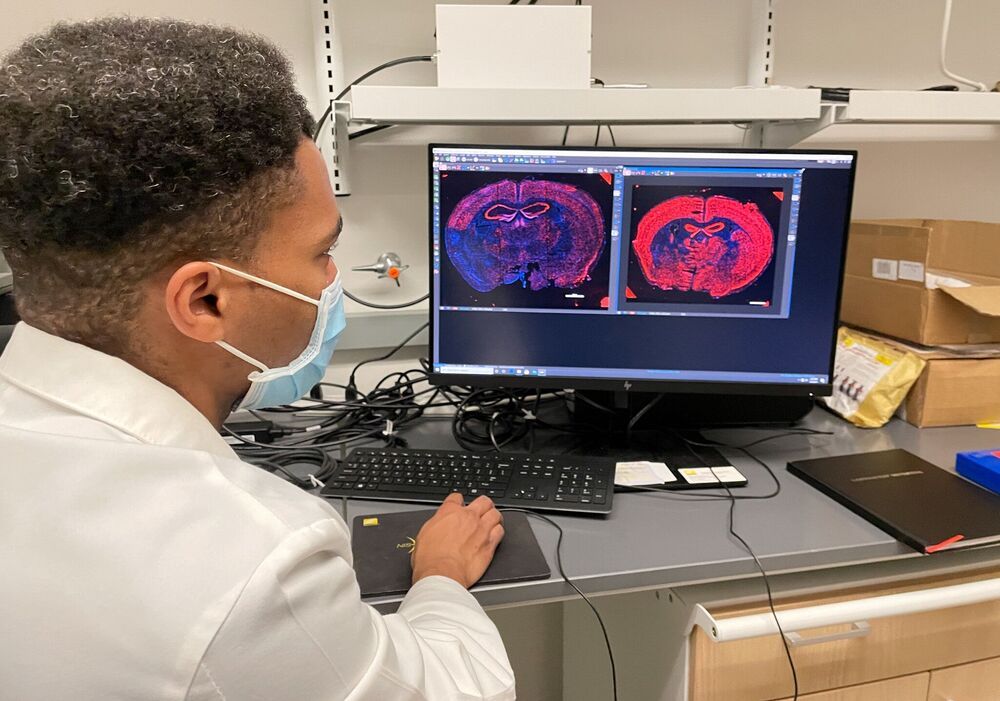
The development of gene therapy, in particular gene editing using the CRISPR-Cas9 method, has prompted a lively discussion around the world about how deeply you can interfere with the human genome. The creators of this method have turned to the world community, including lawyers, to undertake a public discussion of the implications that it can create (The National Academies of Sciences Engineering Medicine, 2015). The most important problem to be resolved in the future, in my opinion, will be the issue of establishing very clear legal principles of liability for damages resulting from the editing of genes in human embryos and reproductive cells. However, before this happens, it is necessary to show the possible legal problems that may arise and that will certainly appear in future legislative work in the world. Questions must be asked to which world legal experts will need to seek answers. The goal of this paper is to show the possible legal problems and ask questions related to the liability for damages resulting from the editing of genes in human embryos and reproductive cells that will be answered in the future.
Private law considerations will be based on Polish law, although it should be pointed out that the conclusions derived from them appear to be of universal nature for different legal systems. Despite the fact that legal considerations will refer to the regulation of Polish law, the subject of the analysis will also be the differences in the legal qualification of reproductive cells and embryos in other European legislations. It seems that nowhere in the world are there special regulations regarding the liability for damage related to the genetic editing of reproductive cells or embryos. Therefore, there is a need to present new challenges for classic private law institutions, such as legal abilities, torts, or liability for damages. Due to the lack of uniform European regulations and different conflicts of rights the subject of analysis will not be wrongful life and wrongful birth actions, but only claims of prenatal damage to a child.
The first major legal problem facing the international community is, of course, the question of the legal acceptability of the editing of genes of human reproductive cells and embryos (van Dijke et al., 2018). In this regard, it should be pointed out that despite the initial demand to ban such editing, over time, increasingly more scientists have pointed to the fact that it is not possible to maintain such a moratorium (Doudna and Sternberg, 2017). Jiankui’s presentation at the Second International Summit on Human Genome Editing on November 272018, showed that the introduction of a moratorium on genetic modifications of embryos in Europe, the condemnation of such research by a group of 120 of the greatest geneticists, even the Chinese regulations (Zhang and Lie, 2018) will not limit its conduct (Cyranoski and Ledford, 2018). Globalization of the medical market means that if any procedures are allowed on other continents, they will also become available to Europeans (Lunshof, 2016).