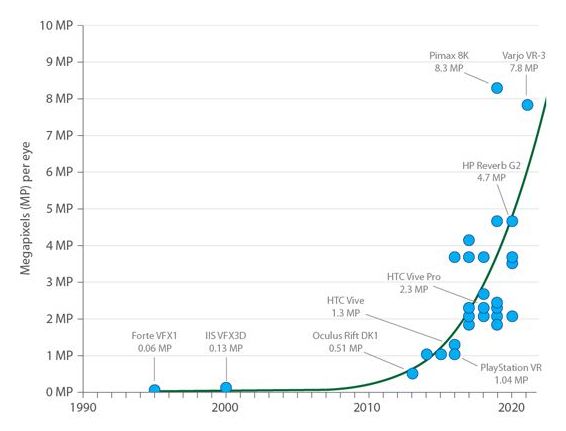
“The quality of VR headsets has improved exponentially since the 1990s. These graphs illustrate how the rapid improvement is likely to continue in the coming decades, with graphical resolutions practically indistinguishable from real life by 2040.”
Virtual reality – future trends.
The quality of virtual reality (VR) headsets has improved exponentially since the 1990s. These graphs illustrate how the rapid improvement is likely to continue in the coming decades, with graphical resolutions practically indistinguishable from real life by 2040.
Early concepts of alternative realities presented to a viewer had emerged as far back as the 19th century. However, it was not until the late 20th century that head-mounted display systems began to see practical and widespread use. Philosopher and computer scientist Jaron Lanier popularised the term “virtual reality” in the 1980s, and the first consumer headsets emerged in the 1990s.