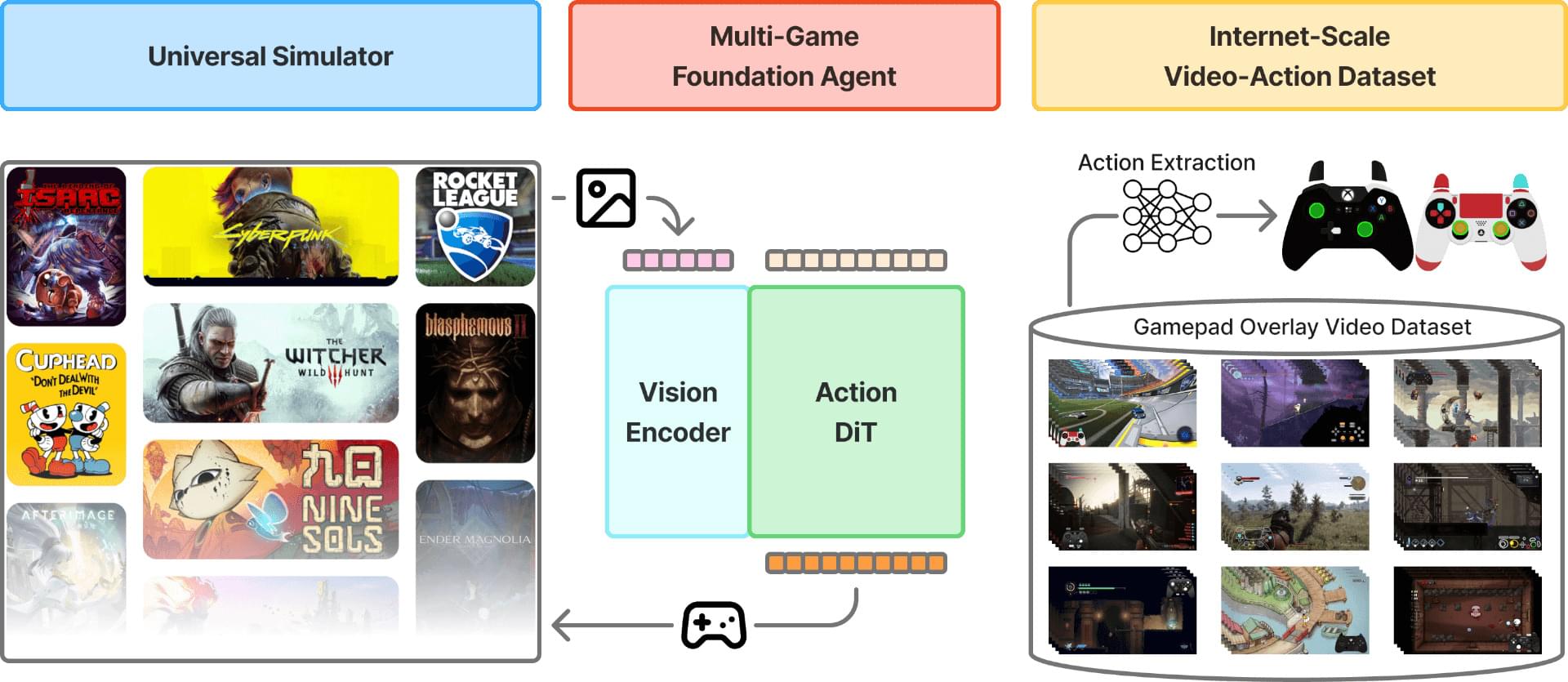
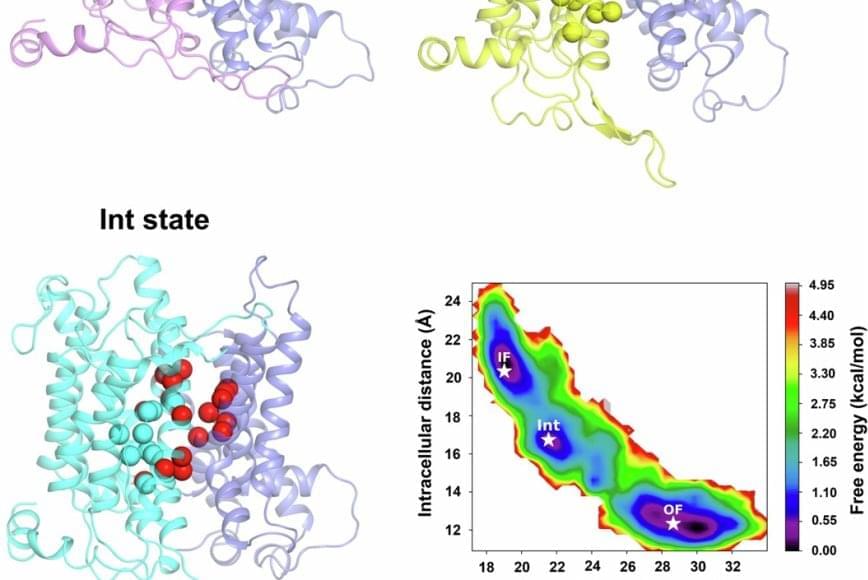
The authors determined the 3.3 Å cryoEM structure of the human NBCn1 outward facing (OF) conformational state with densities corresponding to the transported ions in the ion coordination site. They also generated NBCn1 inward facing (IF) and intermediate (occluded) structures and characterized the transport cycle and the ion dynamics in the IF and OF states.
The results showed that NBCn1 utilizes an elevator-type transport mechanism with a small vertical shift of the ion coordination site between OF and IF conformational states and that the transported ions permeate without significant energy barriers.
The researchers showed that NBCn1 moves two sodium ions and one carbonate ion through an efficient “elevator-like” motion that minimizes energy use. This allows NBCn1 to achieve a high transport rate of approximately 15,000 ions per second, helping tumor cells maintain an internal pH that promotes survival, division and resistance to acidic stress.
By understanding the structure and function of NBCn1, the study provides a blueprint for designing drugs that could potentially block this transporter and disrupt the internal chemical balance that cancer cells depend on. Targeting this protein in cancer cells specifically could offer a precise way to weaken tumors while minimizing harm to normal tissue.
Scientists have characterized the structure and function of a key survival protein in breast cancer cells that helps explain how these tumors resist environmental stress and thrive in acidic, low-oxygen environments that would normally be toxic to healthy cells.
Breast cancer cells rely on a transporter protein called NBCn1 to bring alkali ions into the cell and maintain a favorable internal pH.