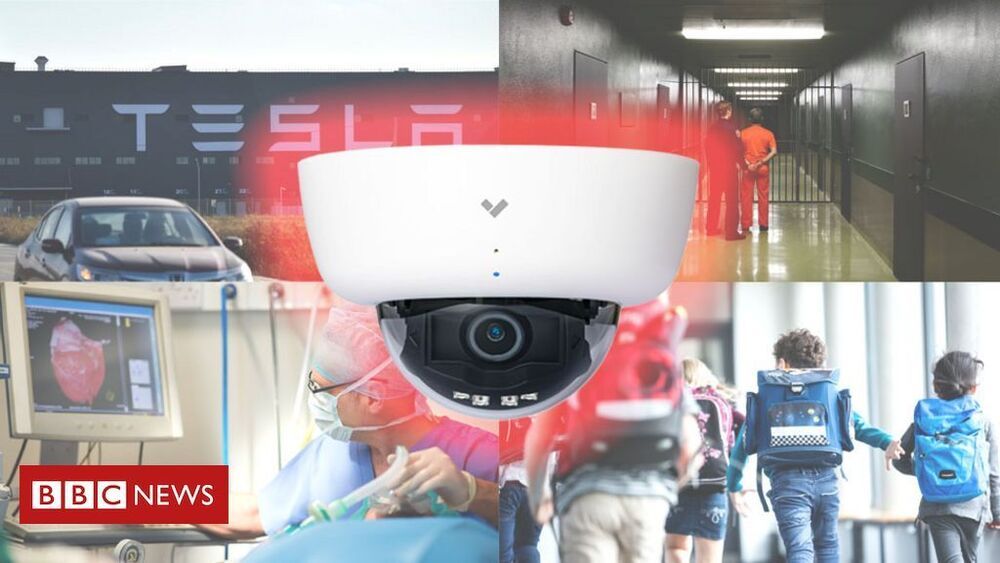
The hack exposed feeds showing the insides of offices, hospitals and businesses, including Tesla.
Category: business – Page 167
Large language models are already business propositions. Google uses them to improve its search results and language translation; Facebook, Microsoft and Nvidia are among other tech firms that make them. OpenAI keeps GPT-3’s code secret and offers access to it as a commercial service. (OpenAI is legally a non-profit company, but in 2019 it created a for-profit subentity called OpenAI LP and partnered with Microsoft, which invested a reported US$1 billion in the firm.) Developers are now testing GPT-3’s ability to summarize legal documents, suggest answers to customer-service enquiries, propose computer code, run text-based role-playing games or even identify at-risk individuals in a peer-support community by labelling posts as cries for help.
A remarkable AI can write like humans — but with no understanding of what it’s saying.
Elevators, Space Edition
Posted in business, government, military, space
Free conference covering the upcoming MOON ELEVATOR project: 9–11 March. Bringing together government, military, private industry, academia and others, this three day event is sure to be an eye opener on where we are and where we are going in the coming 5–10 years. Don’t miss out! Get your tickets free today.
- Gravitational Elevators (Lunar Space Elevator Infrastructure)
- Centripetal Elevators (Space Elevators from Earth).
We’ll look at both through the lens of.
1) hardware, 2) business, 3) outreach, and 4) framework.
The hackers started their attack in January but escalated their efforts in recent weeks, security experts say. Business and government agencies were affected.
The China National Space Administration (CNSA) on Thursday released three high-resolution images of Mars captured by the country’s Tianwen-1 probe.
http://www.cctvplus.com/news/20210304/8180114.shtml#!language=1
Welcome to subscribe us on:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/NewsContent.CCTVPLUS
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CCTV_Plus.
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/cctv-news-content.
Video on Demand: www.cctvplus.com.
If you are in demand of this video footage, please contact with our business development team via email: [email protected]
Innovating And Investing In The New Space Age — Space 2.0 — Hélène Huby, VP, Orion-ESM, Airbus Defence and Space.
Hélène Huby is Vice-President of the Orion European Service Module (Orion-ESM), at Airbus Defence & Space.
Airbus Defence & Space is a division of the Airbus Group, a European multinational aerospace corporation and the world’s largest airliner manufacturer.
The Orion-ESM is the European Space Agency’s contribution to NASA’s Orion spacecraft, which will send astronauts back to the Moon, and beyond. It provides electricity, water, oxygen and nitrogen, as well as keeping the spacecraft at the right temperature and on course.
Hélène was previously Head of Innovation at Airbus Defence & Space where she grew a portfolio of over 50 new businesses, ranging from space data-based services to electrical-powered stratospheric drones, and was responsible for setting up Airbus Ventures, and an innovation center in Silicon Valley, for the Airbus Group.
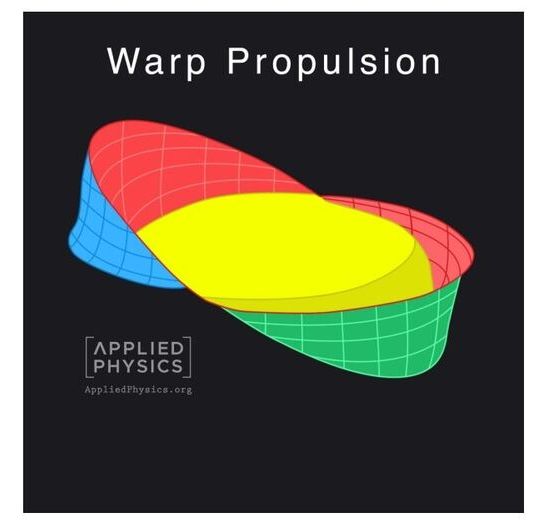
NEW YORK—(BUSINESS WIRE)—Scientists at Applied Physics are excited to announce they have recently constructed the first model of physical warp drives.
“While we still can’t break the speed of light, we don’t need to in order to become an interstellar species” Tweet this
Applied Physics is an independent group of scientists, engineers, and inventors that advise companies and governments on science and technology for both commercial and humanitarian applications.
Japanese space startup Gitai has raised a $17.1 million funding round, a Series B financing for the robotics startup. This new funding will be used for hiring, as well as funding the development and execution of an on-orbit demonstration mission for the company’s robotic technology, which will show its efficacy in performing in-space satellite servicing work. That mission is currently set to take place in 2023.
Gitai will also be staffing up in the U.S., specifically, as it seeks to expand its stateside presence in a bid to attract more business from that market.
“We are proceeding well in the Japanese market, and we’ve already contracted missions from Japanese companies, but we haven’t expanded to the U.S. market yet,” explained Gitai founder and CEO Sho Nakanose in an interview. So we would like to get missions from U.S. commercial space companies, as a subcontractor first. We’re especially interested in on-orbit servicing, and we would like to provide general-purpose robotic solutions for an orbital service provider in the U.S.”
AgeX 2020 Shareholder Meeting
Posted in biotech/medical, business
Summary of bio-tech history and technology. iTR at 26 minutes.
Annual corporate presentation from AgeX’s annual stockholder meeting in 2020, presented by Dr. Michael West.
1:39 — Mission of AgeX
7:52 — PureStem.
9:58 — UniverCyte.
13:04 — Business Strategy.
18:28 — Brown Adipose Tissue cell therapy (BAT-1)
23:52 — Vascular cell therapy (VASC-1)
25:14 — Induced Tissue Regeneration (iTR)
31:06 — 2021 milestones.
31:42 — Summary
The Aidan Meller Galley (www.aidanmeller.com) is Oxford’s longest established specialist gallery dealing in Modern, Contemporary and Old Master works.
Today we are joined by Aidan Meller, the Gallery Director, who with 20 years’ experience in the art business, works closely with private collectors, is often consulted by those who wish to begin, or further develop their collections, and is the creator of the Aidan Meller Art Prize, a valuable resource for the development of the arts.
Aidan regularly has original works in the gallery by the likes of Picasso, Matisse, Chagall, as well as older works such as John Constable, Turner and Millais, was involved in a discovery of a collection of Pre-Raphaelite cartoons for stained glass, is working with other experts in the field of scientific procedures for the authentication of artwork, and has been interviewed on a variety of current affair topics including the exhumation of Salvador Dali.
On today’s show we are going to be focusing on a rather new artist in the Meller portfolio, and that would be Ai-Da (www.ai-darobot.com), the world’s first ultra-realistic, humanoid, artificial intelligence (AI) robot artist, who makes drawings, painting, and sculptures.
Ai-Da is named after the mathematician Ada Lovelace, combines the latest in computing, robotics, and AI innovations, including those developed at Leeds University, and University of Oxford, and represents a fascinating milestone in AI innovation, human collaboration and creativity.