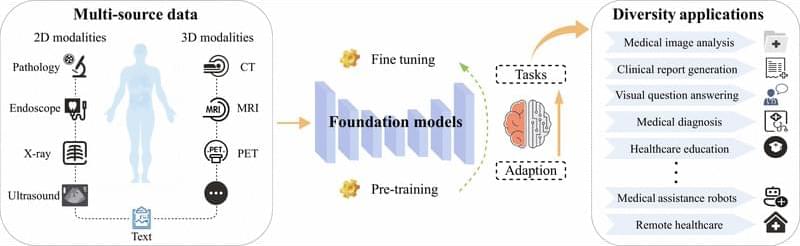
In contrast, traditional deep learning methods in the medical domain have long been constrained by scarce annotations data, weak cross-modal semantic correlation, and insufficient generalization capabilities. FMs can effectively alleviate these issues by extracting semantic representations from large-scale unlabeled data, reducing dependence on expert annotations, and enhancing cross-modal understanding and transferability [7]. This provides technical support to address challenges such as long-tail distributions, data scarcity, and modality imbalance, thereby promoting a shift in medical decision-making from experience-driven to data-driven approaches.
Unlike traditional specialist models such as nnU-Net [8], which are typically designed for a single modality and specific tasks, FMs emphasize modality unification and task generalization, enabling cross-domain transfer and knowledge sharing. With mechanisms such as prompt engineering and PEFT, these models support few-shot and even zero-shot transfer (ZST). For example, Med-PaLM [9] is based on a unified medical pretraining model, which can generate structured pathology reports and perform lesion localization from medical images. It effectively overcomes the limitations of traditional methods that require separate architectures for different tasks, significantly improving modeling efficiency and system integration. Driven by such unified model architecture, medical AI systems are evolving toward greater generality and reusability.
Despite these advancements, the unique characteristics of the medical domain pose multiple challenges to the application of FMs. On one hand, medical data are highly heterogeneous, with pronounced differences in resolution, contrast, and noise distribution across imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound [10]. This limits the ability of traditional single-modality pretraining strategies to achieve effective cross-domain knowledge integration. On the other hand, clinical applications demand higher standards for model performance. Clinical decision-making relies on interpretable diagnostic evidence, yet pretraining models often behave as “black boxes”, limiting their clinical traceability [11]. In addition, the long-tail distribution of rare diseases poses fairness challenges for model generalization [12].