A less severe strain of bird flu had been detected along the North Carolina and South Carolina state recently but the case in Chesterfield County, South Carolina discovered on Monday was found to be a more fatal and easily spread strain.
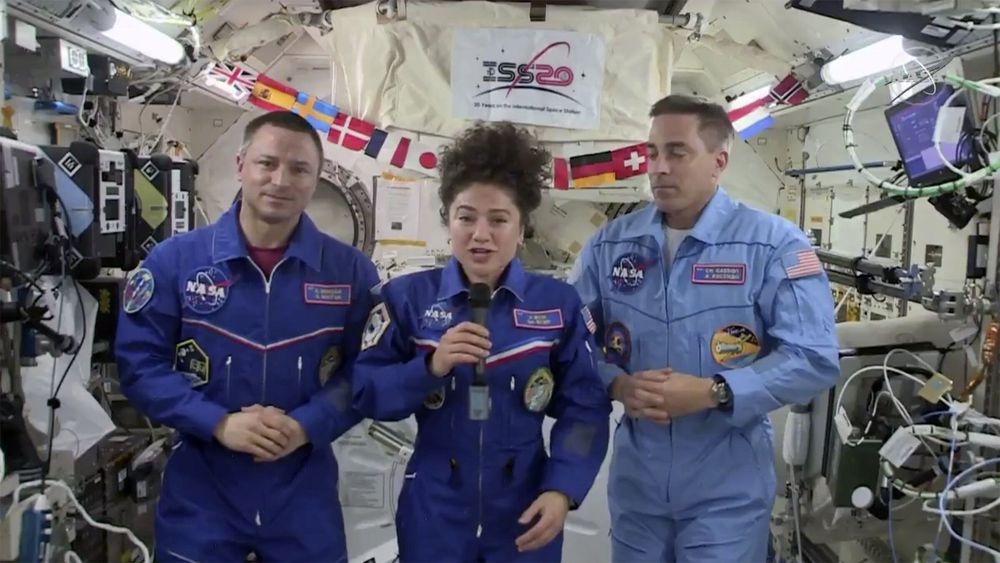




Two NASA astronauts said Friday they expect it will be tough returning to such a drastically changed world next week, after more than half a year at the International Space Station.
Andrew Morgan said the crew has tried to keep atop the pandemic news. But it’s hard to comprehend what’s really going on and what to expect, he noted, when his nine-month mission ends next Friday.
“It is quite surreal for us to see this whole situation unfolding on the planet below,” said Jessica Meir, who took part in the first all-female spacewalk last fall. “We can tell you that the Earth still looks just as stunning as always from up here, so it’s difficult to believe all the changes that have taken place since both of us have been up here.”
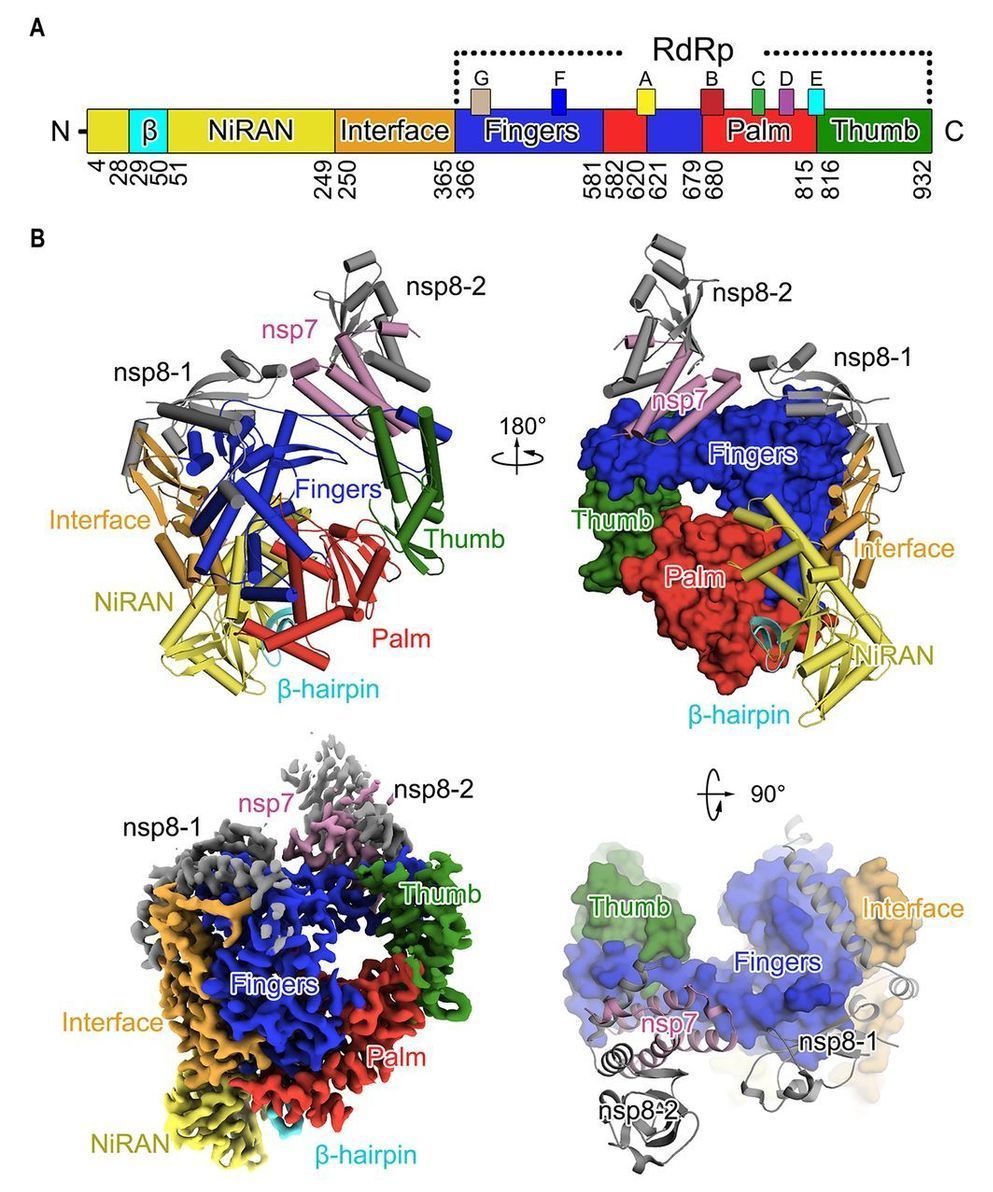
A novel coronavirus (COVID-19 virus) outbreak has caused a global pandemic resulting in tens of thousands of infections and thousands of deaths worldwide. The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp, also named nsp12) is the central component of coronaviral replication/transcription machinery and appears to be a primary target for the antiviral drug, remdesivir. We report the cryo-EM structure of COVID-19 virus full-length nsp12 in complex with cofactors nsp7 and nsp8 at 2.9-Å resolution. In addition to the conserved architecture of the polymerase core of the viral polymerase family, nsp12 possesses a newly identified β-hairpin domain at its N terminus. A comparative analysis model shows how remdesivir binds to this polymerase. The structure provides a basis for the design of new antiviral therapeutics targeting viral RdRp.
Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by a novel coronavirus emerged in December 2019 (1–3) and has since become a global pandemic. COVID-19 virus is reported to be a new member of the betacoronavirus genus and is closely related to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and to several bat coronaviruses (4). Compared to SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, COVID-19 virus exhibits faster human-to-human transmission, thus leading to the WHO declaration of a world-wide public health emergency (1, 2).
CoVs employ a multi-subunit replication/transcription machinery. A set of non-structural proteins (nsp) produced as cleavage products of the ORF1a and ORF1ab viral polyproteins (5) assemble to facilitate viral replication and transcription. A key component, the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp, also known as nsp12), catalyzes the synthesis of viral RNA and thus plays a central role in the replication and transcription cycle of COVID-19 virus, possibly with the assistance of nsp7 and nsp8 as co-factors (6). Nsp12 is therefore considered a primary target for nucleotide analog antiviral inhibitors such as remdesivir, which shows potential for the treatment of COVID-19 viral infections (7, 8). To inform drug design we have determined the structure of nsp12, in complex with its cofactors nsp7 and nsp8 by cryo-Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM) using two different protocols, one in the absence of DTT (Dataset-1) and the other in the presence of DTT (Dataset-2).
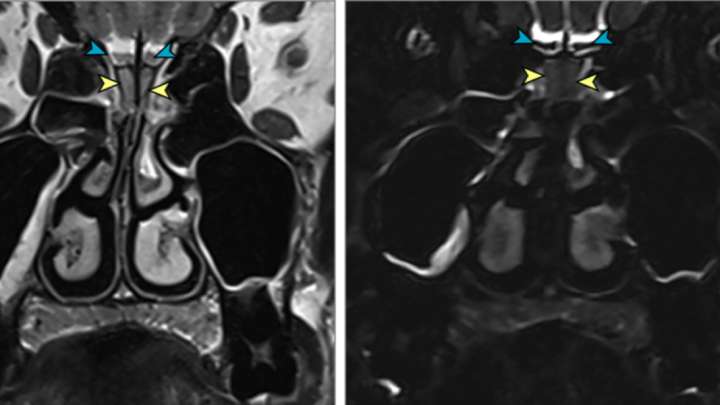
A woman in her forties has become the latest known case of SARS-CoV-2 infection associated with a “sudden and complete” loss of smell. Known as anosmia, loss of smell is regarded as one of the tell-tale signs of COVID-19.
When an odor enters the nose, neurons in the nasal cavity send messages to the olfactory bulb, a structure in the front part of the brain. These signals are then shipped off to different parts of the brain, leading some medical experts to wonder whether the novel coronavirus could cause adverse neurological reactions.
But how could a virus associated with respiratory infections impact the brain? Researchers are trying to find out. Dr Serena Spudich, a neurologist at the Yale School of Medicine specializing in infectious diseases, says that it is too early to say definitively whether SARS-CoV-2 directly infects the brain but limited data suggests it is a possibility.


A 29-year-old coronavirus patient has improved from serious to serious, but stable condition after receiving multiple doses of plasma from a donor who recovered from coronavirus.
A 29-year-old haredi (ultra-Orthodox) coronavirus patient who is being treated at Samson Assuta Ashdod University Hospital has improved from serious to serious but stable condition, after receiving multiple doses of plasma over the weekend from a donor who recovered from coronavirus, a spokesperson for the hospital told The Jerusalem Post.
On Friday, “with the assistance of Health Minister Ya’acov Litzman and his assistant, a suitable donor, a resident of Jerusalem, was found,” explained MDA director-general Eli Bin.

Some hospitals have reported unusually high death rates for coronavirus patients on ventilators, and some doctors worry that the machines could be harming certain patients. When people talk of the safety of medicines, they need to also talk of the safety of ventilators as the wrong treatment can kill a patient, and we have enough evidence that ventilators are not working.
NEW YORK (AP) — As health officials around the world push to get more ventilators to treat coronavirus patients, some doctors are moving away from using the breathing machines when they can.
The reason: Some hospitals have reported unusually high death rates for coronavirus patients on ventilators, and some doctors worry that the machines could be harming certain patients.
The evolving treatments highlight the fact that doctors are still learning the best way to manage a virus that emerged only months ago. They are relying on anecdotal, real-time data amid a crush of patients and shortages of basic supplies.
