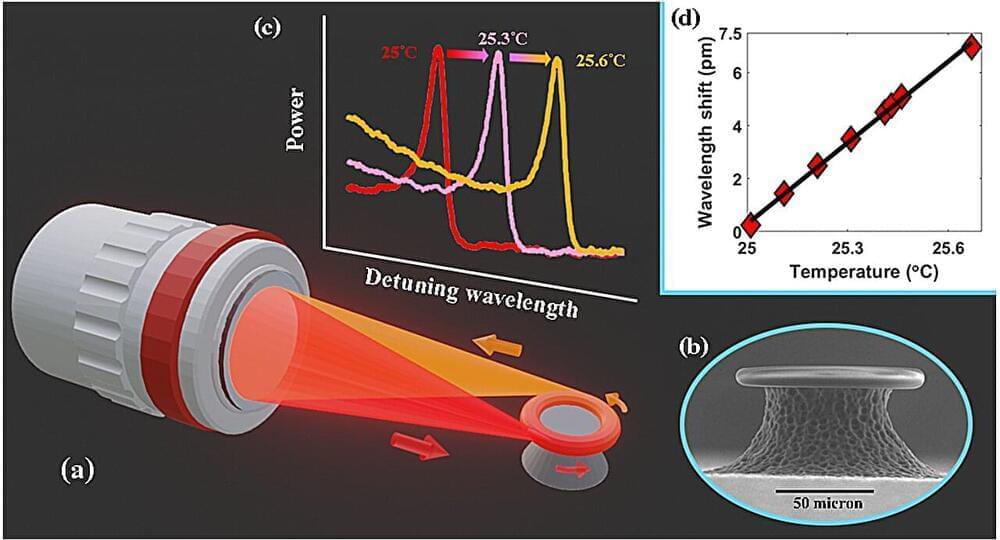
Two-terminal devices are electronic components connected to electrical circuits via two electrical terminals. Although these components are the key building blocks of most existing devices, they can limit a system’s performance and functions.


Now, new research reveals yet another engineering feat of this ancient animal’s structure: its ability to filter feed using only the faint ambient currents of the ocean depths, no pumping required.
This discovery of natural ‘“zero energy” flow control by an international research team co-led by University of Rome Tor Vergata and NYU Tandon School of Engineering could help engineers design more efficient chemical reactors, air purification systems, heat exchangers, hydraulic systems, and aerodynamic surfaces.
In a study published in Physical Review Letters, the team found through extremely high-resolution computer simulations how the skeletal structure of the Venus flower basket sponge (Euplectella aspergillum) diverts very slow deep sea currents to flow upwards into its central body cavity, so it can feed on plankton and other marine detritus it filters out of the water.

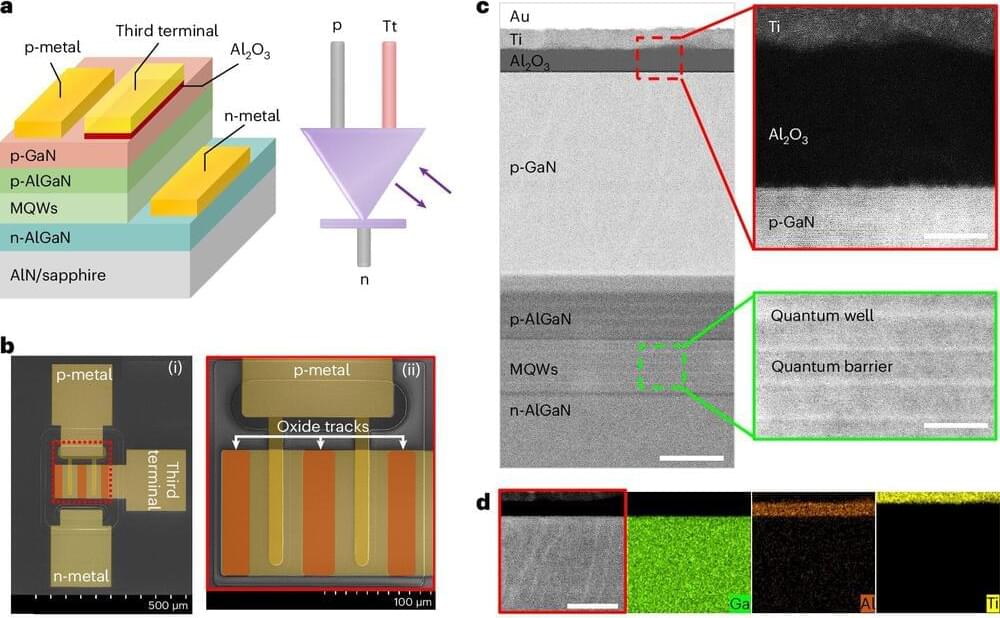
Researchers at the University of Bristol have made an important breakthrough in scaling quantum technology by integrating the world’s tiniest quantum light detector onto a silicon chip. The paper, “A Bi-CMOS electronic photonic integrated circuit quantum light detector,” was published in Science Advances.
For quantum computers to go from research curiosities to practically useful devices, researchers need to get their errors under control. New research from Microsoft and Quantinuum has now taken a major step in that direction.
Today’s quantum computers are stuck firmly in the “noisy intermediate-scale quantum” (NISQ) era. While companies have had some success stringing large numbers of qubits together, they are highly susceptible to noise which can quickly degrade their quantum states. This makes it impossible to carry out computations with enough steps to be practically useful.
While some have claimed that these noisy devices could still be put to practical use, the consensus is that quantum error correction schemes will be vital for the full potential of the technology to be realized. But error correction is difficult in quantum computers because reading the quantum state of a qubit causes it to collapse.

Genomics is revolutionizing medicine and science, but current approaches still struggle to capture the breadth of human genetic diversity. Pangenomes that incorporate many people’s DNA could be the answer, and a new project thinks quantum computers will be a key enabler.
When the Human Genome Project published its first reference genome in 2001, it was based on DNA from just a handful of humans. While less than one percent of our DNA varies from person to person, this can still leave important gaps and limit what we can learn from genomic analyses.
That’s why the concept of a pangenome has become increasingly popular. This refers to a collection of genomic sequences from many different people that have been merged to cover a much greater range of human genetic possibilities.


A quantum internet would essentially be unhackable. In the future, sensitive information—financial or national security data, for instance, as opposed to memes and cat pictures—would travel through such a network in parallel to a more traditional internet.
Of course, building and scaling systems for quantum communications is no easy task. Scientists have been steadily chipping away at the problem for years. A Harvard team recently took another noteworthy step in the right direction. In a paper published this week in Nature, the team says they’ve sent entangled photons between two quantum memory nodes 22 miles (35 kilometers) apart on existing fiber optic infrastructure under the busy streets of Boston.
“Showing that quantum network nodes can be entangled in the real-world environment of a very busy urban area is an important step toward practical networking between quantum computers,” Mikhail Lukin, who led the project and is a physics professor at Harvard, said in a press release.