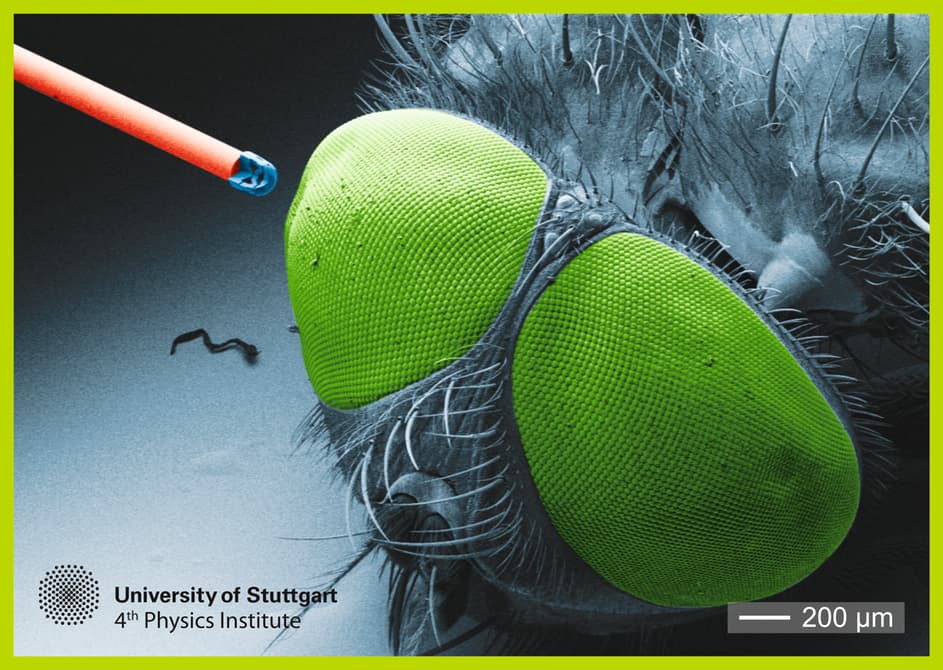
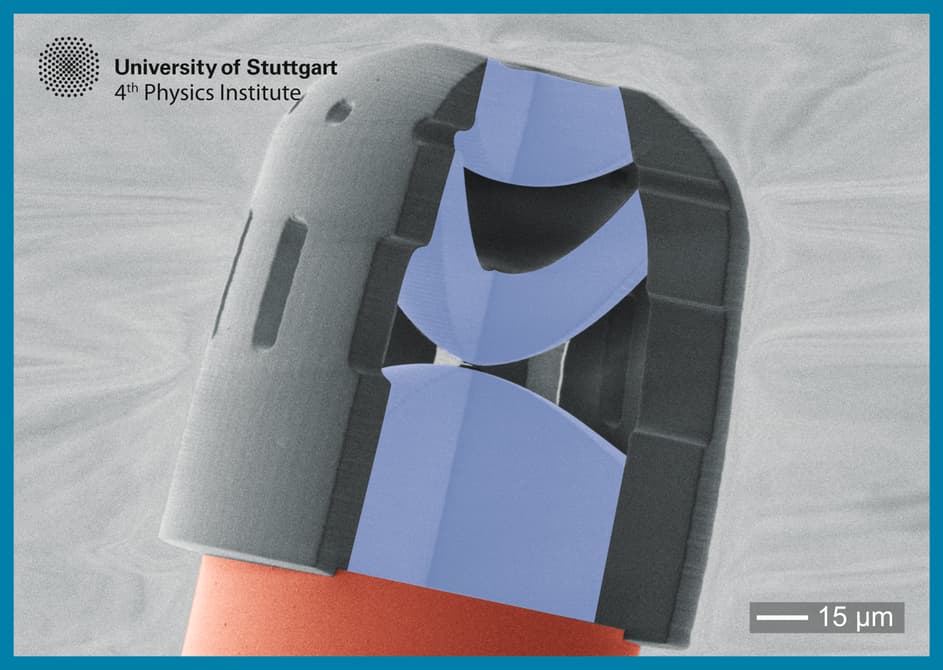
3D printing has has a presence in the medical industry since the 1980s for modelling body parts that are otherwise untouchable without invasive surgery, but research into the potential of this technology is bringing clinicians closer to getting a good look up close at the real thing. Instead of scans, what about injecting a camera no bigger than a grain of salt into your patient?
A group of German researchers have been working on a complex lens system that is small enough to fit inside a syringe, and applications aren’t just limited to the medical industry. They have the potential to also be used in many products which need parts to be as small and light as possible, such as drones and smart phones.