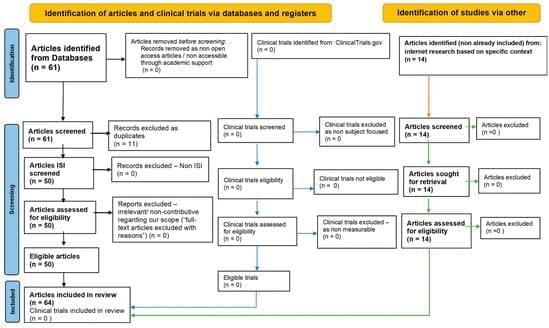
The intricate relationship between hydrogen sulfide (H2S), gut microbiota, and sirtuins (SIRTs) can be seen as a paradigm axis in maintaining cellular homeostasis, modulating oxidative stress, and promoting mitochondrial health, which together play a pivotal role in aging and neurodegenerative diseases. H2S, a gasotransmitter synthesized endogenously and by specific gut microbiota, acts as a potent modulator of mitochondrial function and oxidative stress, protecting against cellular damage. Through sulfate-reducing bacteria, gut microbiota influences systemic H2S levels, creating a link between gut health and metabolic processes. Dysbiosis, or an imbalance in microbial populations, can alter H2S production, impair mitochondrial function, increase oxidative stress, and heighten inflammation, all contributing factors in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.