Scientists have found that a process called neurotransmitter switching—where neurons alter their chemical signals—plays a role in the development of autism-related traits.



YORKTOWN HEIGHTS, N.Y., Nov. 13, 2024 /PRNewswire/ — Today at its inaugural IBM Quantum Developer Conference, IBM (NYSE: IBM) announced quantum hardware and software advancements to execute complex algorithms on IBM quantum computers with record levels of scale, speed, and accuracy.
IBM Quantum Heron, the company’s most performant quantum processor to-date and available in IBM’s global quantum data centers, can now leverage Qiskit to accurately run certain classes of quantum circuits with up to 5,000 two-qubit gate operations. Users can now use these capabilities to expand explorations in how quantum computers can tackle scientific problems across materials, chemistry, life sciences, high-energy physics, and more.

A research team reports in the journal Angewandte Chemie that gamma radiation can transform methane into a diverse range of products at room temperature, including hydrocarbons, oxygenated molecules, and amino acids. This reaction likely plays a significant role in the formation of complex organic molecules in the universe—and may even contribute to the origins of life. Additionally, it presents new opportunities for industrially converting methane into high-value products under mild conditions.
With these research results, the team led by Weixin Huang at the University of Science and Technology of China (Hefei) has contributed to our fundamental understanding of the early development of molecules in the universe.
“Gamma rays, high-energy photons commonly existing in cosmic rays and unstable isotope decay, provide external energy to drive chemical reactions of simple molecules in the icy mantles of interstellar dust and ice grains,” states Huang. “This can result in more complex organic molecules, presumably starting from methane (CH4), which is widely present throughout the interstellar medium.”
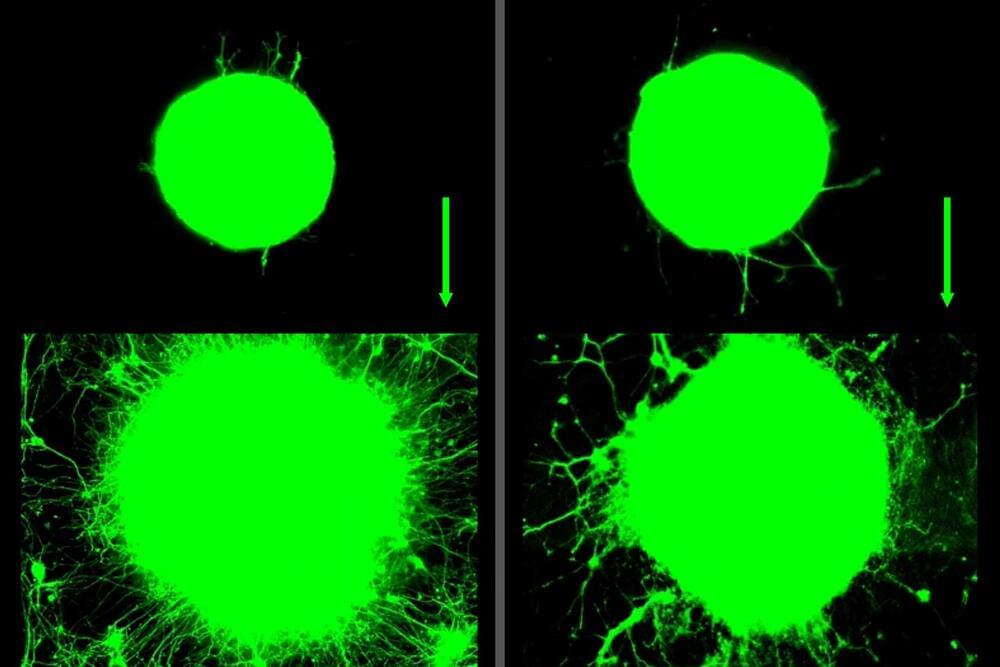
This study explores how muscle contractions, such as those that occur during exercise, influence motor neurons—the cells responsible for controlling muscle movement.
There’s no doubt that exercise does a body good. Regular activity not only strengthens muscles but can bolster our bones, blood vessels, and immune system.
Now, MIT engineers have found that exercise can also have benefits at the level of individual neurons. They observed that when muscles contract during exercise, they release a soup of biochemical signals called myokines.
In the presence of these muscle-generated signals, neurons grew four times further compared to neurons that were not exposed to myokines. These cellular-level experiments suggest that exercise can have a significant biochemical effect on nerve growth.

Summary: Researchers found that exercise promotes neuron growth through both biochemical signals (myokines) and physical stretching. Muscle cells, when contracted, release myokines that boost neuron growth and maturity. Furthermore, neurons that were “exercised” through mechanical movement grew just as much as those exposed to myokines.
These findings reveal the dual role of exercise in stimulating nerves, offering hope for developing therapies targeting nerve repair and neurodegenerative diseases. This research opens new avenues in treating nerve damage through “exercise as medicine.”
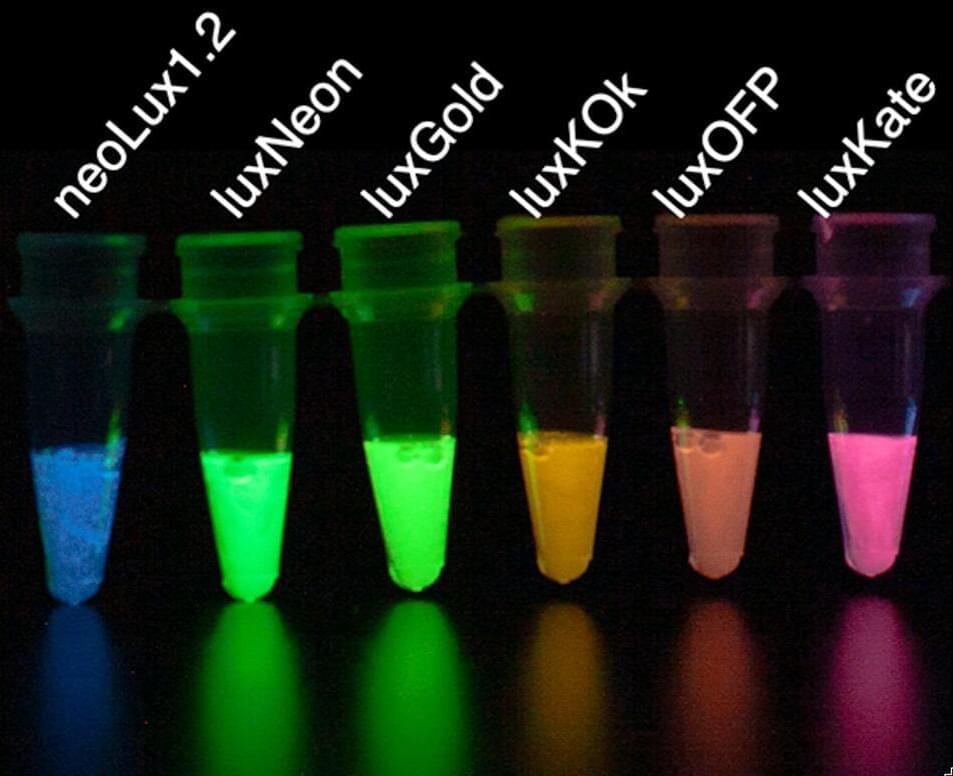

Bioluminescence is the natural chemical process of light creation in some living creatures that makes fireflies flicker and some jellyfish glow. Scientists have long been interested in borrowing the secrets of these animals’ light-producing genes to create similar effects in vertebrates, for a variety of biomedical applications.
“Solar system formation models using the new solar composition successfully reproduce the compositions of large Kuiper Belt objects (KBOs) and carbonaceous chondrite meteorites, in light of the newly returned Ryugu and Bennu asteroid samples from JAXA’s Hayabusa-2 and NASA’s OSIRIS-REx missions.”
To make this discovery, the team combined new measurements of solar neutrinos and data about the solar wind composition from NASA’s Genesis mission, together with the abundance of water found in primitive meteorites that originated in the outer solar system. They also used the densities of large KBOs such as Pluto and its moon Charon, as determined by NASA’s New Horizons mission.
“This work provides testable predictions for future helioseismology, solar neutrino and cosmochemical measurements, including future comet sample return missions,” Truong said.

Carbon is a gregarious little atom, bending over backwards to link with a wide variety of elements in what is collectively referred to as organic chemistry. Life itself wouldn’t be possible without carbon’s knack for making connections.
Yet even this friendly fellow has its limits. Take Bredt’s rule for instance, which says stable two-laned connections known as covalent double bonds won’t form adjacent to any V-shaped bridges that happen to form across ‘bicyclic’ molecules.
Now a team of chemists from the University of California, Los Angeles has uncovered a solution that violates Bredt’s century-old rule. This encourages future drug research to explore the use of molecules that we thought could not exist.
Google DeepMind has unexpectedly released the source code and model weights of AlphaFold 3 for academic use, marking a significant advance that could accelerate scientific discovery and drug development. The surprise announcement comes just weeks after the system’s creators, Demis Hassabis and John Jumper, were awarded the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their work on protein structure prediction.
AlphaFold 3 represents a quantum leap beyond its predecessors. While AlphaFold 2 could predict protein structures, version 3 can model the complex interactions between proteins, DNA, RNA, and small molecules — the fundamental processes of life. This matters because understanding these molecular interactions drives modern drug discovery and disease treatment. Traditional methods of studying these interactions often require months of laboratory work and millions in research funding — with no guarantee of success.
The system’s ability to predict how proteins interact with DNA, RNA, and small molecules transforms it from a specialized tool into a comprehensive solution for studying molecular biology. This broader capability opens new paths for understanding cellular processes, from gene regulation to drug metabolism, at a scale previously out of reach.

“This paper shows a fun way to make carbon-neutral fuels and chemicals,” said Dr. Curtis P. Berlinguette. “We’ll need plastic on Mars one day, and this technology shows one way we can make it there.”
Can we use the planetary environment of Mars to help power a future colony on the Red Planet? This is what a recent study published in Device hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated how current thermoelectric generators—which can operate in a myriad of environments—on Mars could convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into fuel and other chemicals that can be used for a future Mars colony. This study holds the potential to help scientists, engineers, and the public better understand how a future Mars colony could be managed and operated without constant need for resupply from Earth.
“This is a harsh environment where large temperature differences could be leveraged to not only generate power with thermoelectric generators, but to convert the abundant CO2 in Mars’ atmosphere into useful products that could supply a colony,” said Dr. Abhishek Soni, who is a postdoctoral research fellow at the University of British Columbia (UBC) and lead author of the study.
For the study, the researchers conducted laboratory experiments with a CO2 electrolyzer, which are powered by thermoelectric generators, and a hot plate and ice bath, which obviously provide a wide range of temperatures to see how the CO2 electrolyzer converts CO2 to useful chemicals. In the end, the researchers found when the temperature difference between the ice bath and hot plate was 104 degrees Fahrenheit (40 degrees Celsius), the electrolyzer was still able to successfully convert CO2 to carbon monoxide (CO).