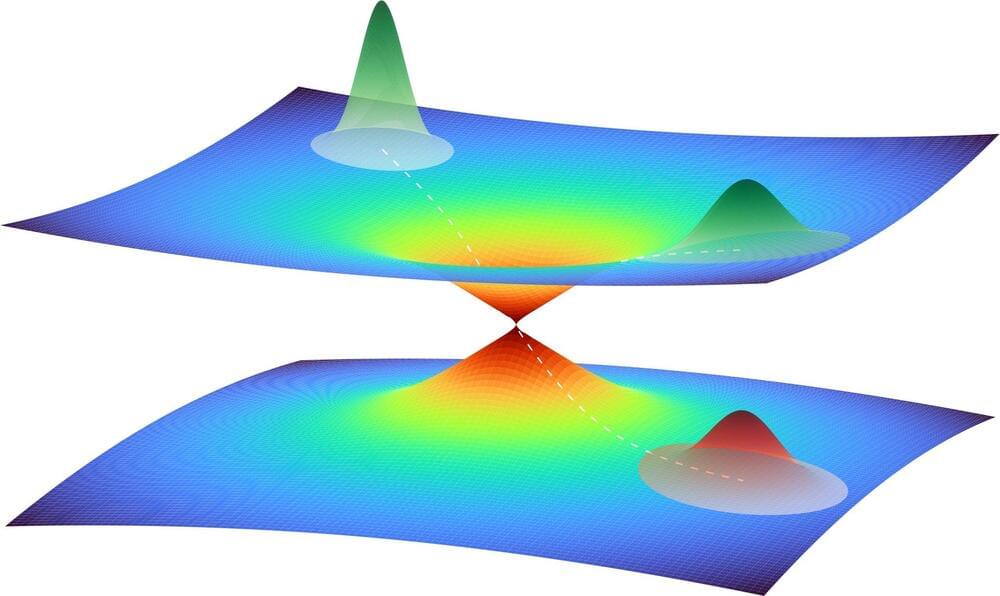
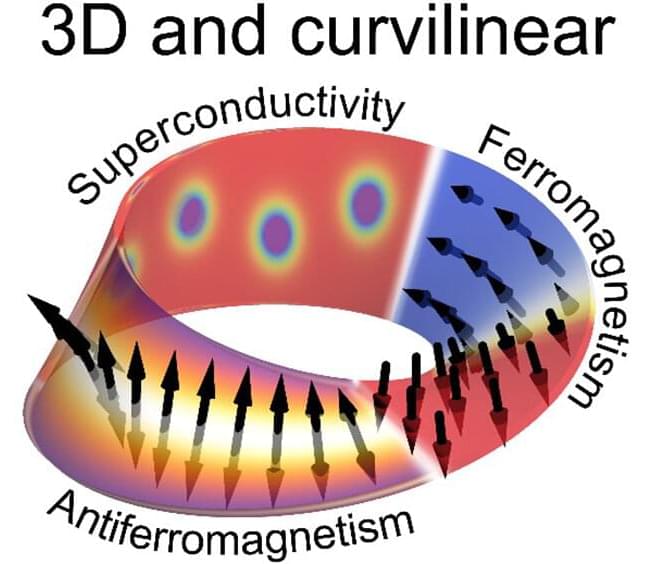
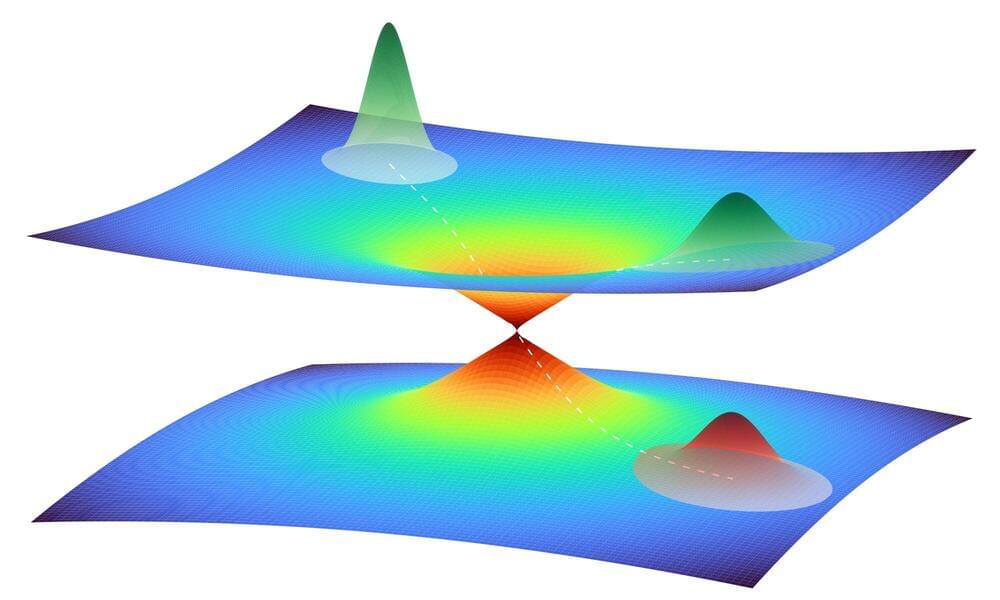
An international team of scientists from Austria and Germany has launched a new paradigm in magnetism and superconductivity, putting effects of curvature, topology, and 3D geometry into the spotlight of next-decade research. The results are published in Advanced Materials.
Traditionally, the primary field in which curvature plays a pivotal role is the theory of general relativity. In recent years, however, the impact of curvilinear geometry has entered various disciplines, ranging from solid-state physics to soft-matter physics to chemistry and biology; and giving rise to a plethora of emerging domains, such as curvilinear cell biology, semiconductors, superfluidity, optics, plasmonics and 2D van der Waals materials. In modern magnetism, superconductivity and spintronics, extending nanostructures into the third dimension has become a major research avenue because of geometry-, curvature-and topology-induced phenomena. This approach provides a means to improve conventional functionalities and to launch novel functionalities by tailoring the curvature and 3D shape.
“In recent years, there have appeared experimental and theoretical works dealing with curvilinear and three-dimensional superconducting and (anti-)ferromagnetic nano-architectures. However, these studies originate from different scientific communities, resulting in the lack of knowledge transfer between such fundamental areas of condensed matter physics as magnetism and superconductivity,” says Oleksandr Dobrovolskiy, head of the SuperSpin Lab at the University of Vienna. “In our group, we lead projects in both these topical areas and it was the aim of our perspective article to build a ‘bridge’ between the magnetism and superconductivity communities, drawing attention to the conceptual aspects of how extension of structures into the third dimension and curvilinear geometry can modify existing and aid launching novel functionalities upon solid-state systems.”