How cells eliminate inefficient ribosomes.
Inside every cell, ribosomes act as tiny but vital factories that build proteins, translating genetic information into the molecules that sustain life. Although ribosomes share the same basic structure, not all of them work with equal precision. Until now, scientists did not fully understand how cells detect and handle ribosomes that underperform.
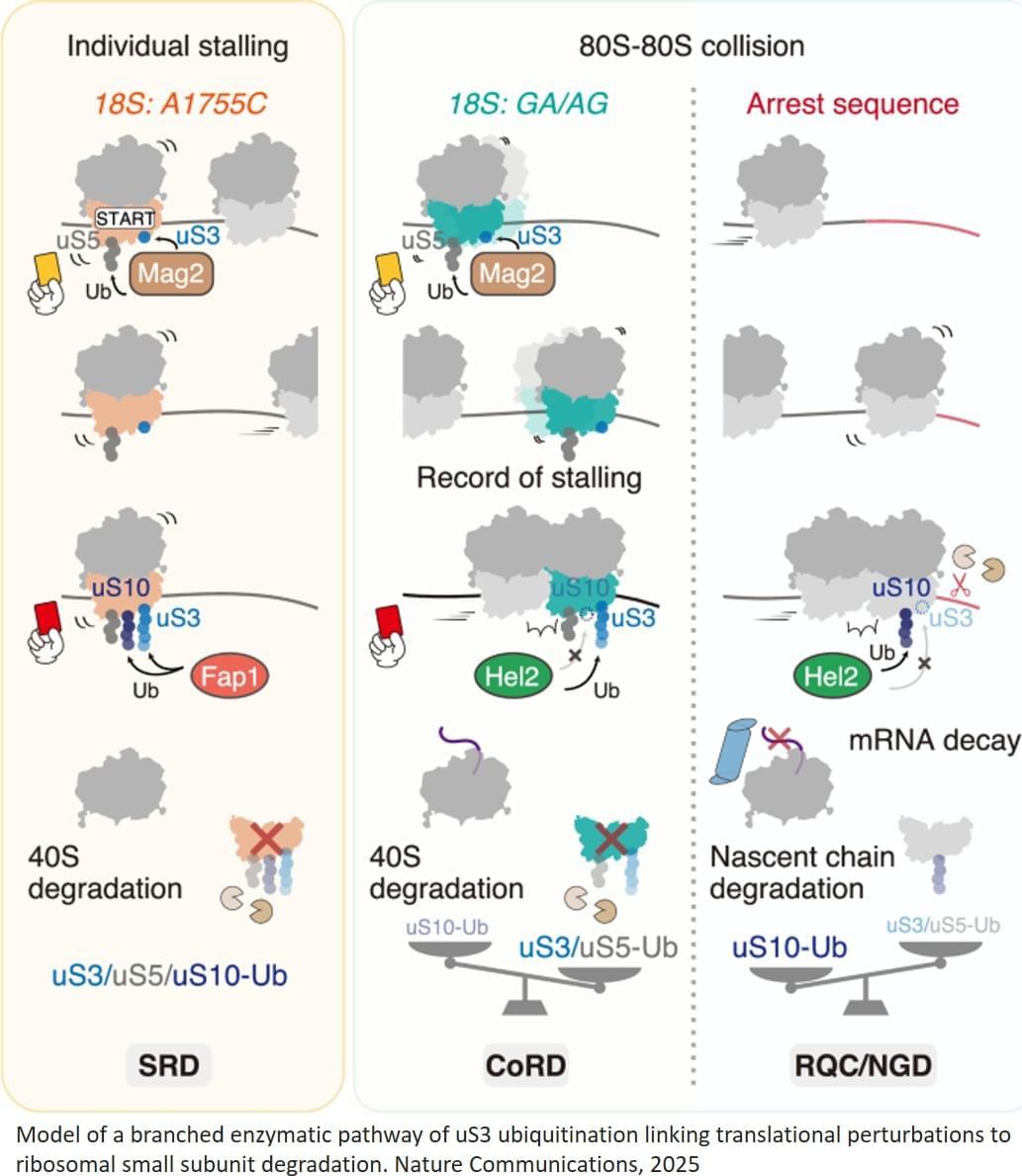
Addressing this question, a team of researchers has identified a quality control mechanism that ensures only the most competent ribosomes survive. Their study, published in Nature Communications shows that ribosomes compete during protein synthesis. When translation is disrupted, the less efficient ribosomes are selectively broken down, while the stronger ones continue functioning.
Using biochemical and genetic analyses in yeast, the researchers examined how ribosomes behave when translation is disrupted. The team engineered cells to contain a functional but suboptimal ribosome variant. These slower-moving ribosomes are overtaken on messenger RNA by faster, native ribosomes, causing the two types to collide. Such ribosome-ribosome collisions activate a ubiquitination-dependent quality control pathway that selectively removes the less efficient ribosomes.
The team also explored how external factors, such as the anticancer drug cisplatin affect this process. Cisplatin, known for binding to RNA and DNA, was found to increase ribosome collisions, which in turn promoted ribosome degradation. This insight could improve understanding of how the drug acts inside cells and why it sometimes causes side effects.
The implications of this discovery extend beyond basic biology. By showing how cells maintain the quality of their protein factories, the study provides a foundation for understanding disorders caused by ribosome malfunction, known as ribosomopathies. It may also open the door to new approaches for improving the safety and effectiveness of certain drugs.