The two tech titans funded an effort to bring metagenomic sequencing and software to poor countries. Now, it’s helping trace the spread of the new coronavirus.
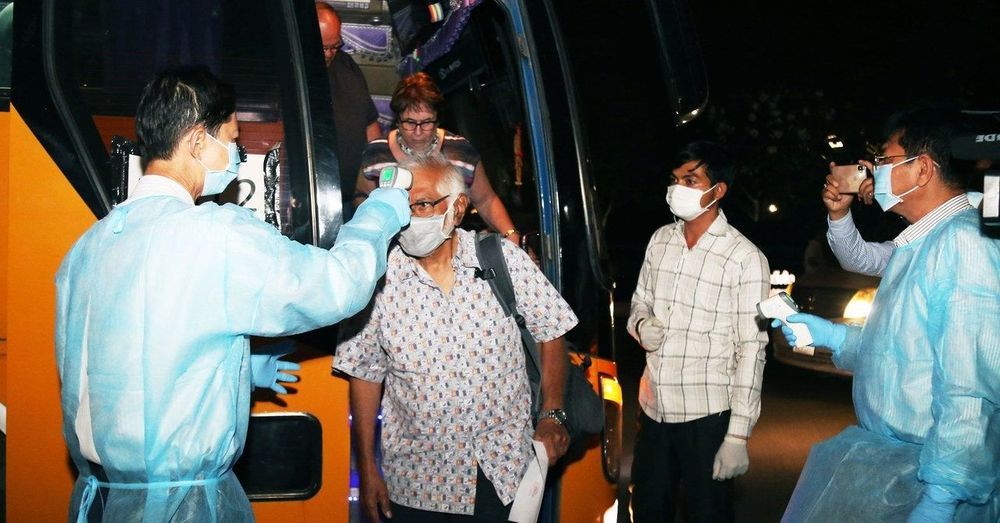


Giacomo Grasselli — a senior Italian government health official who is coordinating the network of intensive care units in Lombardy — explains the “critical” situation in Italy, brought about by the Covid-19 outbreak (Subscribe: https://bit.ly/C4_News_Subscribe)
——
Follow us:
Facebook — https://www.facebook.com/Channel4News/
Twitter — https://twitter.com/Channel4News
Get more news at our site — https://www.channel4.com/news/
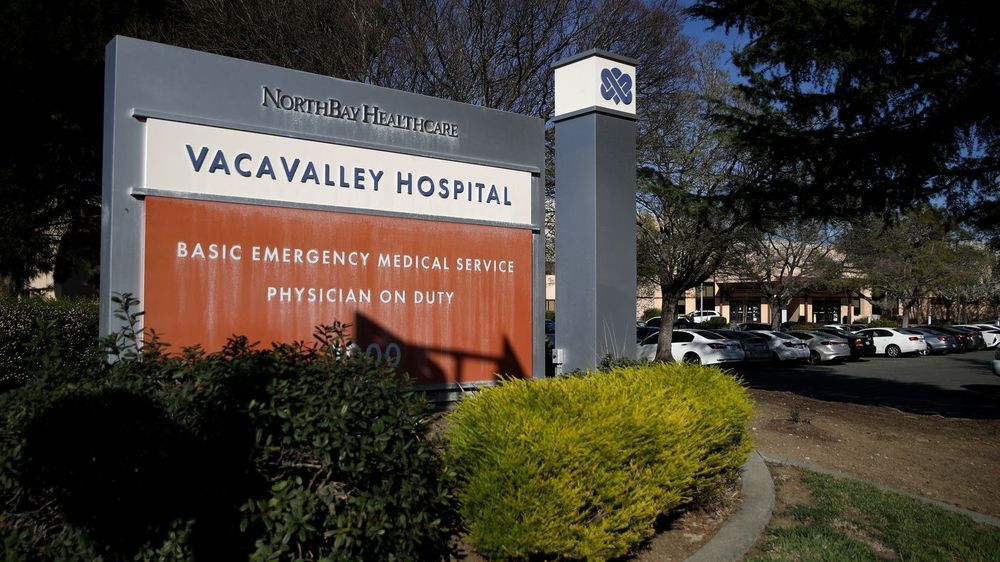
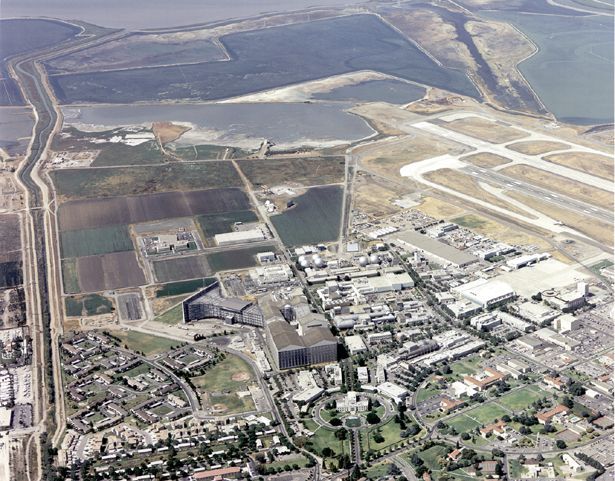


NASA’s Ames Research Center in California has issued a mandatory policy for employees to work from home after one worker tested positive for the coronavirus responsible for COVID-19.
The research center, which is located in Moffett Field in the Silicon Valley, has been placed on restricted access after the employee was confirmed to have the coronavirus on Sunday (March 8).
Check your blood glucose without fingersticks using the FreeStyle Libre System, a continuous glucose monitoring system that includes a sensor and reader.
Circa 2018 we need crispr pills for this.
The steady march of aging might not have to be so steady, according to a growing body of research. Now a team from the University at Buffalo has isolated a single gene that controls senescence, the process that stops cells from dividing and contributes to aging symptoms. Ramping it up, they found how easily the effect can spread among neighboring cells. That makes the gene a crucial target for future work into anti-aging and cancer therapies.
Living cells have a natural limit to the amount of times they can divide, before they stop and become what are known as senescent cells. The problem is, over time these senescent cells build up in the body, eventually contributing to the physical symptoms we associate with aging, such as increased risk of diabetes, heart disease, arthritis and cataracts. On the other hand though, completely halting senescence can lead to cancer, as the cells continue to divide unchecked.
Realizing this mechanism, scientists have been developing ways to clear out these senescent cells, including a new class of drugs known as senolytics. In tests, these drugs have been found to extend the lifespan of mice by up to an impressive 35 percent, and keep them in better health for longer.
Let’s say it was possible to buy your health by the day. How much would you be willing to pay for each year of perfect health? What if you could buy years of health for your loved ones, too? At what price point would you draw the line?
This sort of difficult calculus, on a much larger and chronologically longer scale, underpins many decisions we make in medicine — not just decisions that we make as patients, but also the decisions that are made for us by employers, health insurance funders and policymakers. We don’t have the resources to pursue every possible treatment, to research every possible breakthrough, so how do we allocate the resources available? It turns out that there is an entire field of healthcare economics devoted to understanding the costs and benefits of conventional medicine, and to navigating the trade-offs between more expense and better healthcare.
Determining the costs and benefits of new areas like genomic medicine is especially tricky, because we have so much less experience in these areas, and even experts cannot yet fully agree on the spectrum of harms and benefits.
Researchers from AgeX Therapeutics and other organizations have proved the feasibility of reprogramming banked cells derived from a supercentenarian. Their discovery portends exciting new possibilities for aging research.
What is cellular reprogramming?
Cellular reprogramming is the process of reverting mature, specialized cells into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which can develop into any cell type found in the human body. Cellular reprogramming technology was pioneered in 2006 by Drs. Takahashi and Yamanaka, who achieved this impressive result by overexpressing just four genes, Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc (OSKM), which became collectively known as the Yamanaka factors. For this breakthrough, Yamanaka was awarded the Nobel Prize in 2012. Fun fact: Yamanaka called these cells iPSCs – with a small “i” – as a nod to the iPod and similarly named devices.

The news did not sit well with Chinese scientists, who are still recovering from the CRISPR baby scandal. “It makes you wonder, if their reason for choosing to do this in a Chinese laboratory is because of our high-tech experimental setups, or because of loopholes in our laws?” lamented one anonymous commentator on China’s popular social media app, WeChat.
Their frustration is understandable. Earlier in April, a team from southern China came under international fire for sticking extra copies of human “intelligence-related” genes into macaque monkeys. And despite efforts to revamp its reputation in biomedical research ethics, China does have slacker rules in primate research compared to Western countries.
If you’re feeling icked out, you’re not alone. The morality and ethics of growing human-animal hybrids are far from clear. But creepiness aside, scientists do have two reasons for wading into these uncomfortable waters.