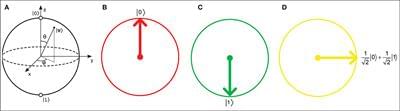
Many current computational models that aim to simulate cortical and hippocampal modules of the brain depend on artificial neural networks. However, such classical or even deep neural networks are very slow, sometimes taking thousands of trials to obtain the final response with a considerable amount of error. The need for a large number of trials at learning and the inaccurate output responses are due to the complexity of the input cue and the biological processes being simulated. This article proposes a computational model for an intact and a lesioned cortico-hippocampal system using quantum-inspired neural networks. This cortico-hippocampal computational quantum-inspired (CHCQI) model simulates cortical and hippocampal modules by using adaptively updated neural networks entangled with quantum circuits. The proposed model is used to simulate various classical conditioning tasks related to biological processes. The output of the simulated tasks yielded the desired responses quickly and efficiently compared with other computational models, including the recently published Green model.
Several researchers have proposed models that combine artificial neural networks (ANNs) or quantum neural networks (QNNs) with various other ingredients. For example, Haykin (1999) and Bishop (1995) developed multilevel activation function QNNs using the quantum linear superposition feature (Bonnell and Papini, 1997).
The prime factorization algorithm of Shor was used to illustrate the basic workings of QNNs (Shor, 1994). Shor’s algorithm uses quantum computations by quantum gates to provide the potential power for quantum computers (Bocharov et al., 2017; Dridi and Alghassi, 2017; Demirci et al., 2018; Jiang et al., 2018). Meanwhile, the work of Kak (1995) focused on the relationship between quantum mechanics principles and ANNs. Kak introduced the first quantum network based on the principles of neural networks, combining quantum computation with convolutional neural networks to produce quantum neural computation (Kak, 1995; Zhou, 2010). Since then, a myriad of QNN models have been proposed, such as those of Zhou (2010) and Schuld et al. (2014).