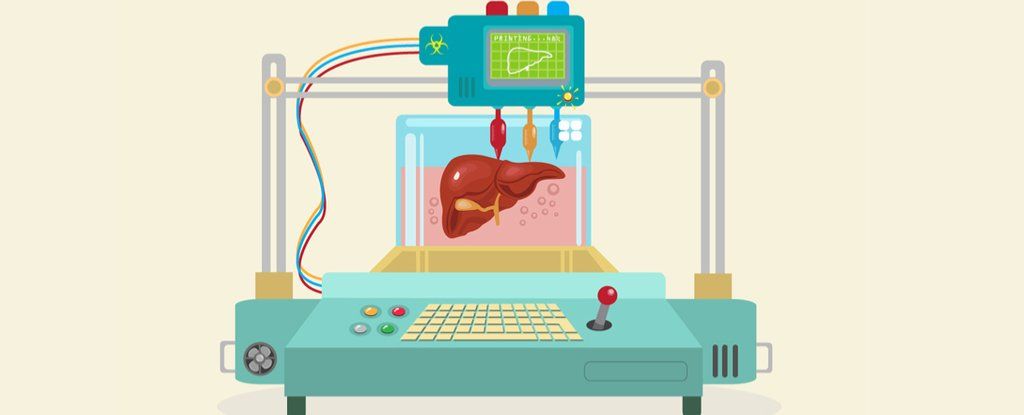
Body organs such as kidneys, livers and hearts are incredibly complex tissues. Each is made up of many different cell types, plus other components that give the organs their structure and allow them to function as we need them to.
For 3D printed organs to work, they must mimic what happens naturally – both in terms of arrangement and serving a biological need. For example, a kidney must process and excrete waste in the form of urine.
Our latest paper shows a new technique for 3D printing of cells and other biological materials as part of a single production process. It’s another step towards being able to print complex, living structures.