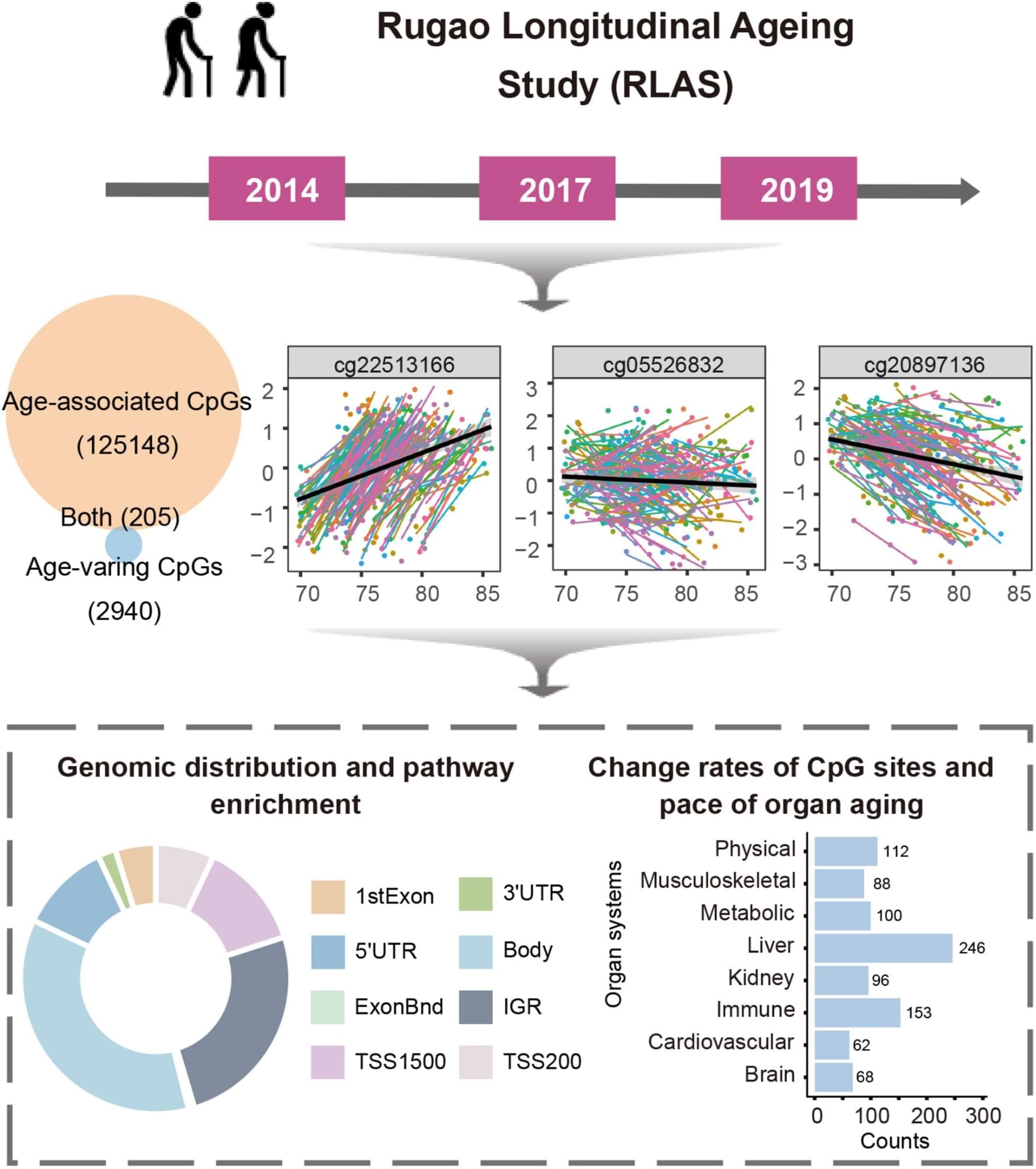
We longitudinally profiled DNA methylation in 135 relatively healthy older adults from the RLAS study, identifying 3145 CpG sites exhibiting increasing inter-individual variability with age and 125,3…

eLife Assessment
This fundamental study provides new evidence of a change in how microglia survey neurons during the chronic phase of neurodegeneration, which researchers studying neuroinflammation and its role in neurodegenerative disease should find interesting. In this research, using time-lapse imaging of acute brain slices from prion-affected mice, the researchers show that, unlike in healthy brains, microglia become reactive, lose their territorial boundaries, and become highly mobile, exhibiting “kiss-and-ride” behavior, migrating into brain tissue and forming reversible, transient body-to-body contact with neurons. The evidence is compelling, with well-executed time-lapse imaging, good quantitative analysis across several disease stages, pharmacological validation of P2Y6 involvement, and the very surprising finding that this mobile behavior persists after microglia are removed from the brain.

A regular heartbeat is essential to vertebrate life. In the mature heart, this function is driven by an anatomically localized pacemaker. By contrast, pacemaking capability is broadly distributed in the early embryonic heart1–3, raising the question of how tissue-scale activity is first established and then maintained during embryonic development. The initial transition of the heart from silent to beating has never been characterized at the timescale of individual electrical events, and the structure in space and time of the early heartbeats remains poorly understood. Using all-optical electrophysiology, we captured the very first heartbeat of a zebrafish and analysed the development of cardiac excitability and conduction around this singular event. The first few beats appeared suddenly, had irregular interbeat intervals, propagated coherently across the primordial heart and emanated from loci that varied between animals and over time. The bioelectrical dynamics were well described by a noisy saddle-node on invariant circle bifurcation with action potential upstroke driven by CaV1.2. Our work shows how gradual and largely asynchronous development of single-cell bioelectrical properties produces a stereotyped and robust tissue-scale transition from quiescence to coordinated beating.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Questions to inspire discussion.
🤖 Q: How quickly will AI and robotics replace human jobs? A: AI and robotics will do half or more of all jobs within the next 3–7 years, with white-collar work being replaced first, followed by blue-collar labor through humanoid robots.
🏢 Q: What competitive advantage will AI-native companies have? A: Companies that are entirely AI-powered will demolish competitors, similar to how a single manually calculated cell in a spreadsheet makes it unable to compete with entirely computer-based spreadsheets.
💼 Q: What forces companies to adopt more AI? A: Companies using more AI must outcompete those using less, creating a forcing function for increased AI adoption, as inertia currently keeps humans doing AI-capable tasks.
📊 Q: How much of enterprise software development can AI handle autonomously? A: Blitzy, an AI platform using thousands of specialized agents, autonomously handles 80%+ of enterprise software development, increasing engineering velocity 5x when paired with human developers.
Energy and Infrastructure.
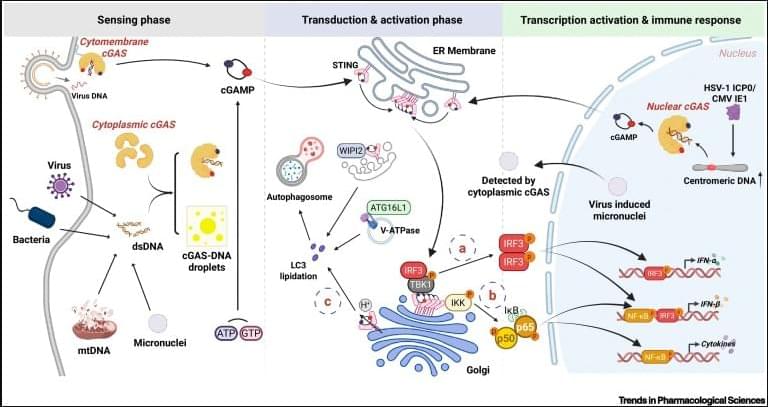
The cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS) and stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway, a crucial component of host innate immunity, detects aberrant DNA during viral infection. It is well established that cGAS-STING signaling activation during viral infections is often insufficient for complete viral clearance, indicating that numerous viruses have evolved countermeasures against this major pathway. However, the precise mechanisms by which viruses antagonize the cGAS-STING pathway to ensure intracellular survival remain incompletely understood. This review synthesizes recent progress in elucidating how diverse RNA and DNA viruses disrupt various stages of cGAS-STING pathway activation. These mechanistic insights into viral evasion have significant implications for the development of targeted therapeutic interventions.


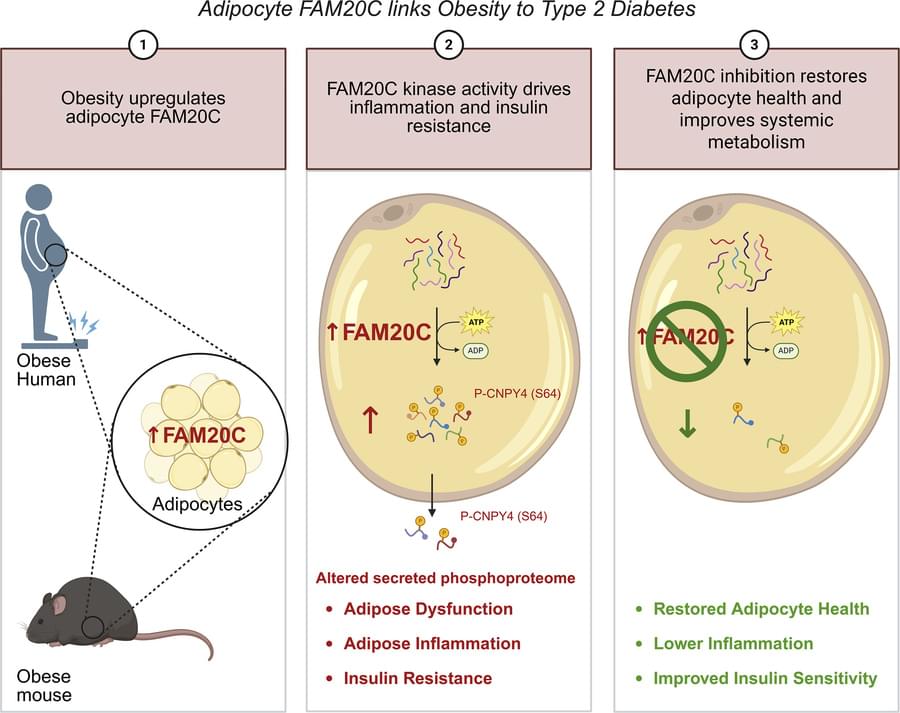
Here, James C. Lo & team identify FAM20C as a key mediator of obesity-induced adipocyte dysfunction and inflammation, suggesting its inhibition as a potential therapy for Type2 Diabetes:
The figure shows visceral white adipose tissue in mice with adipocyte-specific deletion of Fam20c shifts shows lower macrophage area compared with controls.
1Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Weill Center for Metabolic Health, Cardiovascular Research Institute, and.
2Department of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, New York, USA.
3Helmholtz Institute for Metabolic, Obesity, and Vascular Research, Helmholtz Center Munich, University of Leipzig and University Hospital Leipzig, Leipzig, Germany.