face_with_colon_three year 2022.
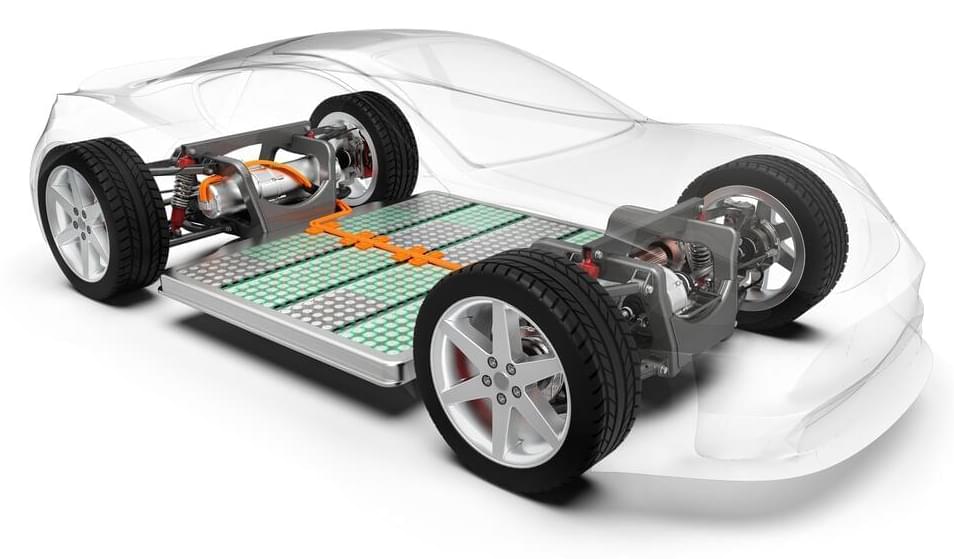
One of the biggest concerns about EVs is that the batteries will need replacing after a few years, at great expense. After all, your smartphone battery is likely to have seen better days within as little as three years. But a Tesla researcher is getting ready to kick this idea into touch once and for all, after demonstrating batteries that could potentially outlive most human beings.
Tesla enthusiasts are likely to have heard of Jeff Dahn already. He’s a professor at Dalhousie University and has been a research partner with Tesla since 2016. His focus has been to increase the energy density and lifetime of lithium-ion batteries, as well as reducing their cost. Dahn appears to have hit the motherload along with colleagues on his research team. In a paper published in the Journal of the Electrochemical Society, the group claims to have created a battery design that could last 100 years under the right conditions.
Dahn’s paper contrasts cells based on Li[Ni0.5Mn0.3Co0.2]O2 chemistry (“NMC 532”) to LiFePO4. The latter is the “Lithium Iron Phosphate” (aka LFP) chemistry that Tesla is currently using in Chinese-built standard Model 3 cars imported into Europe. The LFP chemistry has lower energy density than more widespread Lithium-Ion alternatives, but is cheaper, more durable, and allegedly safer, too. LFP can last up to 12,000 charge-discharge cycles, so beating it in this regard is no mean feat. Dahn’s NMC 532 cells showed no capacity loss after nearly 2,000 cycles. The paper extrapolates this out to imply a 100-year lifespan (they obviously haven’t been testing the battery that long).