Want it all? Get unlimited access when you subscribe.


Red wine has been known to be healthy for many reasons, but some recent studies show that antioxidants in red wine can actually kill cancer.
Not only is it helpful in preventing cancer, but it can also help to fight it once it has been detected.
Cancer is a life-threatening disease that can kill people of any age.
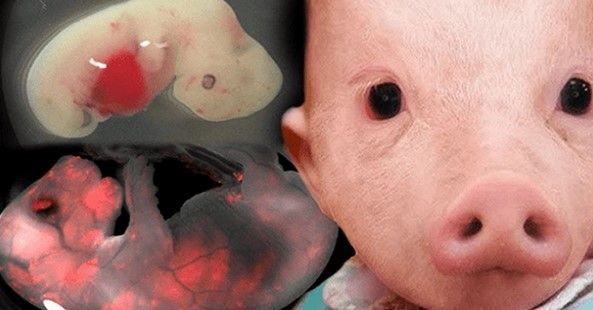
Human-animal hybrids are set to be developed at the University of Tokyo after the Japanese government recently lifted a ban on the controversial stem-cell research.
Hiromitsu Nakauchi—director for Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine at the University of Tokyo and team leader at Stanford’s Nakauchi Lab—is the first to receive approval for the questionable experiments which will attempt to grow human cells in rat and mouse embryos before being brought to term in a surrogate animal.
Despite many feeling that such studies are the equivalent of playing God, scientists say that the objective is far from sinister. It’s theorized that developing animals with organs constructed from human cells will create organs that can then be used for transplants in humans, cutting the long organ donation waitlists.
This episode will take you through Dr. Aubrey de Grey’s Seven Pillars of aging, the research that he’s currently doing, his opinion on biological age, AGEs and the different sources, and the impact of growth hormone on biological age.
Who is Dr. Aubrey de Grey?
Aubrey de Grey is an English author and biomedical gerontologist. He is the Chief Science Officer of the SENS Research Foundation and VP of New Technology Discovery at AgeX Therapeutics, Inc. He is the editor-in-chief of the academic journal Rejuvenation Research, author of The Mitochondrial Free Radical Theory of Aging and co-author of Ending Aging. He is known for his view that medical technology may enable human beings alive today not to die from age-related causes.
He is also an amateur mathematician who has contributed to the study of the Hadwiger–Nelson problem. His research focuses on whether regenerative medicine can prevent the aging process. He works on the development of what he calls “Strategies for Engineered Negligible Senescence” (SENS), a collection of proposed techniques to rejuvenate the human body and stop aging.
To this end, he has identified seven types of molecular and cellular damage caused by essential metabolic processes. SENS is a proposed panel of therapies designed to repair this damage. De Grey is an international adjunct professor of the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, a fellow of the Gerontological Society of America, the American Aging Association, and the Institute for Ethics and Emerging Technologies.
He has been interviewed in recent years in a number of news sources, including CBS 60 Minutes, the BBC, The New York Times, Fortune Magazine, The Washington Post, TED, Popular Science, The Colbert Report, Time, the Skeptics’ Guide to the Universe, and The Joe Rogan Experience. He is also a member of Flooved advisory board.
A team of researchers affiliated with multiple institutions in China has found that the makeup of the gut microbiome can be a determiner for the efficacy of exercise with prediabetics. In their paper published in the journal Cell Metabolism, the group describes their study of prediabetic volunteers and exercise and what they found.
In the medical community, type 2 diabetes is considered to be preventable in most people—all it takes is a change in diet and an increase in exercise. But things may not be as simple as that as the researchers with this new effort discovered—they found that exercise does not always lead to reductions in glucose metabolism.
The study by the team involved asking 29 male prediabetic volunteers to undergo glucose metabolism and gut microbe testing. Then the group was divided into two—20 volunteers were asked to undergo an exercise regimen for three months while the other 19 were asked to maintain their normal eating and exercise habits. At the end of the three-month period, all of the volunteers once again underwent glucose and gut microbe metabolic testing.
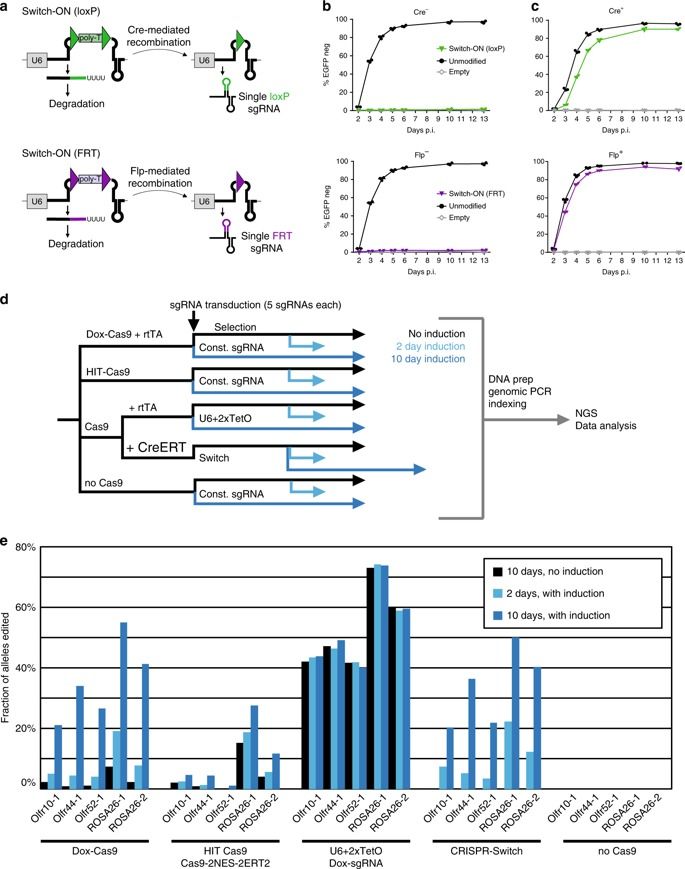
CRISPR-Cas9 is an efficient and versatile tool for genome engineering in many species. However, inducible CRISPR-Cas9 editing systems that regulate Cas9 activity or sgRNA expression often suffer from significant limitations, including reduced editing capacity, off-target effects, or leaky expression. Here, we develop a precisely controlled sgRNA expression cassette that can be combined with widely-used Cre systems, termed CRISPR-Switch (SgRNA With Induction/Termination by Cre Homologous recombination). Switch-ON facilitates controlled, rapid induction of sgRNA activity. In turn, Switch-OFF-mediated termination of editing improves generation of heterozygous genotypes and can limit off-target effects. Furthermore, we design sequential CRISPR-Switch-based editing of two loci in a strictly programmable manner and determined the order of mutagenic events that leads to development of glioblastoma in mice. Thus, CRISPR-Switch substantially increases the versatility of gene editing through precise and rapid switching ON or OFF sgRNA activity, as well as switching OVER to secondary sgRNAs.

Do you know why only Vitamin C in the form of L-ascorbic acid is truly effective against cancer?
The Molecular Structure of Ascorbic Acid – MasterKey to Health & Disease
Most living organisms including plants, insects and animals produce ascorbic acid. Ascorbic acid exists naturally in the form of L-ascorbic acid [24]. In physiological pH, L-ascorbic acid exists predominantly in the ionic form of L-ascorbate.
In their 2019 landmark study, Osipyants et al. not only showed that prolyl hydroxylase depended upon ascorbic acid as substrate, but demonstrated definitively for the first time that ascorbic acid MUST BE IN THE SPECIFIC MOLECULAR STRUCTURE of L-ASCORBATE in order to suppress HIF-1a [25]!!
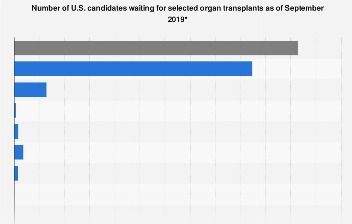
This statistic displays the number of organ transplant candidates in the United States by organ, as of as of September 25, 2019. At this moment, there were 230 candidates in the country waiting for an intestine donation. Organ donation can be given through both a deceased and living donor if blood and oxygen are flowing through the organs until the time of recovery to ensure viability. There are over 120,000 people in the country waiting for an organ transplant.

Medication prescribed for a certain type of epilepsy may offer a new method for treating malignant infantile brain tumors. A specific mTOR inhibitor has the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier to both reach and attack the tumor at source. This has been demonstrated by researchers from Uppsala University, in collaboration with US and UK colleagues, whose research has now been published in the scientific journal Cell Stem Cell.
Approximately 100 children suffer infantile brain tumors in Sweden each year. The most common type of malignant brain tumor in infants and children is medulloblastoma. Radiation therapy is part of the standard treatment for medulloblastomas and modern radiation therapy has saved the lives of many children suffering from these often aggressive cancers; however, as it often comes with serious side effects for healthy brain tissue, it is seldom prescribed for infants. Although a presumably better solution would be to give more targeted treatment, in order to establish such a therapy it would naturally need to be proven to be both more effective and come with fewer side effects than current treatments.
Many infantile medulloblastomas are amplified by MYCN, an oncogene that drives tumor growth and metastasis to the spinal column, leading to a very poor prognosis. In the study in question, the researchers cultivated a particular type of neural stem cell and were able to demonstrate that MYCN was quickly able to turn these into cancer cells. This suggests that these cells are likely to be the origin of infantile medulloblastomas.

Anzalone’s prime editor is a little different. Its enzyme is actually two that have been fused together—a molecule that acts like a scalpel combined with something called a reverse transcriptase, which converts RNA into DNA. His RNA guide is a little different too: It not only finds the DNA in need of fixing, but also carries a copy of the edit to be made. When it locates its target DNA, it makes a little nick, and the reverse transcriptase starts adding the corrected sequence of DNA letter by letter, like the strikers on a typewriter.
A less error-prone DNA editing method could correct many more harmful mutations than was previously possible.