Glue can stick to wet surfaces and form a seal within 15 seconds.


A team of researchers may have found an antibody that can neutralize all known novel coronavirus strains, including the developing variants.
GlaxoSmithKline and Vir Biotechnology recently conducted a huge collaborative study by scientists and developed a new antibody therapy, called Sotrovimab. During the project, they discovered a new natural antibody “that has remarkable breadth and efficacy,” according to the Berkeley Lab.
The scientists reportedly discovered a new antibody, called S309, which “neutralizes all known SARS-CoV-2 strains — including newly emerged mutants that can now ‘escape’ from previous antibody therapies — as well as the closely related original SARS-CoV virus,” according to a press release from the Berkeley Lab.
Favorite part at 19:06, Bioinformatics with Rutgers University attacking the hallmarks of aging.
#genetherapy, #immortality, #bioinformatics.
Awesome Health Podcast Episode 155
According to this episode’s guest: Liz Parrish, people should be demanding access to the latest gene therapy treatments.
According to Liz, effective gene therapy that treats and heals a plethora of diseases could be in place today if not for the human race’s mistakes in prioritizing our funds. Trillions of dollars have been invested in war machines, for example, when we could have used that money to advance humanity into a healthier, more productive, and enjoyable way of life.

Pioneering mouse study offers new therapeutic avenues for reducing visceral fat stores, which have been associated with cardiovascular disease and multiple types of cancer.
Obesity has been linked to no less than 13 cancers, including the two most prevalent (breast and colorectal), as well as to cardiovascular disease, which remains a leading cause of death worldwide.
The most harmful type of obesity is caused by the excessive accumulation of so-called “deep” fat. Contrary to fat stores located directly under the skin, deep, or “visceral,” fat stores reside inside our abdominal cavity, where they envelop vital organs. In normal amounts, visceral fat supports various fundamental functions, such as reproduction. However, when it is too abundant, it produces unhealthy levels of proteins and hormones that negatively affect neighboring tissues and organs.
Nad plus works for alzheimers.
In June of 2,018 the World Health Organization (WHO) released the 11th edition of its International Classification of Diseases, and for the first time added aging.1 The classification of aging as a disease paves the way for new research into novel therapeutics to delay or reverse age-related illnesses such as cancer, cardiovascular and metabolic disease, and neurodegeneration.2,3 Nutrient sensing systems have been an intense focus of investigation, including mTOR (the mammalian target of rapamycin) for regulating protein synthesis and cell growth; AMPK (activated protein kinase) for sensing low energy states; and sirtuins, a family of seven proteins critical to DNA expression and aging, which can only function in conjunction with NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), a coenzyme present in all living cells.4
Across the kingdom of life, an increase in intracellular levels of NAD+ triggers shifts that enhance survival, including boosting energy production and upregulating cellular repair.5 In fact, the slow, ineluctable process of aging has been described as a “cascade of robustness breakdown triggered by a decrease in systemic NAD+ biosynthesis and the resultant functional defects in susceptible organs and tissues.”6 Aging is marked by epigenetic shifts, genomic instability, altered nutrient sensing ability, telomere attrition, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, stem cell exhaustion, and dysregulated intercellular communication.7,8
By middle age, our NAD+ levels have plummeted to half that of our youth.9 Numerous studies have demonstrated that boosting NAD+ levels increases insulin sensitivity, reverses mitochondrial dysfunction, and extends lifespan.10,11 NAD+ levels can be increased by activating enzymes that stimulate synthesis of NAD+, by inhibiting an enzyme (CD38) that degrades NAD+, and by supplementing with NAD precursors, including nicotinamide riboside(NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN).12,13 A conceptual framework called NAD World, formulated over the last decade by developmental biologist Shin-ichiro Imai, MD, PhD, of Washington University School of Medicine, posits NMN as a critical, systemic signaling molecule that maintains biological robustness of the communication network supporting NAD+.6.
The global revenue of the pharmaceutical market is 1.2 trillion dollars. With such capital at stake and with the pace of technological disruption, the pharma industry has to embrace new technologies, therapies, and innovations and put a greater focus on prevention and digital health.
In this video, we take a dive into the five trends of how big pharma will adapt to these changing times:
1. Artificial intelligence for drug research and development.
2. Patient design — DIY medicine movements.
3. In silico trials to bypass in vivo clinical testing.
4. New technologies, such as blockchain, in the supply chain.
5. New drug strategies by big pharma companies.
Get access to exclusive content and express your support for The Medical Futurist by joining our Patreon community: https://www.patreon.com/themedicalfuturist.
Read our magazine for further updates and analyses on the future of healthcare:
https://medicalfuturist.com/magazine.
#pharmaceutics #digitalhealth #pharma
Join us on Patreon!
https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Papers referenced in the video:
Human microbiome: an academic update on human body site specific surveillance and its possible role.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32524177/
Taxonomic signatures of cause-specific mortality risk in human gut microbiome.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33976176/
The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids From Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32082260/
Inhibiting antibiotic-resistant Enterobacteriaceae by microbiota-mediated intracellular acidification.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30563917/
Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood.
A new coronavirus variant, C.1.2, has been detected in South Africa and a number of other countries, with concerns that the variant could be more infectious and evade vaccines, according to a new preprint study by South Africa’s National Institute for Communicable Diseases and the KwaZulu-Natal Research Innovation and Sequencing Platform. The study is awaiting peer review.
The C.1.2 variant first detected in South Africa is more mutated compared to the original virus than any other known variant.
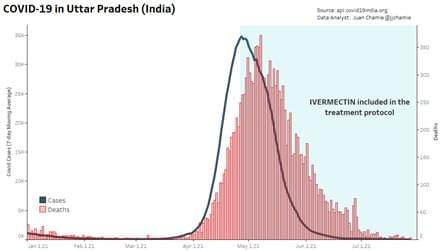
Article at gnews reports on announcement by Dr. Ozaki, chairman of the Tokyo Metropolitan Medical Association Greenlight for Ivermectin in Japan. Excerpts in italics with my bolds.
Since Tokyo summer Olympic Game ended on August 8 2021, the urgent status of the pandemic as Japan is now in its worst surge of the COVID-19 pandemic since the onset of the crisis in such a megacity of 14 million. Most recently, a record number of new cases were reported at 20,140 on August 14. Deaths aren’t as high as successive waves of the pandemic from February2021to the end of May, but nerves are frayed with record numbers of infections. Dr. Ozaki, The chairman of the Tokyo Metropolitan Medical Association, recently led an emergency press conference on August 13 Dr. Haruo Ozaki shared those 18,000 new infections are reported daily. However, the death count has eased as compared to previous surges.
How to deal with the current dilemma is a huge challenge to Japanese government and medical agencies? Fortunately, India has an excellent testimonial. Since April 28 India medical officials started providing Hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin to its massive population. As India is the major pharmaceutical manufacture in the world, they were ready for this massive drug distribution. Miraculously, COVID cases have plummeted quickly since then thanks to the new rules.
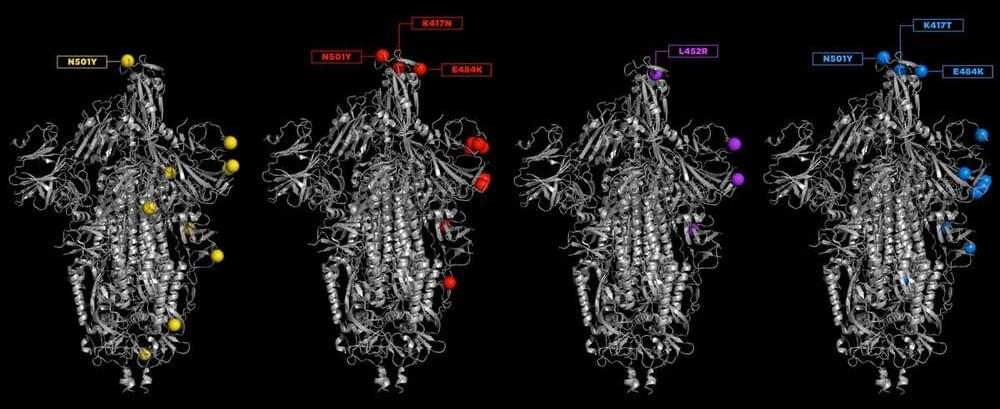
Mutations are a part of life. Every time a virus replicates, there is a chance that its genetic code won’t be copied accurately. These typos travel inside new virus particles as they leave one body and move on to infect the next. Some of these mutations die out; others survive and circulate widely. Some mutations are harmless; others increase infectivity or allow a virus to better escape the immune system—that’s when public health bodies might deem that strain a variant of concern.
Swaps or deletions of single amino acids can change the shapes of different proteins. Mutations can happen in any of the proteins of SARS-CoV-2, and these may change the virus’s properties. Many of the worrisome mutations are found on the spike protein, as it is the target of antibody treatments and is mimicked by the currently authorized COVID-19 vaccines. Researchers are especially troubled when typos occur in two parts of the spike protein—the N-terminal domain, which is at the beginning of the protein and which some antibodies target, and the receptor-binding domain (RBD), which grabs hold of ACE2 receptors on human cells and starts the process of infection.
To understand how specific mutations affect the structure and function of the spike protein and what those changes mean for treatments and vaccines, C&EN talked to Priyamvada Acharya, Rory Henderson, and Sophie Gobeil at Duke University. With colleagues, these researchers have combined biochemical assays, cryo-electron microscopy, and modeling to show how the mutations seen in the variants of concern work together to change the stability of the spike protein. The spike is a trimer of three identical protein strands folded and interwoven together. Before the virus has infected a cell, the spike takes on two conformations: a down state, in which the RBD is hidden, and an up state, in which the RBD faces out, ready to bind to ACE2. The team found that different mutations can increase binding in different ways. This process, in which similar features are arrived at independently, is called convergent evolution.
SARS-CoV-2 variants are emerging and gaining traction around the world. What does that mean for our vaccines and treatments for COVID-19?