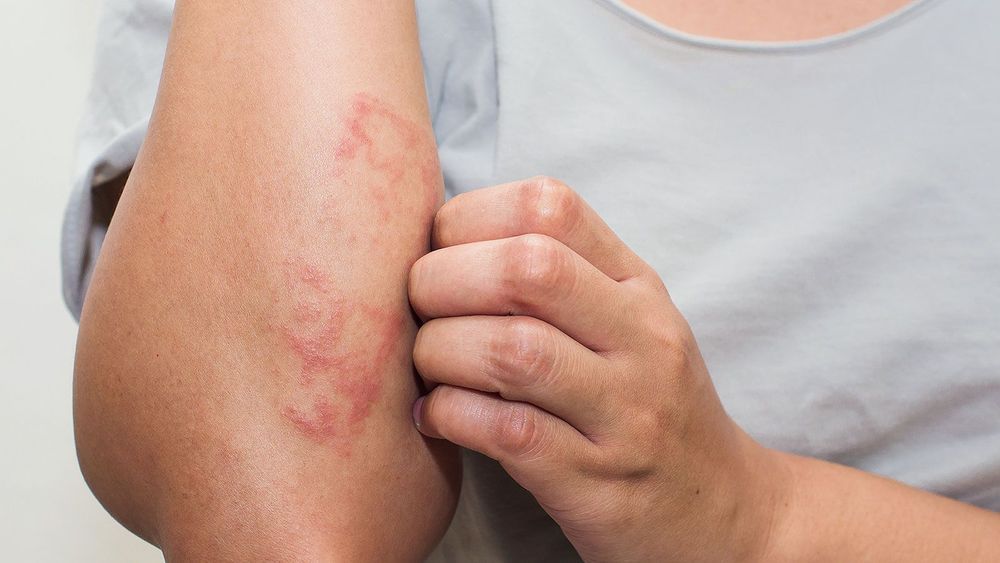
Over 3 million new cases of dermatitis appear in the US per year. Although dermatitis is broadly defined by the sensitivity of the skin, the condition is actually further segmented by a group of diseases. By far the most popular of these is atopic dermatitis, alternatively and perhaps more popularly known as eczema, affecting about 30% of the population. Genetics and environmental factors are the most conclusive predictors but no cause has ever been explicitly determined. The pathology is able to be determined physically, as inflamed skin grows craked and hardens.
Though a new report published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology presents some internal risk increases for sufferers to consider. The Danish researchers set out to examine the association between hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis and atrial fibrillation, writing in the report, “Atopic dermatitis is characterized by chronic inflammation, which is a risk factor for atrial fibrillation. P atients with hospital-diagnosed atopic dermatitis have a 20% increased long-term risk of atrial fibrillation, but the absolute risk remains low.”