Quantum computing is no longer just for physicists — it’s for anyone who wants to push the boundaries of what’s computationally possible, thanks to open source.



Researchers have created gyromorphs, a new material that controls light more effectively than any structure used so far in photonic chips.
These hybrid patterns combine order and disorder in a way that stops light from entering from any angle. The discovery solves major limitations found in quasicrystals and other engineered materials. It may open the door to faster, more efficient light-powered computers.
Light-based computers and the need for better materials.

Gate-all-around (GAA) nanosheet field-effect transistors (FETs) based on 2D semiconductors hold promise to complement silicon in future integrated circuits. Here, the authors report the wafer-scale growth of high-κ dielectric/semiconductor β-Bi2SeO5/Bi2O2Se/α-Bi2SeO5 heterostructures and their application for high performance 2D GAA FETs.

Over the past decades, physicists and quantum engineers introduced a wide range of systems that perform desired functions leveraging quantum mechanical effects. These include so-called quantum sensors, devices that rely on qubits (i.e., units of quantum information) to detect weak magnetic or electric fields.
Researchers at the HUN-REN Wigner Research Center for Physics, the Beijing Computational Science Research Center, the University of Science and Technology of China and other institutes recently introduced a new quantum sensing platform that utilizes silicon carbide (SiC)-based spin qubits, which store quantum information in the inherent angular momentum of electrons. This system, introduced in a paper published in Nature Materials, operates at room temperature and measures qubit signals using near-infrared light.
“Our project began with a puzzle,” Adam Gali, senior author of the paper told Phys.org. “Quantum defects that sit just a few nanometers below a surface are supposed to be fantastic sensors—but in practice, they pick up a lot of ‘junk’ signals from the surface itself. This is especially true in SiC. Its standard oxide surface is full of stray charges and spins, and those produce noise that overwhelms the quantum defects we actually want to use for sensing. We wanted to break out of this limitation.”
A new paper published in Nature Communications could put scientists on the path to understanding one of the wildest, hottest, and most densely packed places in the universe: a neutron star.
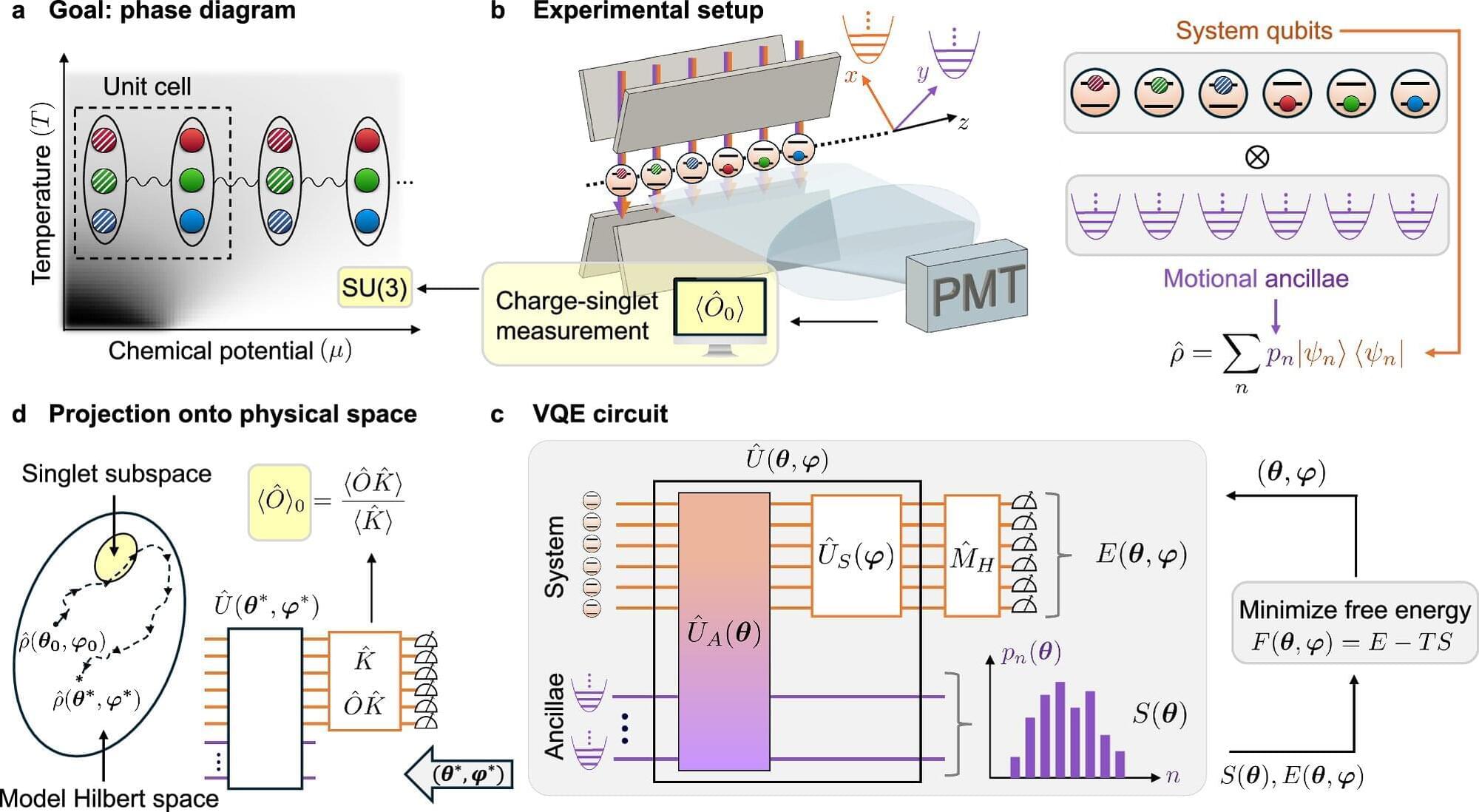
Christine Muschik, a faculty member at the University of Waterloo Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC) and a research associate faculty member at Perimeter Institute is part of a U.S.–Canadian research group using a quantum computer to build on a theory of quantum chromodynamics that describes how different varieties of quarks and gluons (the most fundamental bits of nature) interact in nuclei.
To really understand the behavior of the quark-gluon plasma in extreme conditions like the beginning of the universe, or the inside of a neutron star, scientists need a map, a so-called “phase diagram” to describe the phase transitions in those conditions that are so extreme—so dense and complex—that classical computer simulations of the models will fail.
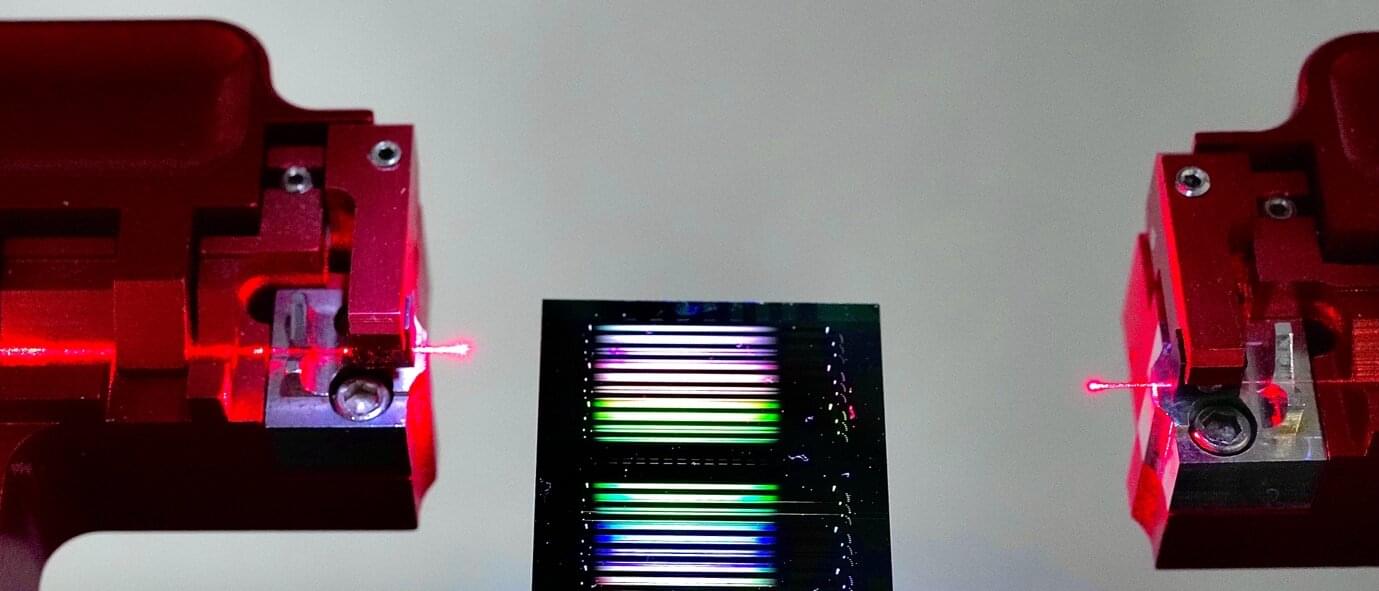

Researchers at the University of Sydney have cracked a long-standing problem in microchip-scale lasers by carving tiny “speed bumps” into the devices’ optical cavity in their quest to produce exceptionally “clean” light. This exquisitely narrow spectrum light could be used in future quantum computers, advanced navigation systems, ultra-fast communications networks and precision sensors.
In a new study published in APL Photonics, the team shows how to eliminate a critical source of noise in Brillouin lasers, a special class of light source known for its extraordinary purity, producing an ultranarrow spectrum that is almost a perfect single wavelength (or color) of light.
Light produced from sources like lightbulbs have a broad wavelength spectrum and are fine for everyday use but are too “noisy” for precision scientific purposes, where lasers are needed.

High‑energy physics has always been one of the main drivers of progress in superconducting science and technology. None of the flagship accelerators that have shaped modern particle physics could have succeeded without large‑scale superconducting systems. CERN continues to lead the efforts in this field. Its next accelerator, the High‑Luminosity LHC, relies on high-grade superconductors that were not available in industry before they were developed for high-energy physics. Tomorrow’s colliders will require a new generation of high‑temperature superconductors (HTS) to be able to realise their research potential with improved energy efficiency and long‑term sustainability.
Beyond the physics field, next‑generation superconductors have the potential to reshape key technological sectors. Their ability to transmit electricity without resistance, generate intense magnetic fields and operate efficiently at high temperatures makes them suitable for applications in fields as diverse as healthcare, mobility, computing, novel fusion reactors, zero‑emission transport and quantum technologies. This wide range of applications shows that advances driven by fundamental physics can generate broad societal impact far beyond the laboratory.
The Catalysing Impact – Superconductivity for Global Challenges event seeks to accelerate the transition from science to societal applications. By bringing together top-level researchers, industry leaders, policymakers and investors, the event provides a structured meeting point for technical expertise and strategic financing. Its purpose is not simply to present progress but to build bridges across sectors, disciplines and funding landscapes in order to move superconducting technologies from early demonstrations to impactful applications.

Before the Internet became widely known as a global tool for terrorists, one perceptive U.S. citizen recognized its ominous potential. Armed with clear evidence of computer espionage, he began a highly personal quest to expose a hidden network of spies that threatened national security. But would the authorities back him up? Cliff Stoll’s dramatic firsthand account is “a computer-age detective story, instantly fascinating [and] astonishingly gripping” (Smithsonian).
Cliff Stoll was an astronomer turned systems manager at Lawrence Berkeley Lab when a 75-cent accounting error alerted him to the presence of an unauthorized user on his system. The hacker’s code name was “Hunter” — a mysterious invader who managed to break into U.S. computer systems and steal sensitive military and security information. Stoll began a one-man hunt of his spying on the spy. It was a dangerous game of deception, broken codes, satellites, and missile bases — a one-man sting operation that finally gained the attention of the CIA…and ultimately trapped an international spy ring fueled by cash, cocaine, and the KGB.