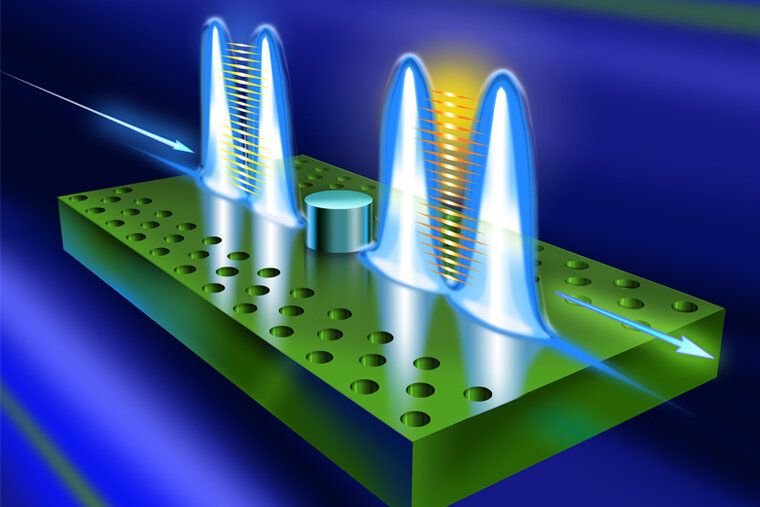
Research from the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis has found a missing piece in the puzzle of optical quantum computing.
Jung-Tsung Shen, associate professor in the Department of Electrical & Systems Engineering, has developed a deterministic, high-fidelity two-bit quantum logic gate that takes advantage of a new form of light. This new logic gate is orders of magnitude more efficient than the current technology.
“In the ideal case, the fidelity can be as high as 97%,” Shen said.