“We know that immune dysregulation causes vascular damage and tissue fibrosis in systemic sclerosis,” says the lead author. “However, it remains unclear why skin symptoms and the level of organ involvement differ from patient to patient.”
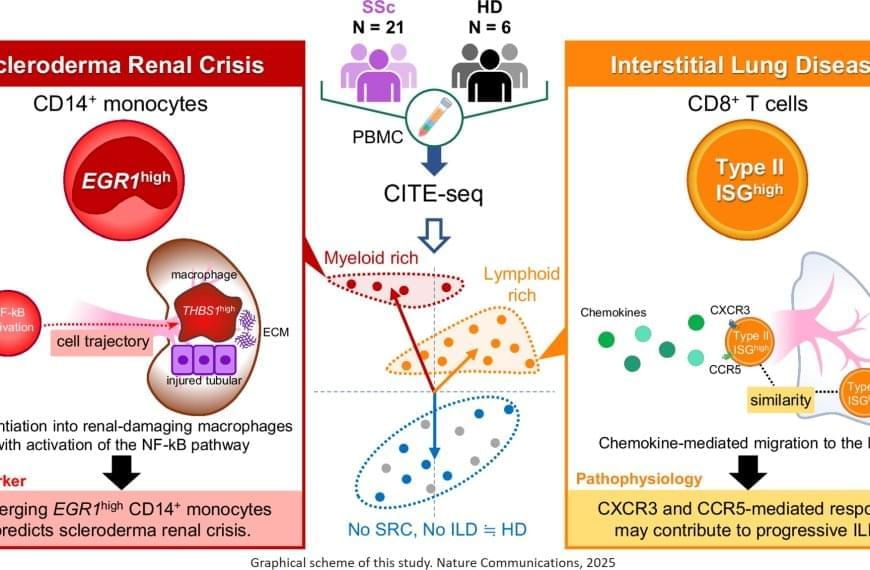
To explore this, the researchers took blood and tissue samples from patients with systemic sclerosis and analyzed them cell by cell, looking for differences in gene expression. Additionally, proteins on the cell surface were examined to identify biomarkers of disease, which are useful for identifying and treating diseases in earlier stages.
“The results were intriguing,” explains the senior author. “We identified a specific subset of immune cells, the EGR1-expressing subpopulation of CD14+ monocytes, that were clearly associated with scleroderma renal crisis, a serious kidney complication in patients with systemic sclerosis.”
While immune cells usually help the body fight infection and disease, in certain cases they can be inappropriately activated through gene expression. In this instance, CD14+ monocytes differentiated – or transformed – into destructive macrophages, which can further promote inflammation near the kidneys and contribute to the thickening and scarring of internal organs.
In addition, the researchers found that CD8+ T cells with a type II interferon signature, which makes the immune cells particularly aggressive and inflammatory, were linked to progressive interstitial lung disease. EGR1-expressing CD14+ monocytes and these peculiar CD8+ T cells are likely to accumulate in the kidney or the lung, respectively, and produce or recruit other factors that contribute to disease progression.
Treating rare diseases can be complicated at the best of times, and it gets even more complicated when different patients with the same disease exhibit different symptoms. Now, researchers have reported a cellular signature that might explain why some patients with autoimmune disease are stable while others face life-threatening complications.