Circa 2019
A common gene-editing enzyme could be used to disable RNA viruses such as flu or Ebola.

Could find the coronavirus kill switch and shut it off then let the immune system eat the remainder.
A single protein derived from a common strain of bacteria found in the soil will offer scientists a more precise way to edit RNA.
The protein, called AcrVIA1, can halt the CRISPR-Cas13 editing process, according to new research from Cornell, Rockefeller University and the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center published in the journal Science July 3.
“We’re expanding our scientific toolbox to effectively use a CRISPR without causing side effects,” said co-author Martin Wiedmann, Ph.D. ’97, the Gellert Family Professor in Food Safety and director of Cornell’s Food Safety Laboratory and Milk Quality Improvement Program. “Thanks to this bacterium, we’re getting a chance to turn off and on our ability to make changes to RNA.”



Sanofi and GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) will be awarded up to $2.1 billion by the U.S. Departments of Health and Human Services (HHS) and Defense (DoD) toward development and manufacturing of the recombinant protein-based COVID-19 vaccine being produced by the companies, they and the U.S. government said.
HHS and DoD are providing the funding as part of Operation Warp Speed—the program through which President Donald Trump’s administration has committed the nation to delivering 300 million vaccine doses protecting against SARS-CoV-2 by January 2021.
“The portfolio of vaccines being assembled for Operation Warp Speed increases the odds that we will have at least one safe, effective vaccine as soon as the end of this year,” HHS Secretary Alex Azar II stated.

It’s also worth noting that some water already naturally contains low amounts of lithium. And in research published last week in The British Journal of Psychiatry, scientists from a cohort of U.K. universities identified a link that naturally-present lithium and lower suicide rates.
Therefore, they suggest, more lives could be saved by putting the drug in high-risk communities’ water supplies.
“In these unprecedented times of COVID-19 pandemic and the consequent increase in the incidence of mental health conditions, accessing ways to improve community mental health and reduce the incidence of anxiety, depression and suicide is ever more important,” Anjum Memon, lead author and epidemiology chair at Brighton and Sussex Medical School, said in a press release.
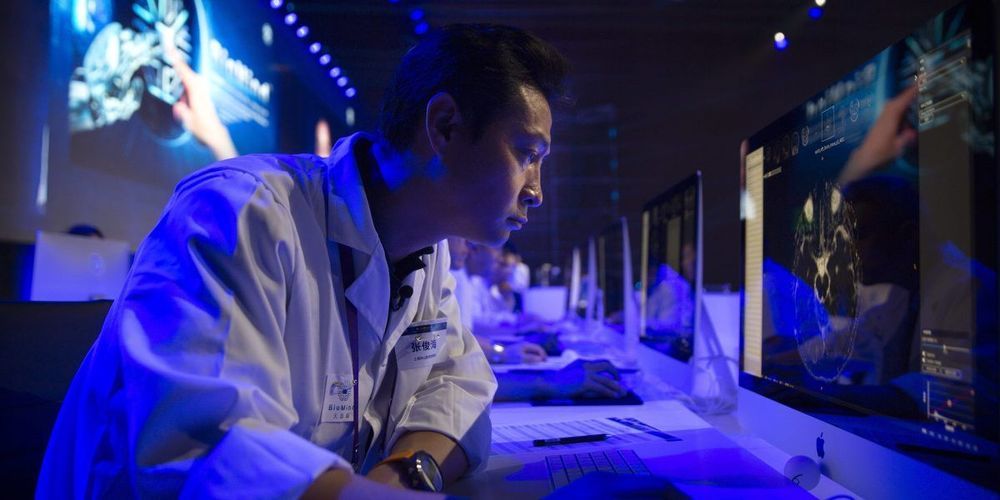

The context: Studies show that when people and AI systems work together, they can outperform either one acting alone. Medical diagnostic systems are often checked over by human doctors, and content moderation systems filter what they can before requiring human assistance. But algorithms are rarely designed to optimize for this AI-to-human handover. If they were, the AI system would only defer to its human counterpart if the person could actually make a better decision.
The research: Researchers at MIT’s Computer Science and AI Laboratory (CSAIL) have now developed an AI system to do this kind of optimization based on strengths and weaknesses of the human collaborator. It uses two separate machine-learning models; one makes the actual decision, whether that’s diagnosing a patient or removing a social media post, and one predicts whether the AI or human is the better decision maker.
The latter model, which the researchers call “the rejector,” iteratively improves its predictions based on each decision maker’s track record over time. It can also take into account factors beyond performance, including a person’s time constraints or a doctor’s access to sensitive patient information not available to the AI system.
#COVID19: There is overwhelming scientific evidence that a mid-range air humidity has significant benefits for human health. It is very possible for us to be managing the indoor air quality of our public buildings in line with this evidence. The time has come for regulations on indoor air quality to include a humidity level of 40-60u0025RH. This is the optimal level for our respiratory immune system, and will reduce the spread of seasonal respiratory illnesses and their burden on society.nn
There is now overwhelming scientific evidence that a mid-range air humidity has significant benefits for human health. It is very possible for us to be managing the indoor air quality of our public buildings in line with this evidence. The time has come for regulations on indoor air quality to include a humidity level of 40–60%RH. This is the optimal level for our respiratory immune system, and will reduce the spread of seasonal respiratory illnesses and their burden on society.
I am calling on the World Health Organization to review the scientific evidence on humidity and health, and recommend a minimum lower limit of indoor humidity in public buildings to reduce respiratory infections.
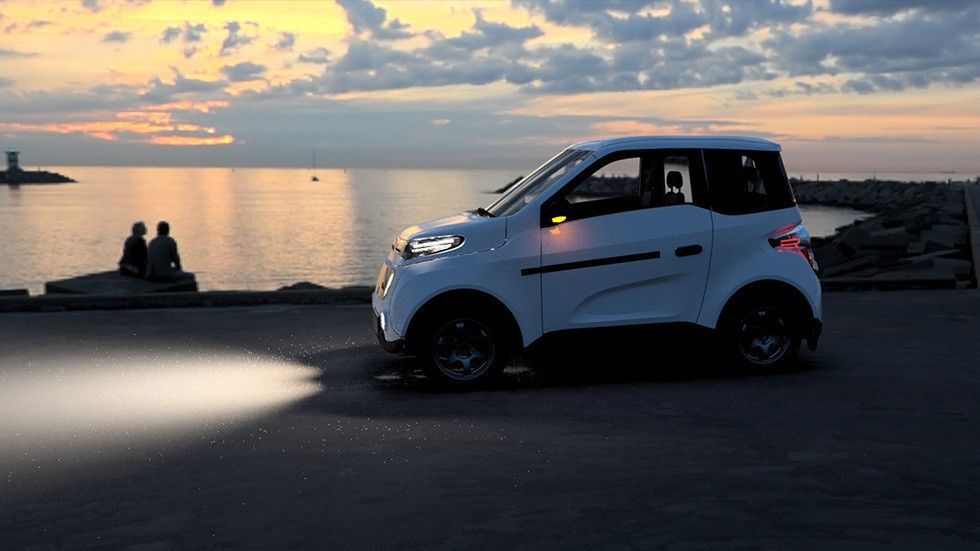

After pandemic-related delays, Russia’s first electric car, called the Zetta, is set to enter serial production in late 2020, the country’s Industry and Trade Minister Denis Manturov has revealed.
The Zetta will roll off the production line in the city of Tolyatti, one of the major centers of Russia’s automotive industry. The cars will first be sold on the domestic market, but the initial business project implies that the Zetta may be exported to other countries, Manturov said.