Sea squirts use stem cells to regenerate their bodies from nothing but fragments of blood vessel, a finding that could help uncover the evolution of regeneration.

Neuromorphic systems carry out robust and efficient neural computation using hardware implementations that operate in physical time. Typically they are event- or data-driven, they employ low-power, massively parallel hybrid analog/digital VLSI circuits, and they operate using the same physics of computation used by the nervous system. Although there are several forums for presenting research achievements in neuromorphic engineering, none are exclusively dedicated to this increasingly large research community. Either because they are dedicated to single disciplines, such as electrical engineering or computer science, or because they serve research communities which focus on analogous areas (such as biomedical engineering or computational neuroscience), but with fundamentally different goals and objectives. The mission of Neuromorphic Engineering is to provide a publication medium dedicated exclusively and specifically to this field. Topics covered by this publication include: Analog and hybrid analog/digital electronic circuits for implementing neural processes, such as conductances, neurons, synapses, plasticity mechanisms, photoreceptors, cochleae, etc. Neuromorphic circuits and systems for implementing real-time event-based neural processing architectures. Hardware models of neural and sensorimotor processing systems, such as selective attention systems, coordinate transformation systems, auditory and/or visual processing systems, sensory fusion systems, etc. Implementations of neural computational systems found in insects, birds, mammals, etc. Embedded neuromorphic systems, including actuated or robotic platforms which process sensory signals and interact with the environment using event-based sensors and circuits. To ensure high quality and state-of-the-art material, publications should demonstrate experimental results, using physical implementations of neuromorphic systems, and possibly show the links between the artificial system and the neural/biological one they model.


A mathematical equation has proven that controlling one of the two major changes in a cell—decay or cancerous growth—enhances the other, causing inevitable death.


Research published today in Nature Medicine by scientists at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) has described a new immunotherapy approach, which led to a complete disappearance of tumors in a woman with advanced metastatic breast cancer who only had months to live.
The findings show how naturally-occurring tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) were extracted from the patient’s tumor, grown outside of her body to boost their numbers and injected back into the patient to tackle the cancer. The patient had previously received several treatments including hormone therapies and chemotherapy, but nothing had stopped the cancer progressing. After the treatment, all of the patient’s tumors disappeared and 22 months later, she is still in remission.
Researchers are particularly enthusiastic about the potential of TILs to treat a group of cancers termed ‘common epithelial cancers’, which include those of the colon, rectum, pancreas, breast and lung, together accounting for 90% of all deaths due to cancer in the U.S, around 540,000 people annually, most of these from metastatic disease.
Imagine buzzing the skin over an internal wound with an electrical device and having it heal over just a few days – that’s the promise of new nanochip technology that can reprogram cells to replace tissue or even whole organs.
It’s called Tissue Nanotransfection (TNT), and while it’s only been tested on mice and pigs so far, the early signs are encouraging for this new body repair tool — and it sounds like a device straight out of science-fiction.
The prototype device, developed by a team at Ohio State University, sits on the skin and uses an intense electrical field to deliver specific genes to the tissue underneath it. Those genes create new types of cells that can be used nearby or elsewhere in the body.
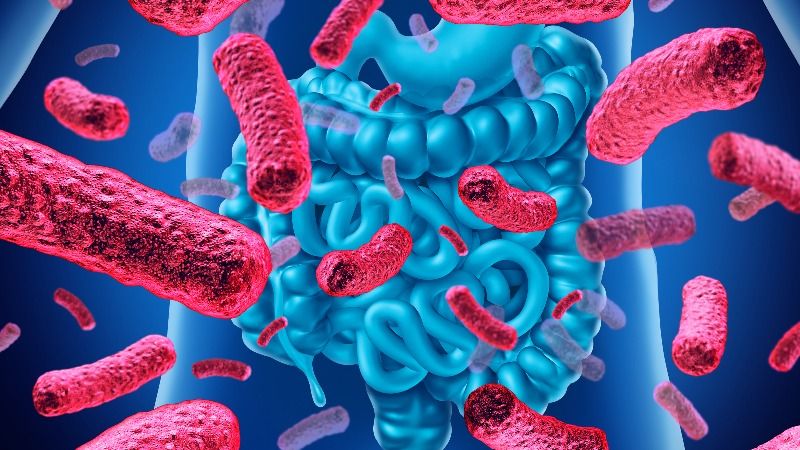
The gut microbiome appears to be increasingly responsible for at least some of the decline of the immune system during aging, and a new mouse study shows that it is reversible.
The gut microbiome
The microbiome describes a varied community of bacteria, archaea, eukarya, and viruses that inhabit our guts. The four bacterial phyla of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria comprise 98% of the intestinal microbiome.