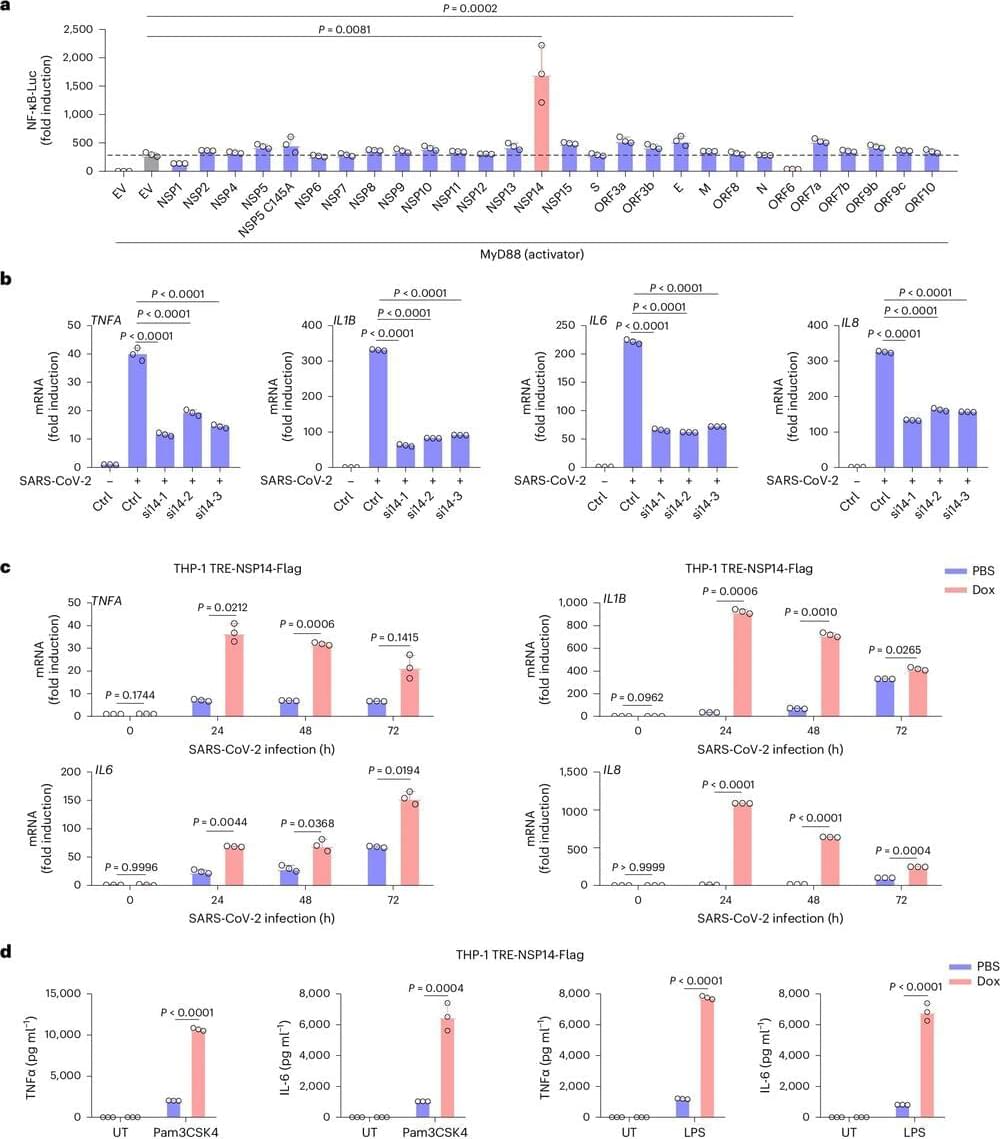
Although schizophrenia can be a very complex illness some new studies show that some major genetic factors could be the cause and then cured much easier through gene therapy.
Summary: Researchers leveraged cutting-edge technology to gain insights into schizophrenia’s neurodevelopmental origins. The researchers grew brain organoids from patients’ skin cells, finding persistent axonal disruptions in those with schizophrenia.
In another study, researchers zeroed in on a schizophrenia risk gene, CYFIP1, revealing its potential role in brain immune cells called microglia and their influence on synaptic pruning – a crucial process for brain health.