Inflammation is a natural biological process, and we need some of it to keep us safe — here’s why inflammation is necessary for survival.


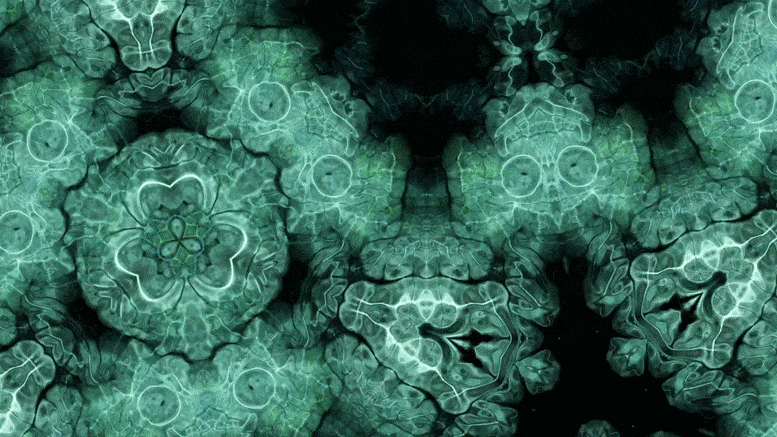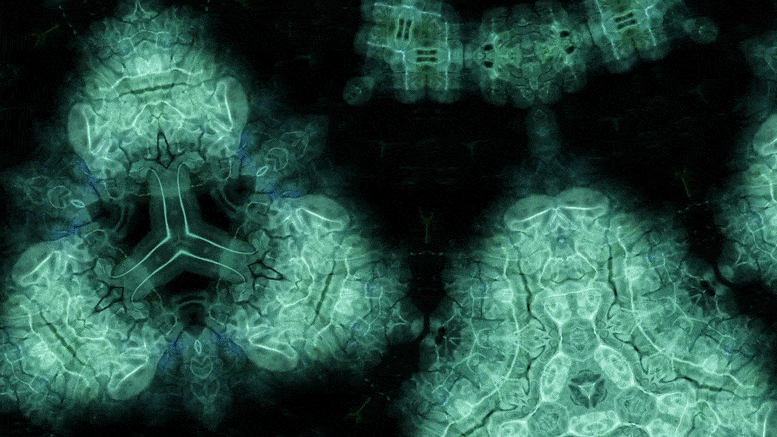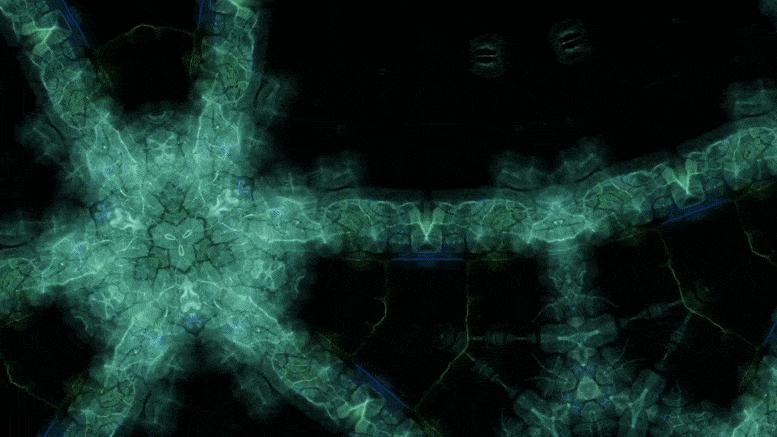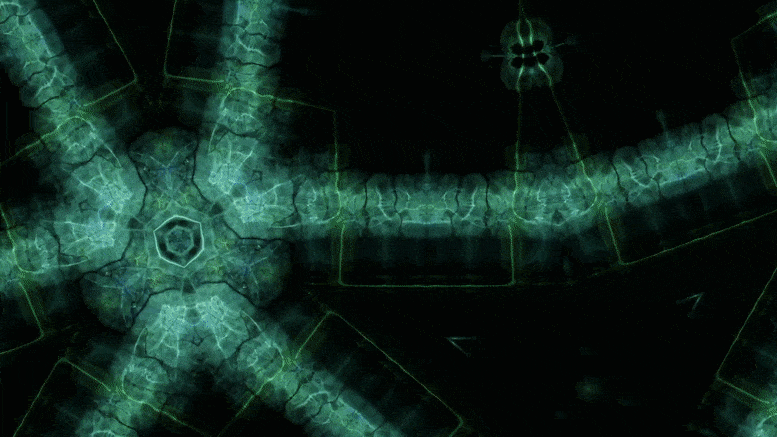
Using an advanced microscopy technique, Texas A&M researchers have uncovered a twin boundary defect in a soft polymer that has never been observed before.
Texas A&M University scientists have for the first time revealed a single microscopic defect called a “twin” in a soft-block copolymer using an advanced electron microscopy technique. This defect may be exploited in the future to create materials with novel acoustic and photonic properties.
“This defect is like a black swan — something special going on that isn’t typical,” said Edwin Thomas, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. “Although we chose a certain polymer for our study, I think the twin defect will be fairly universal across a bunch of similar soft matter systems, like oils, surfactants, biological materials, and natural polymers. Therefore, our findings will be valuable to diverse research across the soft matter field.”
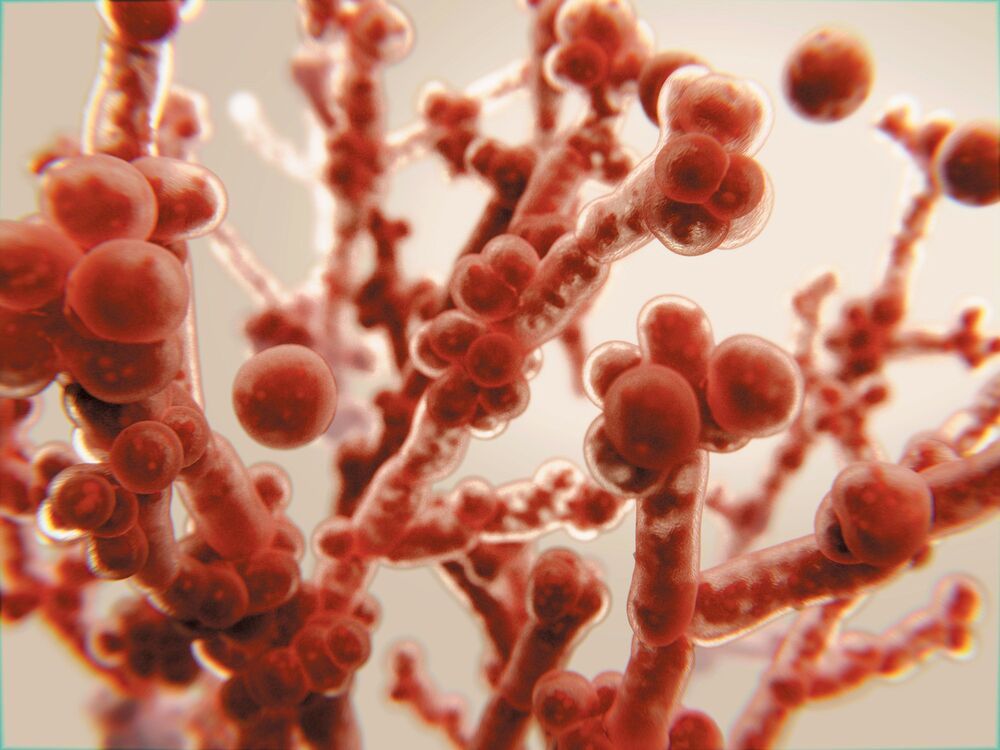
These pathogens already kill 1.6 million people every year, and we have few defenses against them.
By: Maryn McKenna
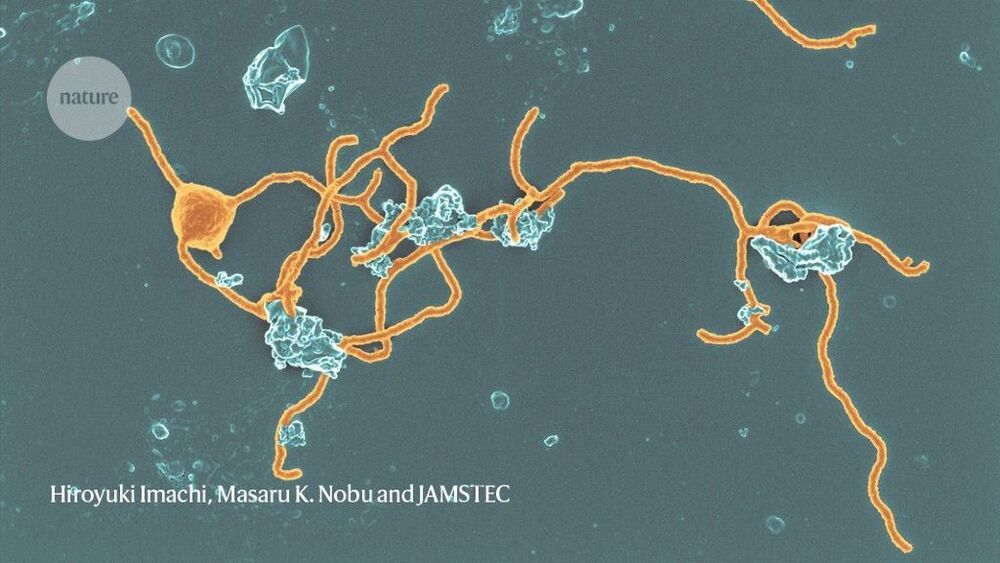
Archaea are more than just oddball lifeforms that thrive in unusual places — they turn out to be quite widespread. Moreover, they might hold the key to understanding how complex life evolved on Earth. Many scientists suspect that an ancient archaeon gave rise to the group of organisms known as eukaryotes, which include amoebae, mushrooms, plants and people — although it’s also possible that both eukaryotes and archaea arose from some more distant common ancestor.
As scientists learn more about enigmatic archaea, they’re finding clues about the evolution of the complex cells that make up people, plants and more.
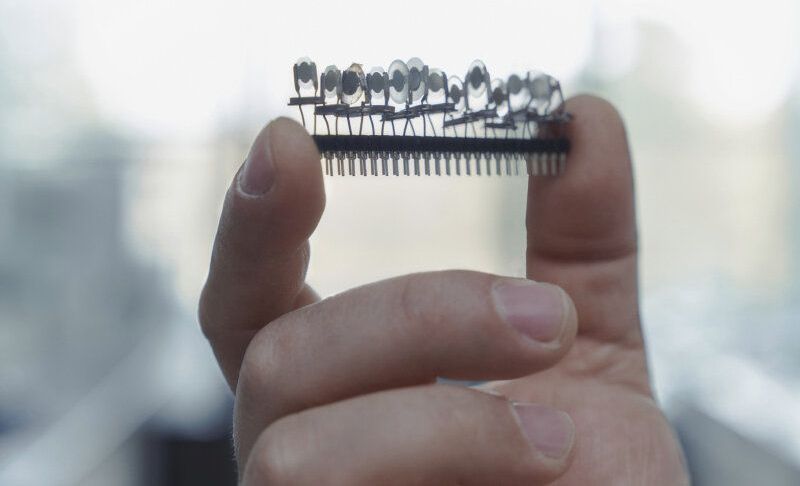

In nature, scents emitted by plants attract animals such as insects. However, scents are also used in the industry, for example in the production of perfumes and aromas. In order to achieve a reliable, quick, and objective discrimination of mint scents in particular, researchers at KIT (Karlsruhe Institute of Technology) embarked on an interdisciplinary collaboration and developed an electronic nose with an artificial sense of smell. This E-nose achieves high precision in recognizing different mint species, which makes it a suitable tool for applications ranging from pharmaceutical quality control to the monitoring of mint oil as an environmentally friendly bioherbicide.
“So far, scientists were able to identify an estimated 100000 different biological compounds through which neighboring plants interact with each other or control other organisms, such as insects,” says Professor Peter Nick from the Botanical Institute of KIT. “These compounds are very similar in plants of the same genus.” A classic example from the plant world is mint, where the different varieties produce with very species-specific scents. Industrial quality control of mint oil, in particular, is subject to strict legal regulations in order to prevent adulteration, is time-consuming, and requires a great deal of expertise, the scientist explains. A new “electronic nose” equipped with sensors made from combined materials will support this process.
In new research, Texas A&M University scientists have for the first time revealed a single microscopic defect called a “twin” in a soft-block copolymer using an advanced electron microscopy technique. This defect may be exploited in the future to create materials with novel acoustic and photonic properties.
“This defect is like a black swan—something special going on that isn’t typical,” said Dr. Edwin Thomas, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. “Although we chose a certain polymer for our study, I think the twin defect will be fairly universal across a bunch of similar soft matter systems, like oils, surfactants, biological materials and natural polymers. Therefore, our findings will be valuable to diverse research across the soft matter field.”
The results of the study are detailed in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Dr. Thomas Lovejoy, is an innovative conservation biologist, who is Founder and President of the non-profit Amazon Biodiversity Center, the renowned Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project, and the person who coined the term “biological diversity”.
Dr. Lovejoy currently serves as Professor in the department of Environmental Science and Policy at George Mason University, and as a senior fellow at the United Nations Foundation based in Washington, DC.
Dr. Lovejoy has also served as the World Bank’s chief biodiversity advisor and the lead specialist for environment for Latin America and the Caribbean, the first Biodiversity Chair of the H. John Heinz III Center for Science, Economics and the Environment, President of the Heinz Center, and chair of the Scientific Technical Advisory Panel (STAP) for the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the multibillion-dollar funding mechanism for developing countries in support of their obligations under international environmental conventions.
Spanning the political spectrum, Dr. Lovejoy has served on science and environmental councils under the Reagan, Bush, and Clinton administrations. At the core of these many influential positions are seminal ideas, which have formed and strengthened the field of conservation biology.
In the 1980s, Dr. Lovejoy brought international attention to the world’s tropical rainforests, and in particular, the Brazilian Amazon, where he has worked since 1965.
With multiple co-edited books (including Biodiversity and Climate Change: Transforming the Biosphere; Drones for Conservation — Field Guide for Photographers, Researchers, Conservationists and Archaeologists; Costa Rican Ecosystems; Climate Change and Biodiversity; On the Edge: The State and Fate of the World’s Tropical Rainforests), Dr. Lovejoy is credited as a founder of the field of climate change biology. He also founded the series Nature, the popular long-term series on public television.
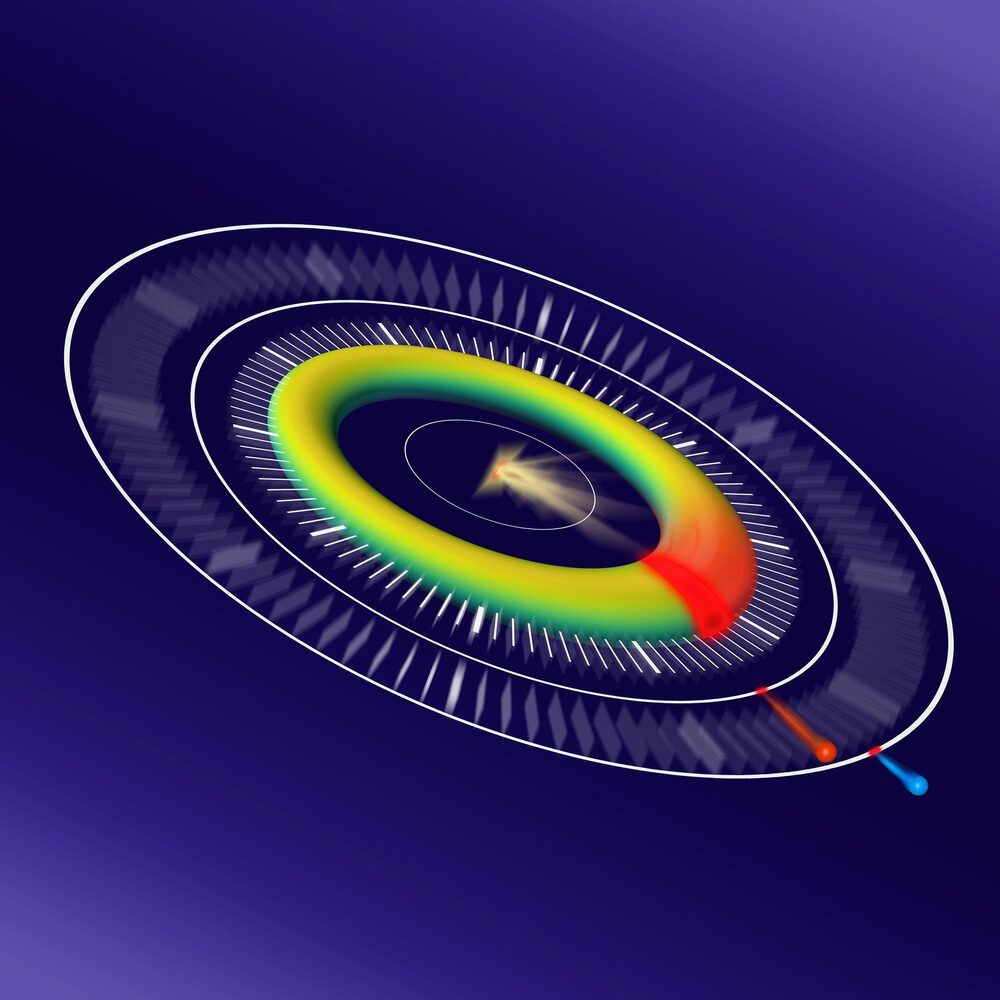
Scientists dramatically enhance the achievable resolution at free-electron lasers with a new technique.
Hard X-ray free-electron lasers (XFELs) have delivered intense, ultrashort X-ray pulses for over a decade. One of the most promising applications of XFELs is in biology, where researchers can capture images down to the atomic scale even before the radiation damage destroys the sample. In physics and chemistry, these X-rays can also shed light on the fastest processes occurring in nature with a shutter speed lasting only one femtosecond – equivalent to a millionth of a billionth of a second.
However, on these minuscule timescales, it is extremely difficult to synchronize the X-ray pulse that sparks a reaction in the sample on the one hand and the laser pulse which ‘observes’ it on the other. This problem is called timing jitter, and it is a major hurdle in ongoing efforts to perform time-resolved experiments at XFELs with ever-shorter resolution.
Nuclear Nonproliferation, Cooperative Threat Reduction and WMD Terrorism — Dr. Natasha Bajema, Director, Converging Risks Lab, The Council on Strategic Risks.
Dr. Natasha Bajema, is a subject matter expert in nuclear nonproliferation, cooperative threat reduction and WMD terrorism, and currently serves as Director of the Converging Risks Lab, at The Council on Strategic Risks, a nonprofit, non-partisan security policy institute devoted to anticipating, analyzing and addressing core systemic risks to security in the 21st century, with special examination of the ways in which these risks intersect and exacerbate one another.
The Converging Risks Lab (CRL) is a research and policy development-oriented program designed to study converging, cross-sectoral risks in a rapidly-changing world, which brings together experts from multiple sectors of the security community, to ask forward-thinking questions about these converging risks, and to develop anticipatory solutions.
Dr. Bajema is also Founder and CEO of Nuclear Spin Cycle, a publishing and production company specializing in national security, entertainment, and publishing.
Prior to this, Dr. Bajema was at the Center for the Study of Weapons of Mass Destruction at the National Defense University, serving as Director of the Program for Emerging Leaders (PEL), as well as serving long-term detail assignments serving in various capacities in the Office of the Secretary of Defense, Acquisitions, Technology and Logistics, Nuclear, Chemical and Biological Defense Programs and in Defense Nuclear Nonproliferation at Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration.
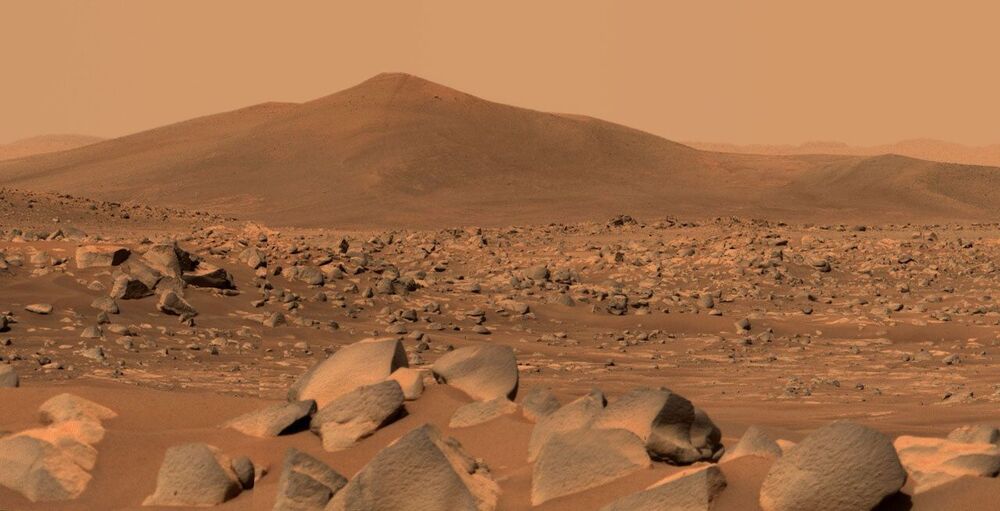

NASA’s newest Mars rover is beginning to study the floor of an ancient crater that once held a lake.
NASA’s Perseverance rover has been busy serving as a communications base station for the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter and documenting the rotorcraft’s historic flights. But the rover has also been busy focusing its science instruments on rocks that lay on the floor of Jezero Crater.
What insights they turn up will help scientists create a timeline of when an ancient lake formed there, when it dried, and when sediment began piling up in the delta that formed in the crater long ago. Understanding this timeline should help date rock samples – to be collected later in the mission – that might preserve a record of ancient microbes.