From January 23
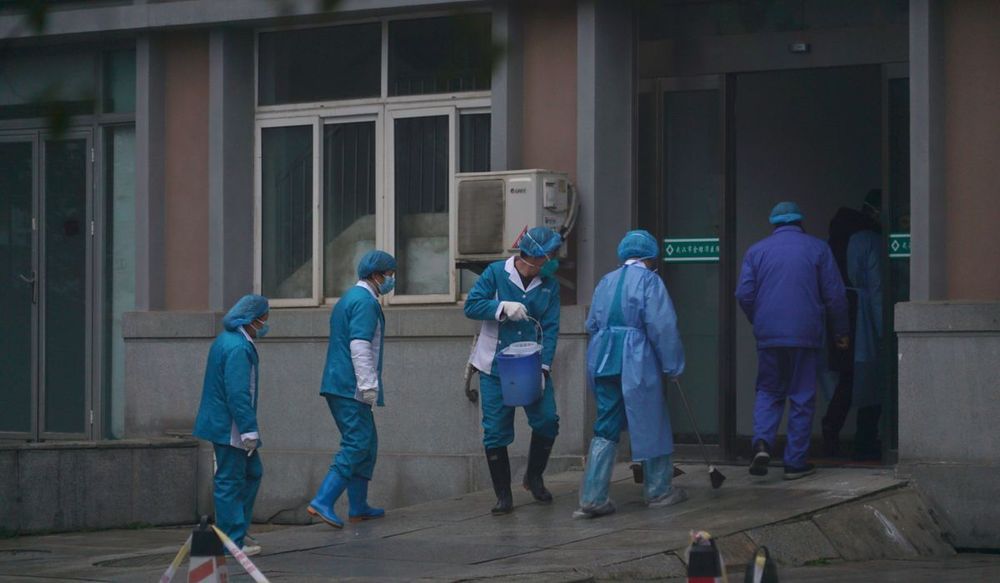
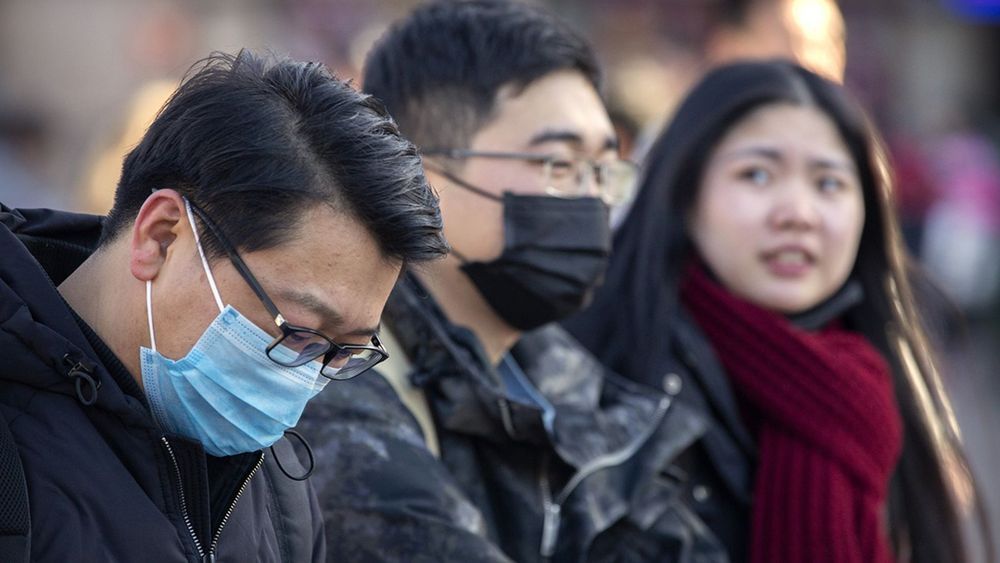
Gilead Sciences Inc said on Thursday it was assessing whether its experimental Ebola treatment could be used against the new coronavirus that has sickened hundreds of people in China and led to at least 18 deaths. “Gilead is in active discussions with researchers and clinicians in the United States and China regarding the ongoing Wuhan coronavirus outbreak and the potential use of remdesivir as an investigational treatment,” a company spokesman said in an emailed statement.
(Reuters) — Gilead Sciences Inc said on Thursday it was assessing whether its experimental Ebola treatment could be used against the new coronavirus that has sickened hundreds of people in China and led to at least 18 deaths.
“Gilead is in active discussions with researchers and clinicians in the United States and China regarding the ongoing Wuhan coronavirus outbreak and the potential use of remdesivir as an investigational treatment,” a company spokesman said in an emailed statement.