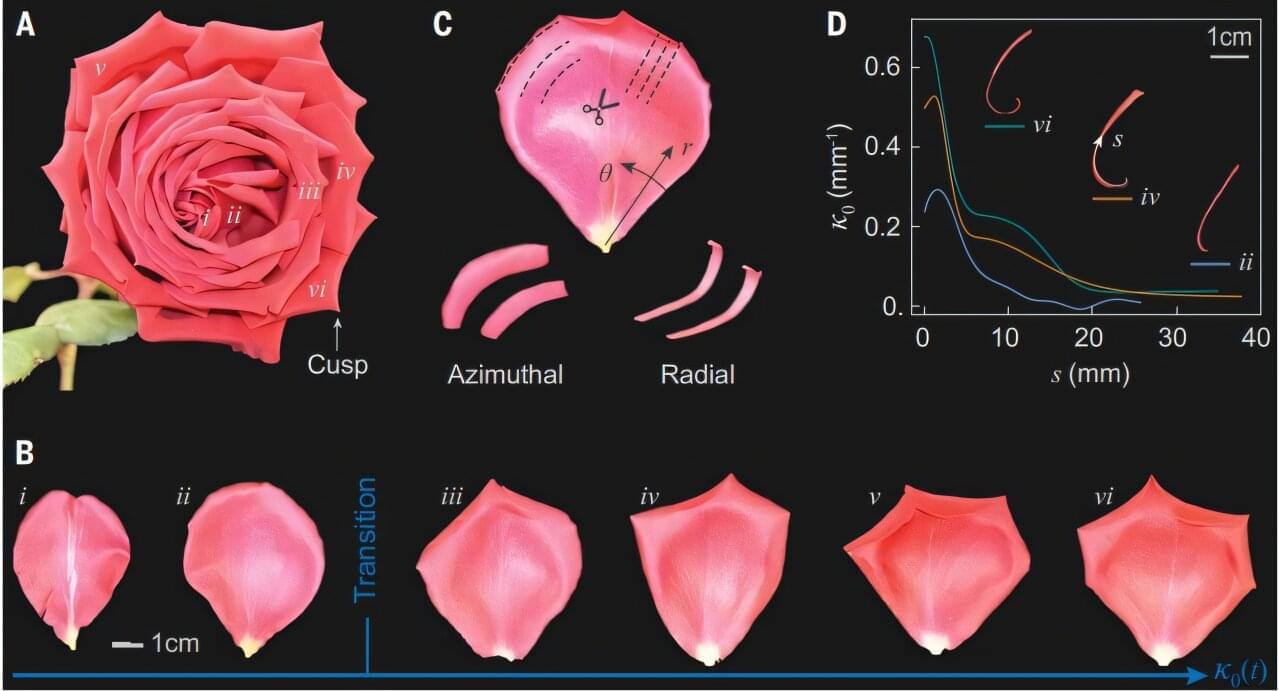
Four physicists at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, in Israel, have unraveled the mechanical process behind the growth of roses as they blossom into their unique shape. In their study published in the journal Science, Yafei Zhang, Omri Cohen, Michael Moshe and Eran Sharon adopted a multipronged approach to learn the secrets behind rose blossom growth. Qinghao Cui and Lishuai Jin, with the University of Hong Kong have published a Perspective piece in the same journal issue outlining the work.
Roses have been prized for their beauty and sweet aromas for thousands of years, but until now, the mechanics behind rose growth have not been explored. To gain a better understanding of the process, the research team undertook a three-pronged approach. First, they conducted a theoretical analysis of the process. Then they created computer models to simulate the ways the flowers might grow and bloom; finally, they created real-world bendable plastic disks to simulate petals and the possible ways they could grow given the constraints of real roses.
They found that the shape of the petals is strongly influenced by the frustration known as the Mainardi-Codazzi-Peterson incompatibility, in which geometric compatibility conditions inherent on a surface made of a particular material are violated, leading to forces that generate rolling and sharp edges.