Today, thanks to remarkable advances in antiretroviral drugs, most people with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can expect to live an almost normal lifespan. But that means staying on medications for life. If those are stopped, HIV comes roaring back in just weeks. Finding a permanent cure for HIV infection, where the virus is completely and permanently eliminated from the body, has proven much tougher. So, I’m encouraged by recent work that shows it may be possible to eliminate HIV in a mouse model, and perhaps—with continued progress—someday we will actually cure HIV in humans.
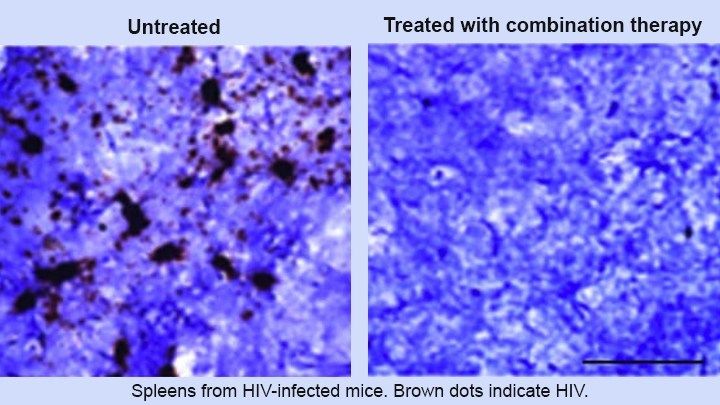
This innovative approach relies on a one-two punch: drugs and genetic editing. First, HIV-infected mice received an experimental, long-acting form of antiretroviral therapy (ART) that suppresses viral replication. This step cleared the active HIV infection. But more was needed because HIV can “hide” by inserting its DNA into its host’s chromosomes—lying dormant until conditions are right for viral replication. To get at this infectious reservoir, researchers infused the mice with a gene-editing system designed to snip out any HIV DNA still lurking in the genomes of their spleen, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and other cells. The result? Researchers detected no signs of HIV in more than one-third of mice that received the combination treatment.
The new study in Nature Communications is the product of a collaboration between the NIH-funded labs of Howard Gendelman, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, and Kamel Khalili, Temple University, Philadelphia [1]. A virologist by training, Khalili years ago realized that HIV’s ability to integrate into the genomes of its host’s cells meant that the disease couldn’t be thought of only as a typical viral infection. It had a genetic component too, suggesting that an HIV cure might require a genetic answer.