The ancient organisms could help us understand the origins of life on Earth, and may also aid the search for life on other planets.
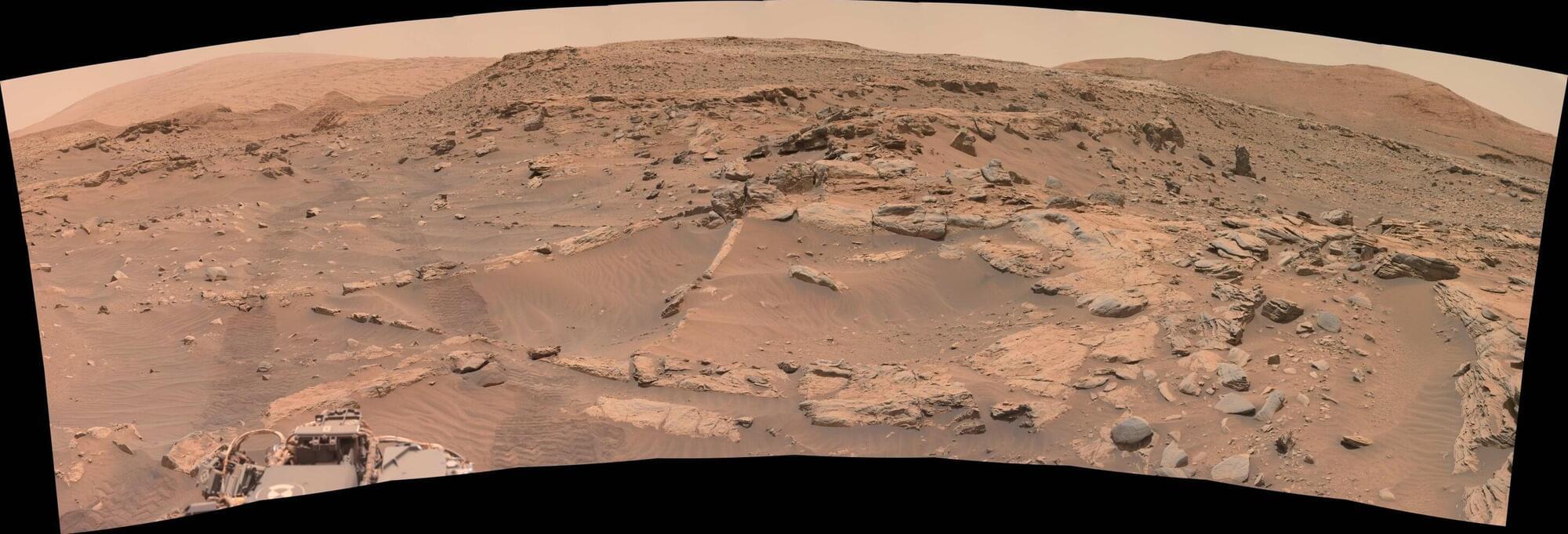


Scientists from New York University Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) have uncovered new evidence that water once flowed beneath the surface of Mars, revealing that the planet may have remained habitable for life much longer than previously thought.
The study, published in the Journal of Geophysical Research—Planets, shows that ancient sand dunes in Gale Crater, a region explored by NASA’s Curiosity rover, gradually turned into rock after interacting with underground water billions of years ago.
Led by Dimitra Atri, Principal Investigator of NYUAD’s Space Exploration Laboratory, with research assistant Vignesh Krishnamoorthy, the research team compared data from the Curiosity rover with rock formations in the UAE desert that formed under similar conditions on Earth.

A new study led by Dr. James De Buizer of the SETI Institute and Dr. Wanggi Lim of IPAC at Caltech has uncovered unexpected findings about how quickly massive stars take shape near the center of the Milky Way. Using data collected primarily from NASAs now-retired SOFIA airborne observatory, the researchers examined three active stellar nurseries, Sgr B1, Sgr B2, and Sgr C, situated in the heart of our Galaxy.
Despite the Galactic Center containing far denser concentrations of gas and dust than other parts of the Milky Way, the formation of massive stars (those more than 8 times the mass of our Sun) appears to occur at a slower pace there.
To investigate further, the team compared these three regions with others of similar size located farther from the center, including areas closer to our solar neighborhood. Their findings confirmed that the rate of new star formation near the Galactic Center is significantly lower than average. Even though the region holds the kind of dense, turbulent clouds that typically give rise to large stars, these environments seem to struggle to produce them.

“Our findings show that Mars didn’t simply go from wet to dry,” said Dr. Dimitra Atri. “Even after its lakes and rivers disappeared, small amounts of water continued to move underground, creating protected environments that could have supported microscopic life.”
How long did Mars have habitable conditions for life? This is what a recent study published in the Journal of Geophysical Research – Planets hopes to address as a team of scientists from New York University Abu Dhabi investigated how surface and subsurface environments could have provided conditions suitable for life for greater periods than previously thought. This study has the potential to help scientists better understand past environments on Mars and what this could mean for finding life beyond Earth.
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from NASA’s Curiosity rover, which is currently exploring Gale Crater, a location of ancient water on Mars. The researchers compared data from wind-formed features called dunes, potential ancient groundwater and subsurface water, and analog studies in the United Arab Emirates. Dunes are widespread on Mars and have long helped researchers understand global weather patterns, specifically regarding dust transportation. In the end, the researchers found that dunes interacting with watery environments could be potential locations to search for life on Mars, specifically regarding how they transported water from the surface to the subsurface.
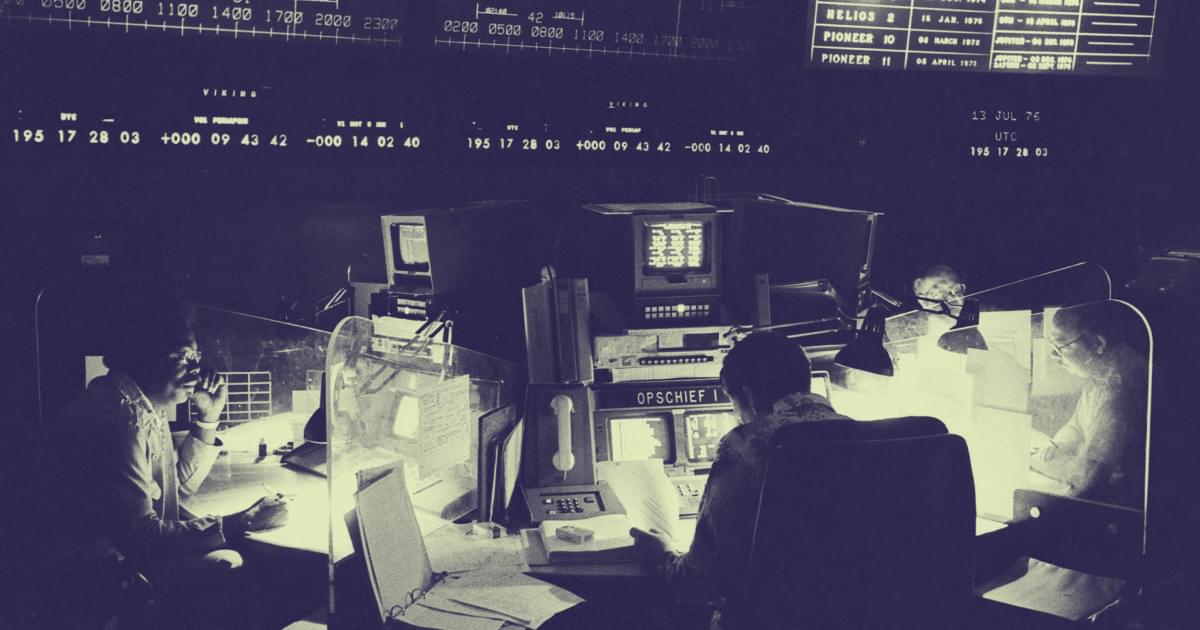

How a scientific mistake derailed Mars exploration for 50 years. What if Viking actually did discover life on Mars? See blog with our link to eLetter in Science at.
(https://bigthink.com/hard-science/how-a-scientific-mistake-f…ploration/)
All blogs and their links also on my website searchforlifeintheuniverse.com
In 1976, NASA’s Viking landers searched for life on Mars. The Viking team announced Mars was lifeless — but the data was ambiguous.
A new study proposes how we could look for signs of self-replicating (Von Neumann) probes that would prove that the Solar System has been explored by an advanced extraterrestrial intelligence (ETI).
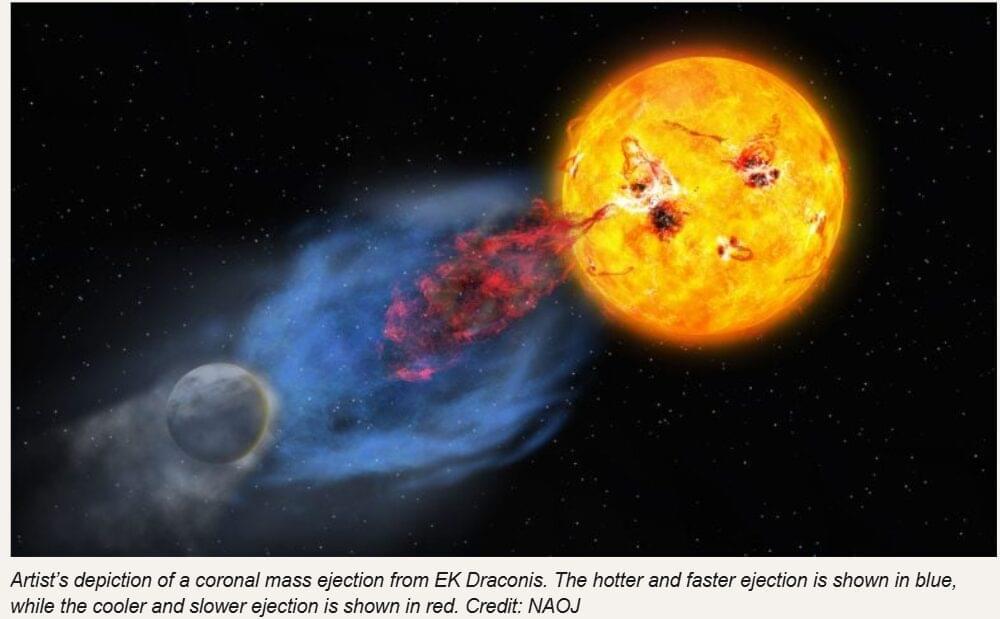
A young Sun’s violent plasma eruptions may have helped ignite the spark of life on Earth. Astronomers observed a massive, multi-temperature plasma eruption from a young Sun-like star, revealing how early solar explosions could shape planets. These fierce events may have influenced the atmosphere and life-forming chemistry of the early Earth.
Although we rarely notice from Earth, the Sun is continuously hurling enormous clouds of charged plasma into space. These events, known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs), often occur alongside sudden bursts of light called solar flares. When particularly strong, CMEs can stretch far enough to disturb Earth’s magnetic field, producing dazzling auroras and sometimes triggering geomagnetic storms that disrupt satellites or even power grids.
Scientists believe that billions of years ago, when the Sun and Earth were both young, solar activity was far more intense than it is today. Powerful CMEs during that period may have influenced the conditions that allowed life to emerge and evolve. Studies of young Sun-like stars — used as stand-ins for our own star’s early years — show that these stars often unleash flares far stronger than any recorded from the modern Sun.
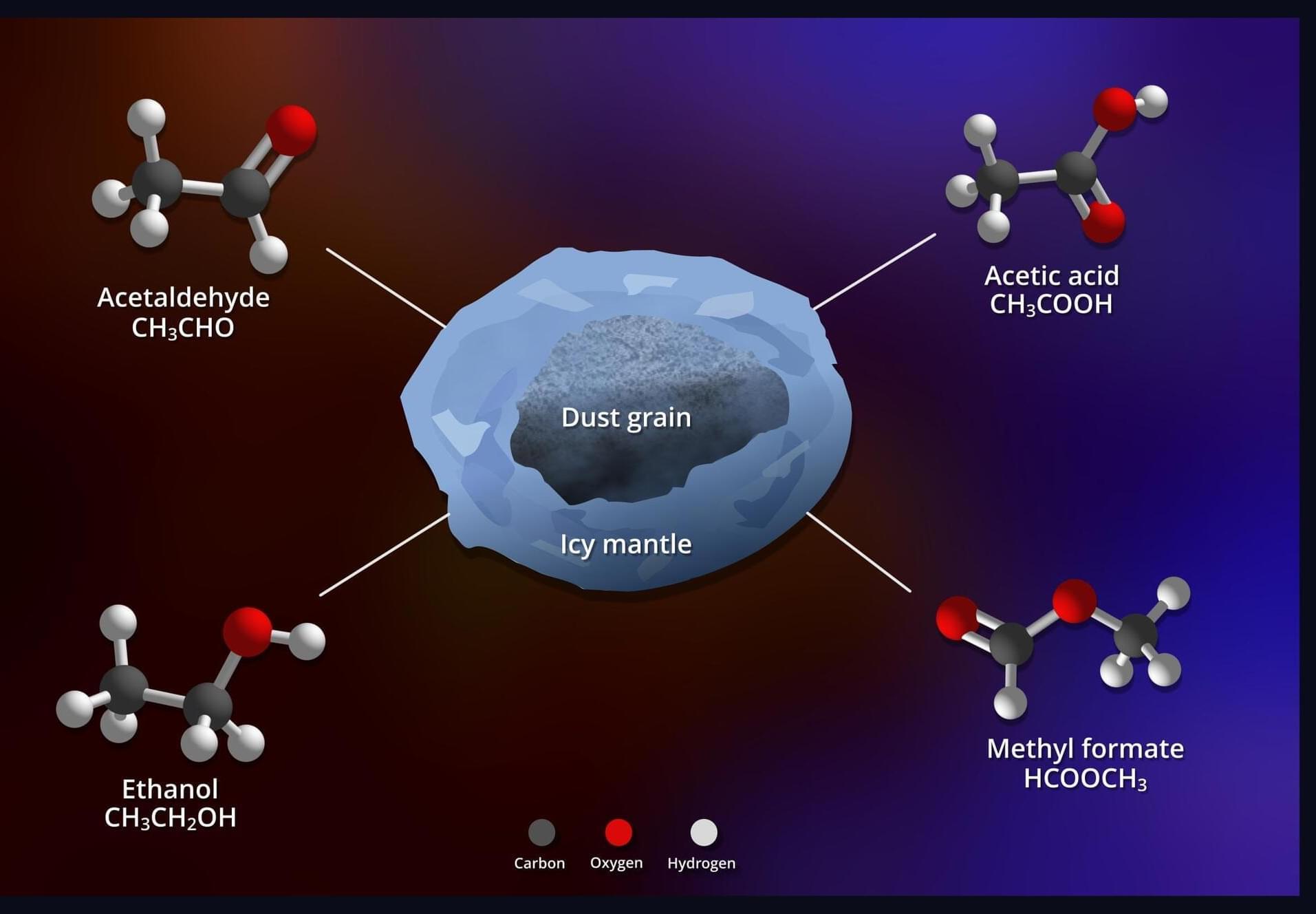
In a finding that may transform our understanding of how life’s chemical precursors are distributed across the universe, astronomers have detected organic molecules containing more than six atoms frozen in ice around a young star named ST6, located in a galaxy beyond the Milky Way.
Using the James Webb Space Telescopes (JWST) Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), the team identified five distinct carbon-based compounds in the Large Magellanic Cloud, our nearest neighboring galaxy. The research, led by University of Maryland and NASA scientist Marta Sewilo, was published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters on October 20, 2025.

In 1949, famed mathematician and physicist John von Neumann delivered a series of addresses at the University of Illinois, where he introduced the concept of “universal constructor.”
The theory was further detailed in the 1966 book, Theory of Self-Reproducing Automata, a collection of von Neumann’s writings compiled and completed by a colleague after his death.
In the years that followed, scientists engaged in the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) considered how advanced civilizations could rely on self-replicating probes to explore the galaxy.

Scientists at Indiana University have made a major advance in understanding how the universe came to exist. Their success comes from a collaboration between two large international research teams studying neutrinos, the nearly massless particles that stream endlessly through space and matter while rarely interacting with anything around them. The findings, published in Nature, bring researchers closer to solving one of science’s most profound mysteries: why the universe is filled with matter, stars, planets, and life, rather than nothing at all.
This breakthrough arose from an unprecedented partnership between two world-leading neutrino experiments: NOvA in the United States and T2K in Japan. By combining their data, scientists are gaining new insight into the hidden behavior of neutrinos and their antimatter counterparts, potentially revealing why the early universe avoided self-destruction immediately after the Big Bang.
In each experiment, beams of neutrinos are generated using powerful particle accelerators and then observed after traveling vast distances underground. Detecting them is an enormous challenge; out of countless particles, only a few interact in a way that leaves measurable traces. Using sophisticated detectors and advanced computing tools, researchers reconstruct these rare interactions to understand how neutrinos change as they move through space.