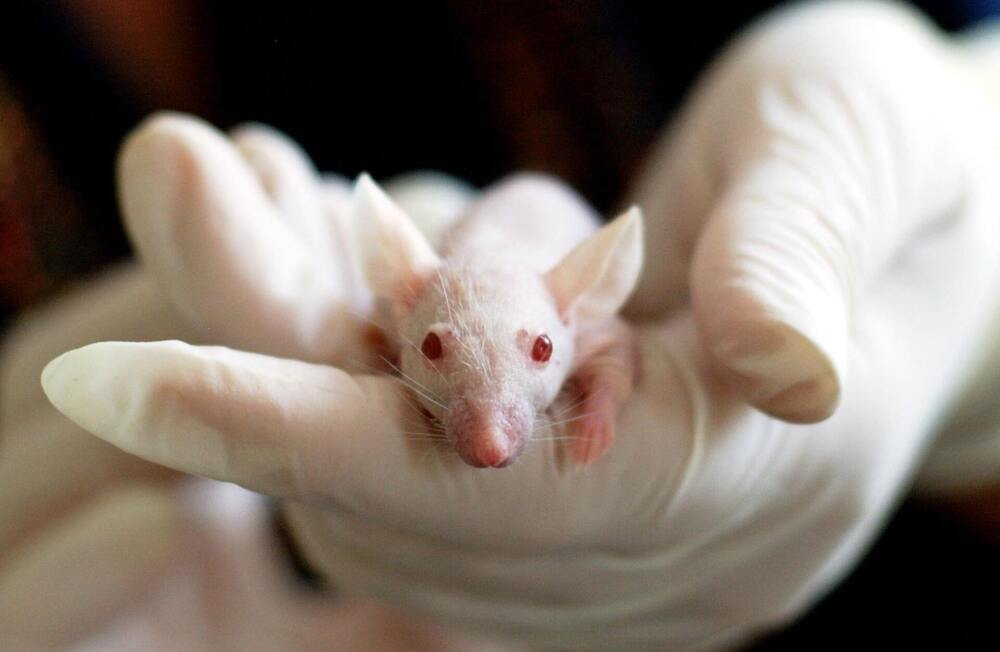
Using a mouse model, Chen and the team delivered a viral construct containing TRPV1 ion channels to genetically-selected neurons. Then, they delivered small burst of heat via low-intensity focused ultrasound to the select neurons in the brain via a wearable device. The heat, only a few degrees warmer than body temperature, activated the TRPV1 ion channel, which acted as a switch to turn the neurons on or off.
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy have had some treatment success with deep brain stimulation, but those require surgical device implantation. A multidisciplinary team at Washington University in St. Louis has developed a new brain stimulation technique using focused ultrasound that is able to turn specific types of neurons in the brain on and off and precisely control motor activity without surgical device implantation.
The team, led by Hong Chen, assistant professor of biomedical engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering and of radiation oncology at the School of Medicine, is the first to provide direct evidence showing noninvasive, cell-type-specific activation of neurons in the brain of mammal by combining ultrasound-induced heating effect and genetics, which they have named sonothermogenetics. It is also the first work to show that the ultrasound-genetics combination can robustly control behavior by stimulating a specific target deep in the brain.
Results of the three years of research, which was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health’s BRAIN Initiative, were published online in Brain Stimulation May 11, 2021.