A team of scientists has used a quantum processor to create an exotic new state of matter, capturing the strange motion of quantum particles in real time.


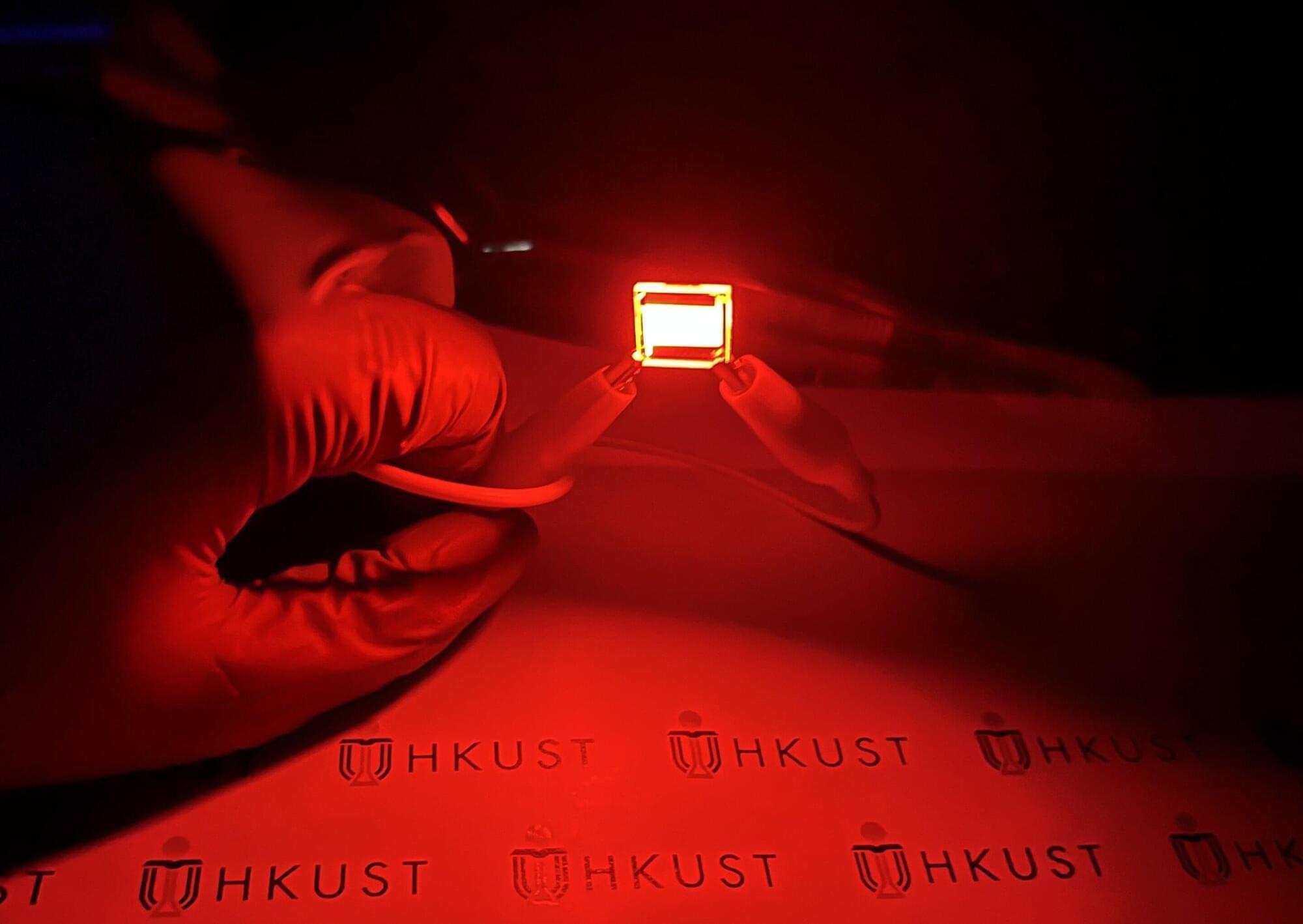
A research team led by the School of Engineering of The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has made significant advances in quantum rod light-emitting diodes (QR-LEDs), setting record-high efficiency level for red QR-LEDs. This innovation is poised to revolutionize next-generation display and lighting technologies, offering smartphone and television users a vibrant and enhanced visual experience. The research is published in the journal Advanced Materials.
LEDs have been widely used in electronic products for decades. Recent developments in quantum materials have given rise to quantum dot LEDs (QD-LEDs) and QR-LEDs. QD-LEDs offer superior color purity (color vividness) and higher brightness compared to current mainstream LEDs. However, outcoupling efficiency has now become the primary obstacle, as it sets a fundamental ceiling for external quantum efficiency (EQE), thereby hindering any further performance improvements.
Quantum rods, on which QR-LEDs are based, are a type of elongated anisotropic nanocrystals with unique optical properties that can be engineered to optimize the light emission direction and ultimately improve outcoupling efficiency. However, QR-LEDs encounter two significant technical challenges: first, the ratio of emitted to absorbed photons (photoluminescence quantum yield) is relatively low after the material absorbs photons; second, there is a substantial leakage current due to poor thin-film quality.

In the mid-nineteenth century, the Harvard College Observatory began employing women as calculators, or “human computers,” to interpret the observations their male counterparts made via telescope each night. At the outset this group included the wives, sisters, and daughters of the resident astronomers, but soon the female corps included graduates of the new women’s colleges —Vassar, Wellesley, and Smith. As photography transformed the practice of astronomy, the ladies turned from computation to studying the stars captured nightly on glass photographic plates.
The “glass universe” of half a million plates that Harvard amassed over the ensuing decades—through the generous support of Mrs. Anna Palmer Draper, the widow of a pioneer in stellar photography—enabled the women to make extraordinary discoveries that attracted worldwide acclaim. They helped discern what stars were made of, divided the stars into meaningful categories for further research, and found a way to measure distances across space by starlight. Their ranks included Williamina Fleming, a Scottish woman originally hired as a maid who went on to identify ten novae and more than three hundred variable stars; Annie Jump Cannon, who designed a stellar classification system that was adopted by astronomers the world over and is still in use; and Dr. Cecilia Helena Payne, who in 1956 became the first ever woman professor of astronomy at Harvard—and Harvard’s first female department chair.

Scientists have achieved a breakthrough in light manipulation by using topological insulators to generate both even and odd terahertz frequencies through high-order harmonic generation (HHG). By embedding these exotic materials into nanostructured resonators, the team was able to amplify light in unprecedented ways, confirming long-theorized quantum effects. This discovery opens the door to new terahertz technologies with vast implications for ultrafast electronics, wireless communication, and quantum computing.

Scientists at Indiana University have made a major advance in understanding how the universe came to exist. Their success comes from a collaboration between two large international research teams studying neutrinos, the nearly massless particles that stream endlessly through space and matter while rarely interacting with anything around them. The findings, published in Nature, bring researchers closer to solving one of science’s most profound mysteries: why the universe is filled with matter, stars, planets, and life, rather than nothing at all.
This breakthrough arose from an unprecedented partnership between two world-leading neutrino experiments: NOvA in the United States and T2K in Japan. By combining their data, scientists are gaining new insight into the hidden behavior of neutrinos and their antimatter counterparts, potentially revealing why the early universe avoided self-destruction immediately after the Big Bang.
In each experiment, beams of neutrinos are generated using powerful particle accelerators and then observed after traveling vast distances underground. Detecting them is an enormous challenge; out of countless particles, only a few interact in a way that leaves measurable traces. Using sophisticated detectors and advanced computing tools, researchers reconstruct these rare interactions to understand how neutrinos change as they move through space.
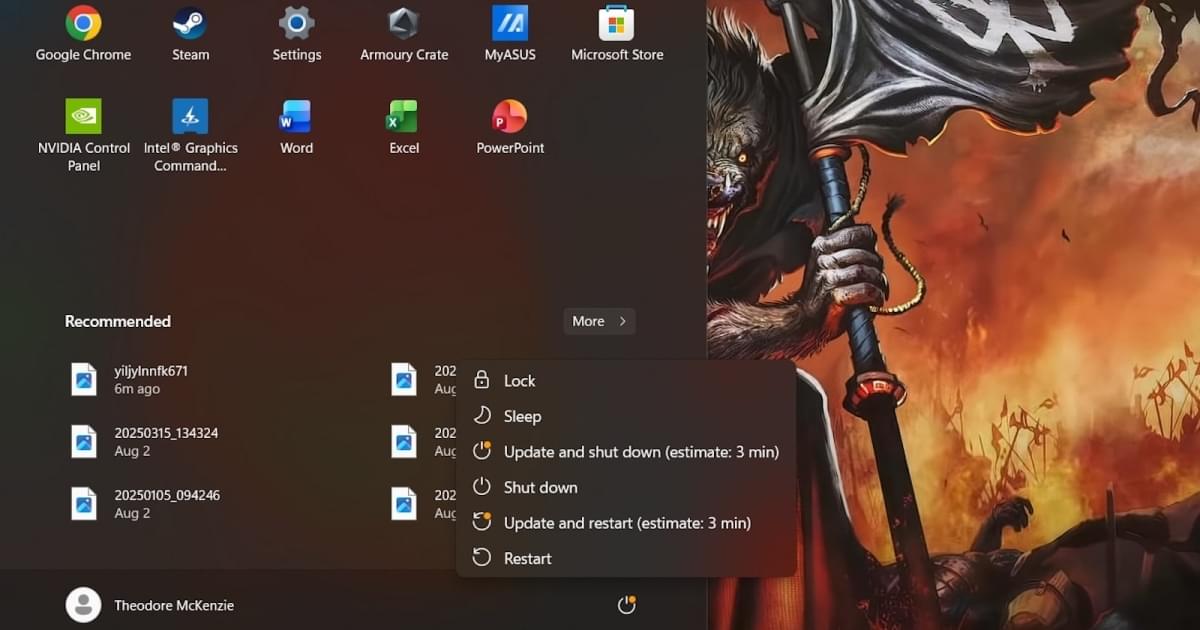
For Mac/Linux users out there who might not be familiar, the bug in question would cause your PC to randomly restart after clicking the “Update and shut down” button, leaving many users wondering if they had accidentally chosen the wrong option. While largely harmless, it became one of the most infamous errors in Microsoft’s OS due to its sheer annoyance and the company’s apparent reluctance to address it for nearly a decade, with some users reporting it as far back as eight years ago in Windows 10.
Marking the end of an era of sorts, the KB5067036 non-security update for Windows 11 has finally resolved the bug, with Microsoft fixing the “underlying issue” that prevented the “Update and shut down” button from actually shutting down your PC. Moreover, the new version also tackles the bug that could cause Windows Update to fail with error 0x800f0983, hopefully making the process of updating your PC a bit less cumbersome.
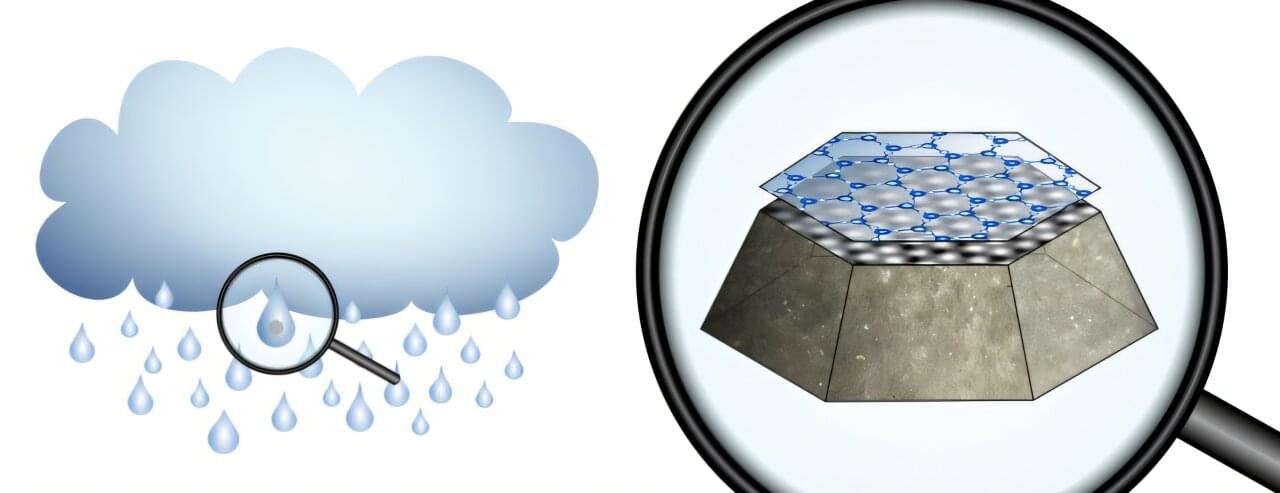

No one can control the weather, but certain clouds can be deliberately triggered to release rain or snow. The process, known as cloud seeding, typically involves dispersing small silver iodide particles from aircraft into clouds. These particles act as seeds on which water molecules accumulate, forming ice crystals that grow and eventually become heavy enough to fall to the ground as rain or snow.
Until now, the microscopic details of this process have remained unclear. Using high-resolution microscopy and computer simulations, researchers at TU Wien have investigated how silver iodide interacts with water at the atomic scale.
Their findings, published in Science Advances, reveal that silver iodide exposes two fundamentally different surfaces, but only one of them promotes ice nucleation. The discovery deepens our understanding of how clouds form rain and snow and may guide the design of improved materials for inducing precipitation.
An amazing paper (link:) where functional ultrasound imaging (fUSI) is used to explore how brain activity in the lateral intraparietal cortex (LIP) can predict visual saccades (eye movements) in two monkeys. An impressive array of computational analyses are used to extract insights from the imaged regions. Indeed, predictive models developed by the authors remained fairly stable over the course of up to 900 days! I happen to know two of the authors (Sumner L Norman and Mikhail Shapiro): congratulations to them and their colleagues on this excellent publication!
Our results demonstrate that PPC contains subregions tuned to different directions. These tuned voxels were predominately within LIP and grouped into contiguous mesoscopic subpopulations. Multiple subpopulations existed within a given coronal plane, i.e., there were multiple preferred directions in each plane. A rough topography exists where anterior LIP had more voxels tuned to contralateral downwards saccades and posterior LIP had more voxels tuned to contralateral upwards saccades. These populations remained stable across more than 100–900 days.
We observed large effect sizes with changes in CBV on the order of 10–30% from baseline activity (Fig. 3). This is much larger than observed with BOLD fMRI where the effect size was ~0.4–2% on similar saccade-based event-related tasks27,32. Our results support a growing evidence base that establishes fUSI as a sensitive neuroimaging technique for detecting mesoscopic functional activity in a diversity of model organisms, including pigeons, rats, mice, nonhuman primates, ferrets, and infant and adult humans23,24,25,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40.
Several studies have reported a patchiness in direction selectivity with many neighboring neurons tuned to approximately the same direction followed by an abruption to a patch of a different preferred direction13,14,41. These results match very closely with the results observed in this study where we found clusters within LIP tightly tuned to one direction with differently tuned clusters in close proximity within a given plane. These results further emphasize the high spatial resolution of fUSI for functional mapping of neuronal activity. These results also closely match a previous study that used fUSI to identify the tonotopic mapping of the auditory cortex and inferior colliculus in awake ferrets where the authors found a functional resolution of 100 µm for voxel responsiveness and 300 µm for voxel frequency tuning34.
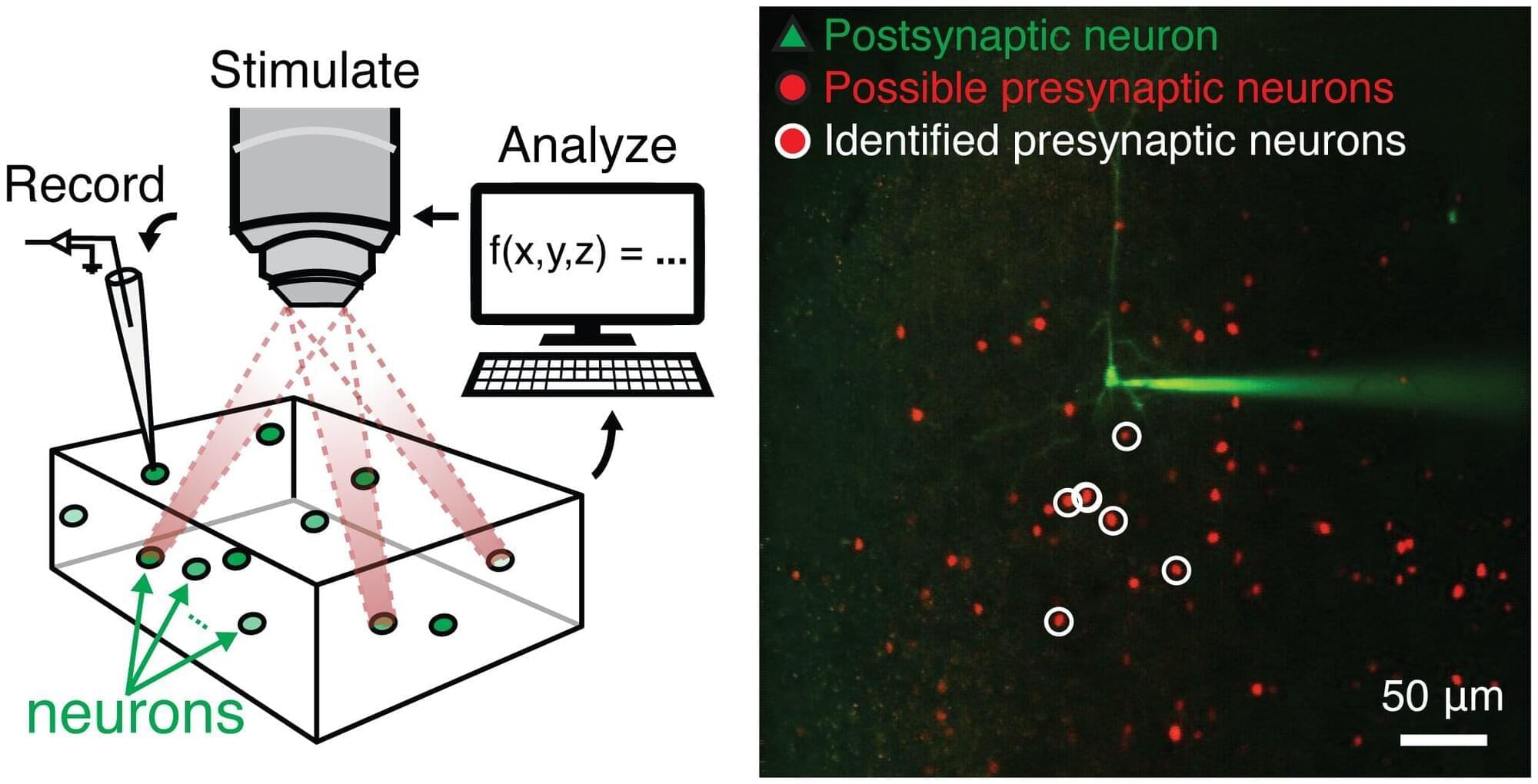
Recent technological advances have opened new possibilities for neuroscience research, allowing researchers to map the brain’s structure and synaptic connectivity (i.e., the junctions via which neurons communicate with each other) with increasing precision.
Despite these developments, most widely employed methods to image synaptic connectivity are slow and fail to precisely record changes in the connections between neurons in vivo, or in other words, while animals are awake and engaging in specific activities.
Two different research groups, one based at Columbia University and UC Berkeley, and the other at the Vision Institute of Sorbonne University in Paris, introduced a promising approach to study synapses in vivo. Their proposed mapping strategies, outlined in two Nature Neuroscience papers, combine holographic optogenetics, a method to selectively and precisely stimulate or silence specific neuron populations, with computational techniques.
