Researchers are still optimistic about finding disease-altering medicines—just not anytime soon.
- By Karen Weintraub on July 18, 2019
For the past quarter century, scientists battled Alzheimer’s disease under a single guiding principle: that protein clumps—beta-amyloid—deposited outside sensitive brain cells gradually damage neuronal functions and trigger memory loss. The solution seems simple: remove junk amyloid, protect the brain.
They could be completely wrong.
Last month, Alzheimer’s disease defeated another promising near-market drug that tried to prevent or remove amyloid deposits, adding to the disease’s therapeutic “graveyard of dreams.” Although the drug removed toxic amyloid, the patients didn’t get better. The failure is once again spurring scientists to confront an uncomfortable truth: targeting amyloid clumps when patients already show memory symptoms doesn’t work. Wiping out soluble amyloid—fragments of proteins before they aggregate into junk—also dead ends.
The journal club hosted by Dr. Oliver Medvedik returns for July and takes a look at the new SIRT6 evolutionary biology paper by Dr. Vera Gorbunova and collaborators, showing a relationship between enhanced SIRT6 function and longevity.
Abstract DNA repair has been hypothesized to be a longevity determinant, but the evidence for it is based largely on accelerated aging phenotypes of DNA repair mutants. Here, using a panel of 18 rodent species with diverse lifespans, we show that more robust DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair, but not nucleotide excision repair (NER), coevolves with longevity. Evolution of NER, unlike DSB, is shaped primarily by sunlight exposure. We further show that the capacity of the SIRT6 protein to promote DSB repair accounts for a major part of the variation in DSB repair efficacy between short- and long-lived species. We dissected the molecular differences between a weak (mouse) and a strong (beaver) SIRT6 protein and identified five amino acid residues that are fully responsible for their differential activities. Our findings demonstrate that DSB repair and SIRT6 have been optimized during the evolution of longevity, which provides new targets for anti-aging interventions.
Literature
Tian, X., Firsanov, D., Zhang, Z., Cheng, Y., Luo, L., Tombline, G., … & Goldfarb, A. (2019). SIRT6 Is Responsible for More Efficient DNA Double-Strand Break Repair in Long-Lived Species. Cell, 177, 622–638.
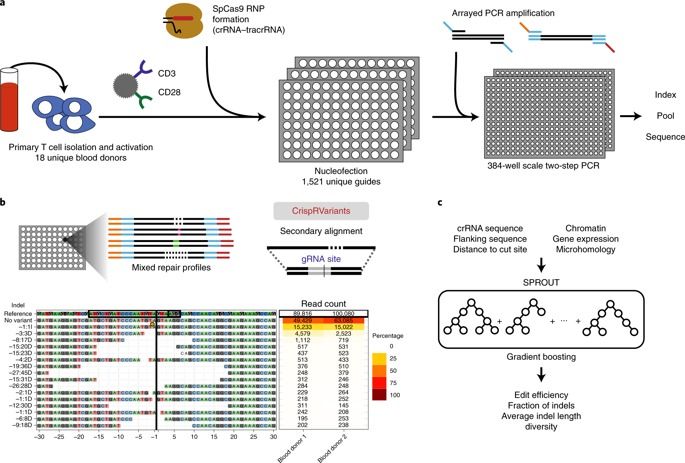
Understanding of repair outcomes after Cas9-induced DNA cleavage is still limited, especially in primary human cells. We sequence repair outcomes at 1,656 on-target genomic sites in primary human T cells and use these data to train a machine learning model, which we have called CRISPR Repair Outcome (SPROUT). SPROUT accurately predicts the length, probability and sequence of nucleotide insertions and deletions, and will facilitate design of SpCas9 guide RNAs in therapeutically important primary human cells.
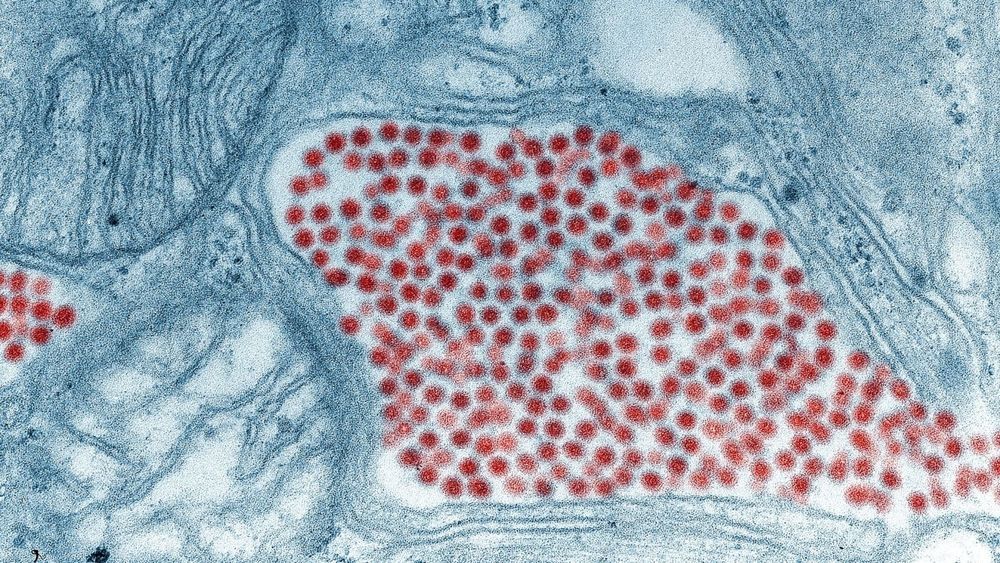
One of the most dangerous but thankfully rare mosquitoborne diseases has been spotted again in Florida, state health officials say. According to a public advisory issued this month by the Florida Department of Health in Orange County, the Eastern equine encephalitis virus (EEEV) was found in the state. The virus is capable of causing severe brain damage that can kill up to a third of its human victims.
EEEV can be spread by several species of mosquitoes, including those that make their home along the warmer areas of the U.S. Though many people infected with EEEV either develop no or only flu-like symptoms, around 5 percent go on to experience serious brain swelling (the titular encephalitis). This swelling can then lead to headaches, drowsiness, convulsions, and coma, with death coming as quickly as two days after symptoms start. And even if you’re lucky enough to survive the experience, you’ll probably be left with lifelong neurological impairment.

Ending Age-Related Diseases 2019 is over, and the dust is starting to settle after what can only be described as a hugely successful event for our organization. This was our second year of running a conference, and once more, we focused on the research and investment areas of rejuvenation biotechnology.
Totally sold out
This year, our venue at the Frederick P. Rose Auditorium at the Cooper Union in New York City was so popular that we totally sold out of tickets this year and had to turn people away! Our advice for next year is definitely to book early to avoid disappointment and take advantage of the lower prices that early booking offers.

Working with mouse and human tissue, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers report new evidence that a protein pumped out of some—but not all—populations of “helper” cells in the brain, called astrocytes, plays a specific role in directing the formation of connections among neurons needed for learning and forming new memories.
Using mice genetically engineered and bred with fewer such connections, the researchers conducted proof-of-concept experiments that show they could deliver corrective proteins via nanoparticles to replace the missing protein needed for “road repairs” on the defective neural highway.
Since such connective networks are lost or damaged by neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s or certain types of intellectual disability, such as Norrie disease, the researchers say their findings advance efforts to regrow and repair the networks and potentially restore normal brain function.
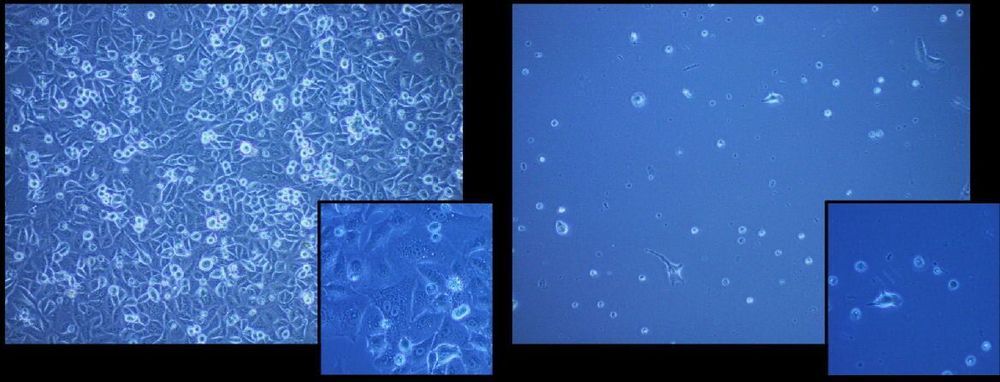
Cell freezing (cryopreservation)—which is essential in cell transfusions as well as basic biomedical research—can be dramatically improved using a new polymeric cryoprotectant, discovered at the University of Warwick, which reduces the amount of ‘anti-freeze’ needed to protect cells.
The ability to freeze and store cells for cell-based therapies and research has taken a step forward in the paper “A synthetically scalable poly(ampholyte) which dramatically Enhances Cellular Cryopreservation.” published by the University of Warwick’s Department of Chemistry and Medical School in the journal Biomacromolecules. The new polymer material protects the cells during freezing, leading to more cells being recovered and less solvent-based antifreeze being required.
Cryopreservation of cells is an essential process, enabling banking and distribution of cells, which would otherwise degrade. The current methods rely on adding traditional ‘antifreezes’ to the cells to protect them from the cold stress, but not all the cells are recovered and it is desirable to lower the amount of solvent added.