In an early trial, patients received a single infusion of a CRISPR-based therapy to knock out the mutated gene responsible for their disease.



As smart watches are increasingly able to monitor the vital signs of health, including what’s going on when we sleep, a problem has emerged: Those wearable, wireless devices are often disconnected from our body overnight, being charged at the bedside.
“Quality of sleep and its patterns contain a lot of important information about patients’ health conditions,” says Sunghoon Ivan Lee, assistant professor in the University of Massachusetts Amherst College of Information and Computer Sciences and director of the Advanced Human Health Analytics Laboratory.
But that information can’t be tracked on smartwatches if the wearable devices are being charged as users sleep, which prior research has shown is frequently the case. Lee adds, “The main reason users discontinue the long-term use of wearable devices is because they have to frequently charge the on–device battery.”

“People are just exhausted.”
As COVID-19 restrictions loosen across the United States, the hospitality industry — which was walloped by the pandemic — is experiencing a new challenge: too few workers available to address soaring demand for dining out.
A furious debate is underway over what’s behind the labor shortage, which is prompting restaurants to adapt by modernizing with kiosks and digital ordering. Many are biting the bullet and ponying up more in compensation just to attract employees.
“A lot of us are paying over time,” Laurie Thomas, executive director of the Golden State Restaurant Association, said in an interview with Yahoo Finance.
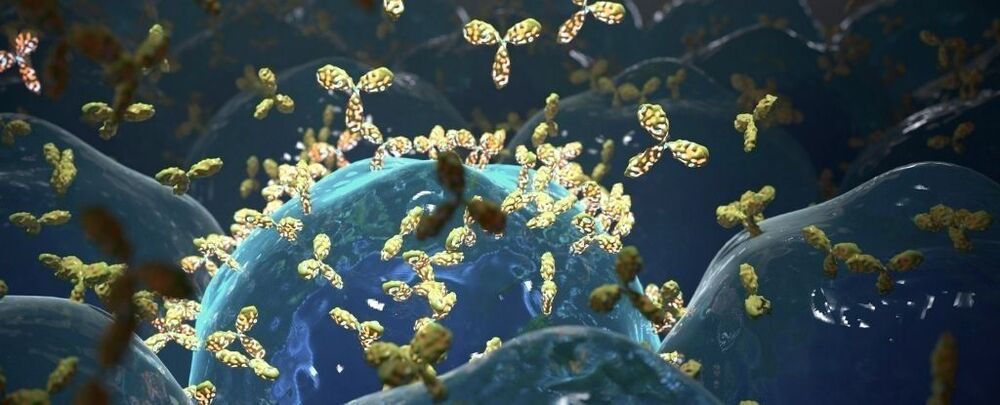
Fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) is one of the most common chronic pain conditions out there, yet we still know shockingly little about it.
For decades, the debilitating condition — marked by widespread pain and fatigue — has been vastly understudied, and while it’s commonly thought to originate in the brain, no one really knows how fibromyalgia starts or what can be done to treat it. Some physicians maintain it doesn’t even exist, and many patients report feeling gaslit by the medical community.
New research on mice has now found further evidence that fibromyalgia is not only real, but may involve an autoimmune response as a driver for the illness.

Starting next year, the US military’s Special Operations Command (SOCOM) will start to test out an experimental pill that it says can actually stave off the effects of aging on soldiers.
The experiment, Breaking Defense reports, is part of a push to augment human ability and keep combatants healthy and operating at peak performance for longer. And, pending successful performance and clinical tests, it could make its way out into the public as a new longevity treatment for the masses as well.
“These efforts are not about creating physical traits that don’t already exist naturally,” SOCOM spokesperson and Navy Commander Tim Hawkins told Breaking Defense. “This is about enhancing the mission readiness of our forces by improving performance characteristics that typically decline with age.”
A team of researchers at Tel Aviv University has developed a breakthrough RNA-based drug delivery system to target diseased cells that could improve the treatment of blood cancers, various types of solid cancers, different inflammatory diseases and viral diseases – including coronavirus.
“We are the first in the world to deliver the drug exclusively to cells that are currently relevant to the disease.”

Of the 88 neurosurgical patients, 30 showed a decrease in self-reported spiritual belief before and after neurosurgical brain tumor resection, 29 showed an increase, and 29 showed no change. Using lesion network mapping, the team found that self-reported spirituality mapped to a specific brain circuit centered on the PAG. The circuit included positive nodes and negative nodes — lesions that disrupted these respective nodes either decreased or increased self-reported spiritual beliefs.
Summary: A new study has identified a specific brain circuit centered in the periaqueductal gray that is linked to spiritual acceptance and religiosity.
Source: Brigham and Women’s Hospital
More than 80 percent of people around the world consider themselves to be religious or spiritual. But research on the neuroscience of spirituality and religiosity has been sparse. Previous studies have used functional neuroimaging, in which an individual undergoes a brain scan while performing a task to see what areas of the brain light up. But these correlative studies have given a spotty and often inconsistent picture of spirituality.
A new study led by investigators at Brigham and Women’s Hospital takes a new approach to mapping spirituality and religiosity and finds that spiritual acceptance can be localized to a specific brain circuit.

“I realized that in the middle-dose group, which is the one that mattered for the no-effects level, they had conveniently left out one of the two baseline measurement days,” said Sheppard. “The outrageous thing was that the group they declared as NOEL was only that because they left out data from their analysis.” In a peer-reviewed paper published in October 2020, Sheppard and her colleagues concluded that “the omission of valid data without justification was a form of data falsification.”
In any case, bifenthrin was not the only pesticide that dodged testing to see if it presented dangers. The EPA’s pesticide office granted 972 industry requests to waive toxicity tests between December 2011 and May 2018, 89 percent of all requests made. Among the tests on pesticides that were never performed were 90 percent of tests looking for developmental neurotoxicity, 92 percent of chronic cancer studies, and 97 percent of studies looking at how pesticides harm the immune system.
By law, the companies that submit their products for review pay for these tests, and in a presentation about the waivers last year, Anna Lowit, a senior science adviser in the office, emphasized the savings to these companies: more than $300 million. Lowit also noted that animal lives were saved — a goal that the Trump administration and the chemical industry prioritized within the agency. The EPA developed the guidelines for waiving the tests along with BASF, Corteva, and Syngenta, pesticide manufacturers that all stand to benefit significantly from having their products bypass toxicity testing.
There is no replacement for these waived experiments, according to pediatrician and epidemiologist Philip Landrigan. “There is no other way to know if a chemical is toxic but to test it,” said Landrigan, who co-authored a landmark report on children’s particular vulnerability to pesticides. “If they allow chemicals to come onto the market and to be used widely in the environment and put on food crops without testing them for toxicity, then EPA is clearly not fulfilling its mandate to protect human health.”
Not just the results, but the vector used. I’ll post the paper below.
In this video we cover an experiment where gene therapies to overexpress TERT and Follistatin were used in a mouse model. The mice saw a 41 and 32% increase in median life span. The study also used a novel viral vector, cytomegalovirus for the delivery. Please note that this a preprint which is not peer-reviewed yet.
Papers referred to in this newsletter.
New intranasal and injectable gene therapy for healthy life extension.
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.06.26.449305v1.full.
********************************************
~ NEW ~
Alive By Science — All products 10% Discount Link.
https://alivebyscience.com/?rfsn=5832249.3a406d&coupon-code=345822
Alive By Science Pure NMN 16g 10% Discount Link.