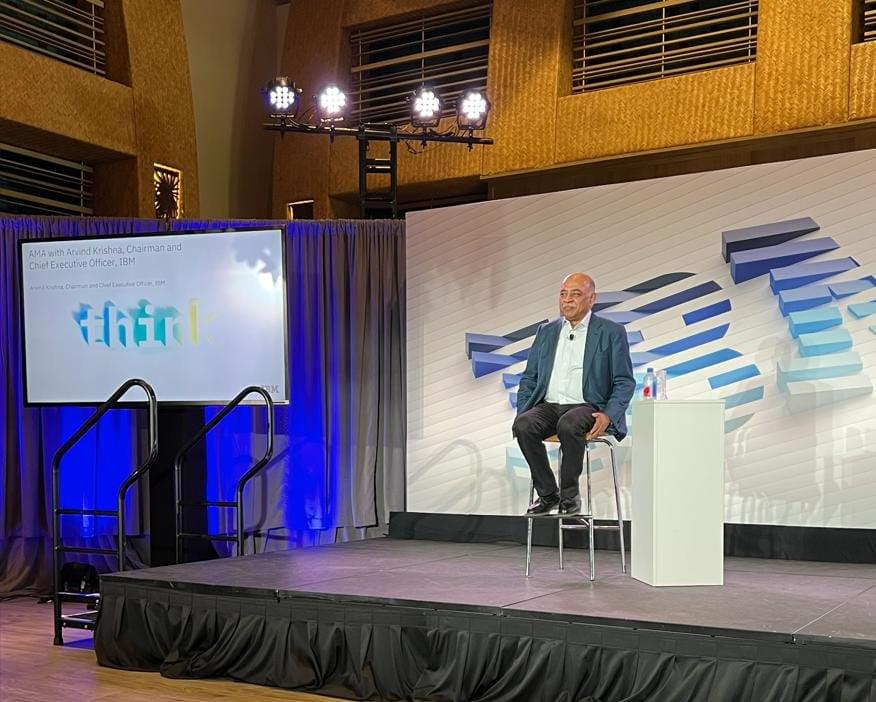
Last week, around 4,000 IBM employees, customers, and partners attended IBM Think, the company’s annual conference, to hear the latest innovations, updates, and news from IBM. This year’s event came with many announcements, but with AI in focus, its announcement of watsonx drew significant attention—with the market zeroing in on the substantial opportunities around AI.
After attending the event, and hearing from IBM executives as well as following the broad swath of recent AI and generative AI announcements, I believe that IBM’s announcement of watsonx is a significant milestone in the advancement of enterprise AI. Built on top of the Red Hat OpenShift platform, watsonx offers a full tech stack for training, deploying, and supporting AI capabilities across any cloud environment This move by IBM is indicative of the growing importance of supporting generative AI, and the potential for businesses to benefit from the ease and reliability of this technology. As I see it, this announcement is one of the more important announcements tying together much of the exciting generative AI news and analysis with the more practical connective tissues that will drive meaningful adoption in the enterprise.
Watsonx features three different components: watsonx.ai, watsonx.data, and watsonx.governance. The first component, watsonx.ai, is a design studio for base models, machine learning, and generative AI. It can be used to train, tune, and deploy AI models including IBM supplied models, open-source models, and client provided models, and is currently in preview with select IBM clients and partners, and is expected to be available to the general public in July.