The interdisciplinary nexus of biology and engineering, known as synthetic biology, is growing at a rapid pace, opening new vistas that could scarcely be imagined a short time ago.


DARPA’s Safe Genes program plans to invest $65 million in seven teams that will collect data and develop gene editing tools to support bio-innovation and combat bio-threats such as invasive species.

Gene editing aims to make precise changes to the target DNA whilst avoiding altering other parts of the DNA. The objective of this is to remove undesirable genetic traits and introduce desirable changes in both plants and animals. For example, it could be used to make crops more drought resistant, prevent or cure inherited genetic disorders or even treat age-related diseases.
As some of you may recall, back in May a study was published which claimed that the groundbreaking gene editing technique CRISPR caused thousands of off target and potentially dangerous mutations[1]. The authors of the paper called for regulators to investigate the safety of the technique, a move that could potentially set back research years if not decades.
This publication has been widely blasted by the research community due to serious questions about the study design being raised. One of the problems with this original paper was that it involved only three mice, this is an extremely poor number to make the kind of conclusions the paper did. There have been calls for the paper to be withdrawn and critical responses to the study.
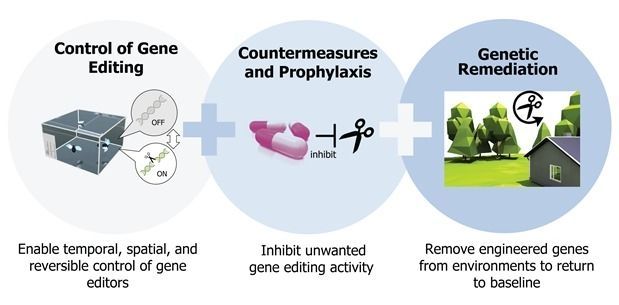
DARPA created the Safe Genes program to gain a fundamental understanding of how gene editing technologies function; devise means to safely, responsibly, and predictably harness them for beneficial ends; and address potential health and security concerns related to their accidental or intentional misuse. Today, DARPA announced awards to seven teams that will pursue that mission, led by: The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard; Harvard Medical School; Massachusetts General Hospital; Massachusetts Institute of Technology; North Carolina State University; University of California, Berkeley; and University of California, Riverside. DARPA plans to invest $65 million in Safe Genes over the next four years as these teams work to collect empirical data and develop a suite of versatile tools that can be applied independently or in combination to support bio-innovation and combat bio-threats.
Gene editing technologies have captured increasing attention from healthcare professionals, policymakers, and community leaders in recent years for their potential to selectively disable cancerous cells in the body, control populations of disease-spreading mosquitos, and defend native flora and fauna against invasive species, among other uses. The potential national security applications and implications of these technologies are equally profound, including protection of troops against infectious disease, mitigation of threats posed by irresponsible or nefarious use of biological technologies, and enhanced development of new resources derived from synthetic biology, such as novel chemicals, materials, and coatings with useful, unique properties.
Achieving such ambitious goals, however, will require more complete knowledge about how gene editors, and derivative technologies including gene drives, function at various physical and temporal scales under different environmental conditions, across multiple generations of an organism. In parallel, demonstrating the ability to precisely control gene edits, turning them on and off under certain conditions or even reversing their effects entirely, will be paramount to translation of these tools to practical applications. By establishing empirical foundations and removing lingering unknowns through laboratory-based demonstrations, the Safe Genes teams will work to substantially minimize the risks inherent in such powerful tools.
For decades, biologists have read and edited DNA, the code of life. Revolutionary developments are giving scientists the power to write it. Instead of tinkering with existing life forms, synthetic biologists may be on the verge of writing the DNA of a living organism from scratch. In the next decade, according to some, we may even see the first synthetic human genome. Join a distinguished group of synthetic biologists, geneticists and bioengineers who are edging closer to breathing life into matter.
Watch the full program here: https://youtu.be/rU_pfCtSWF4
Visit our Website: http://www.worldsciencefestival.com/
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/worldsciencefestival
Follow us on twitter: https://twitter.com/WorldSciFest


Rudrapur, Uttrakhand, India — July 02, 2017
Revita Life Sciences, (http://revitalife.co.in) a biotechnology company focused on translational regenerative therapeutic applications, has announced that it is continuing to advance their novel, multi-modality clinical intervention in the state of brain death in humans.
“We have proactively continued to advance our multi-modality protocol, as an extended treatment before extubation, in an attempt to reverse the state of brain death” said Mr.Pranjal Agrawal, CEO Revita Life Sciences. “This treatment approach has yielded some very encouraging initial outcome signs, ranging from minor observations on blood pressure changes with response to painful stimuli, to eye opening and finger movements, with corresponding transient to permanent reversal changes in EEG patterns.”
This first exploratory study, entitled “Non-randomized, Open-labelled, Interventional, Single Group, and Proof of Concept Study with Multi-modality Approach in Cases of Brain Death Due to Traumatic Brain Injury Having Diffuse Axonal Injury” is ongoing at Anupam Hospital, Rudrapur, Uttrakhand. The intervention primarily involves intrathecal administration of minimal manipulated (processed at point of care) autologous stem cells derived from patient’s fat and bone marrow twice a week.
This study was inappropriately removed from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) database. ICMR has no regulatory oversight on such research in India.
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO), Drug Controller General of India, had no objection to the program progressing. Regulatory approval as needed for new drugs, is currently not required when research is conducted on the recently deceased, although IRB and family consent is definitely required. CDSCO, the regulator of such studies, clearly states that “no regulatory requirements are needed for any study with minimal manipulated autologous stem cells in brain death subjects”.
Death is defined as the termination of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Brain death, the complete and irreversible loss of brain function (including involuntary activity necessary to sustain life) as defined in the 1968 report of the Ad Hoc Committee of the Harvard Medical School, is the legal definition of human death in most countries around the world. Either directly through trauma, or indirectly through secondary disease indications, brain death is the final pathological state that over 60 million people globally transfer through each year.
“We are in process of publishing our initial retrospective results, as well ongoing early results, in a peer reviewed journal. These initial findings will prove invaluable to the future evolution of the program, as well as in progressing the development multi-modality regenerative therapeutics for the full range of the severe disorders of consciousness, including coma, PVS, the minimally conscious state, and a range of other degenerative CNS conditions in humans,” said Dr. Himanshu Bansal, Chief Scientific Officer, Revita Life Sciences and Director of Mother Cell.
With the maturation of the tools of medical science in the 21st century, especially cell therapies and regenerative medicines, tissues once considered irretrievable, may finally be able to be revived or rejuvenated. Hence many scientists believe that brain death, as presently defined, may one day be reversed. While the very long term goal is to find a solution for “re-infusing life”, the short term purpose of these types of studies is much less dramatic, which is to confirm if the current definition of brain irreversibility still holds true. There have been many anecdotal reports of brain death reversal across the world over the past decades in the scientific literature. Studies of this nature serve to verify and establish this very fact in a scientific and controlled manner. It will also one day give a fair chance to individuals, who are declared brain dead, especially after trauma.
About Revita Life Sciences
Revita Life Sciences is a biotechnology company focused on the development of stem cell therapies and regenerative medicine interventions that target areas of significant unmet medical need. Revita is led by Dr. Himanshu Bansal MD, who has spent over two decades developing novel MRI based classifications of spinal cord injuries as well as comprehensive treatment protocols with autologous tissues including bone marrow stem cells, Dural nerve grafts, nasal olfactory tissues, and omental transposition.

Philadelphia, PA, USA / Moscow, Russia — Bioquark, Inc., (www.bioquark.com) a life sciences company focused on the development of novel bio-products for regeneration, disease reversion, and healthy aging, and Moscow based, Lakmus LLC, a diversified investment company with business interests in pharmacies, restaurants, and real estate, announced a multi-disciplinary research collaboration with the FSBI Zakusov Institute of Pharmacology, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences (http://www.academpharm.ru/), and the Pavlov Institute of Physiology of the Russian Academy of Sciences (http://www.infran.ru/), to jointly study the pharmacotherapeutic longevity enhancement properties of its combinatorial regenerative biologic candidates.
“We are very excited about this continued collaboration with Lakmus,” said Ira S. Pastor, CEO, Bioquark Inc. “The disciplined development of our combinatorial biologic candidates (Bioquantines) for healthy longevity enhancement, represents another important step in our continued evolution as a company focused on a broad range of therapeutic products and services in the regenerative healthcare space.”
Throughout the 20th century, natural products formed the basis for a majority of all pharmaceuticals, biologics, and consumer healthcare products used by patients around the globe, generating trillions of dollars of wealth. However, many scientists believe we have only touched the surface with what the natural world, and its range of organisms, which from a health and wellness perspective are much further advanced than human beings, has to teach us.
The integration of a complex set of newer research disciplines, including interkingdom signaling, semiochemical communication, and evolutionary biology, as well as significant recent activity in the areas of the microbiome, are highlighting a myriad of new ways that non-human bio-products can affect the human genome for positive transitions in health and wellness dynamics.
“Bioquark has spent several years studying the natural ability of many species to turn back biological time in order to maintain health, fitness, and survival, developing a broad understanding of the combinatorial biochemical approaches they use to control nested hierarchies of disease (i.e. gene, cell, tissue, organism, environment),” said Dr. Sergei Paylian, Founder, CSO, and President, Bioquark Inc. “This research initiative is one more step in the path in allowing humans to recapture these capabilities to effectively counter our unfortunate progression into aging, disease and degeneration.”
About Bioquark, Inc.
Bioquark Inc. is focused on the development of natural biologic based products, services, and technologies, with the goal of curing a wide range of diseases, as well as effecting complex regeneration. Bioquark is developing both biological pharmaceutical candidates, as well as products for the global consumer health and wellness market segments.


Researchers at the Scripps Research Institute Florida campus have refined the already state-of-the-art gene-editing system CRISPR. The new improvements boost the ability of CRISPR to target, cut and paste genes in human and animal cells and helps to address the concerns of off target gene mutations raised in a recent study [1].
What is CRISPR?
CRISPR is short for “Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat,” and is a gene editing system that exploits an ancient bacterial immune defense process. Some microbes combat viral infection by sequestering a piece of a virus’ foreign genetic material within its own DNA, to serve as a template. The next time the viral sequence is encountered by the microbe, it is detected immediately and cut up for disposal with the help of two types of RNA. Molecules called guide RNAs show the location of the invader, and the CRISPR effector proteins act as the scissors that cut it apart and destroy it.