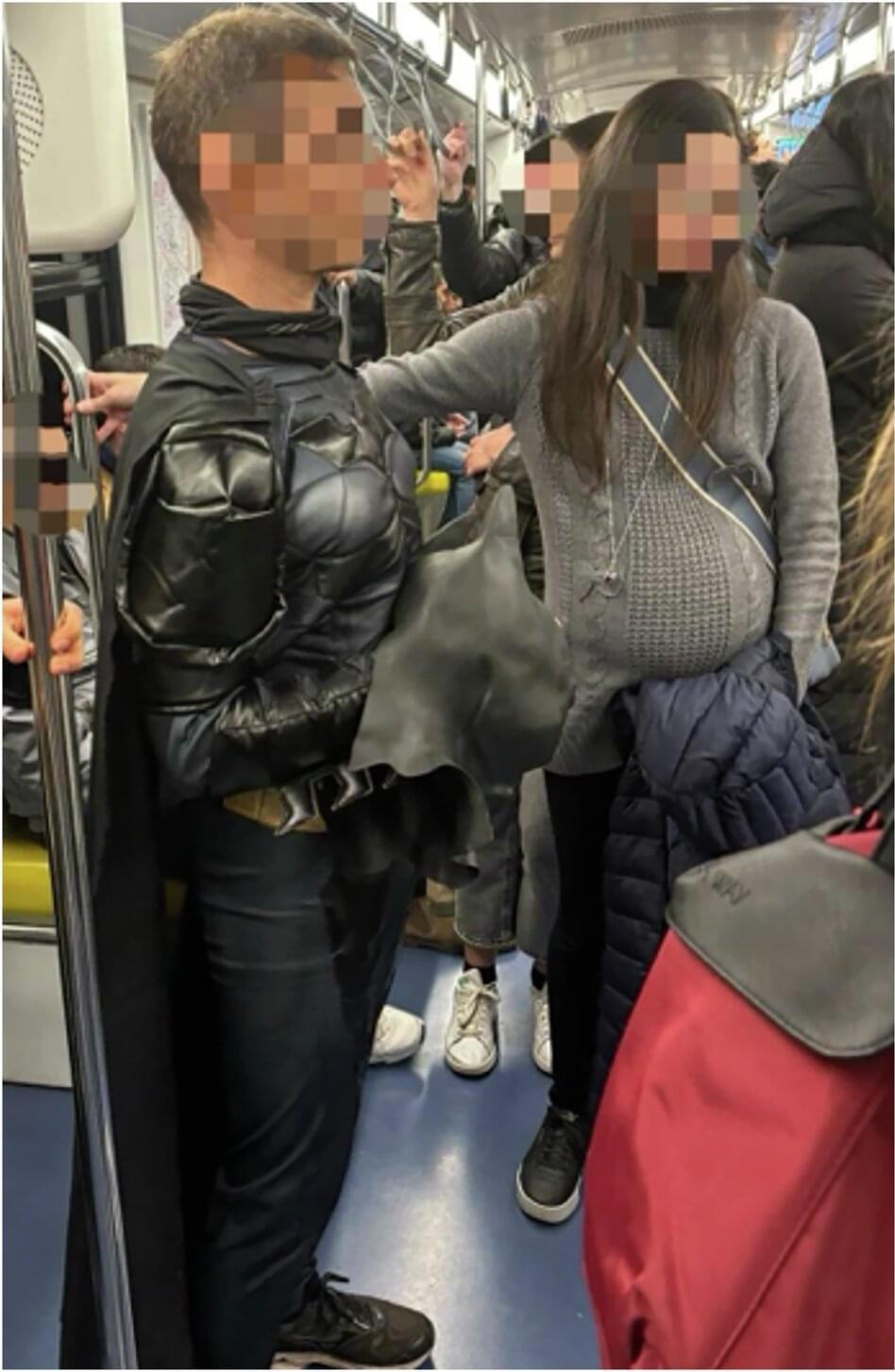
If “Batman” appears on the scene, we immediately become more altruistic: in fact, research conducted by psychologists from the Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Milan, shows that the sudden appearance of something unexpected—Batman—disrupts the predictability of everyday life and forces people to be present, breaking free from autopilot.
The study was published in the journal npj Mental Health Research, and was led by Francesco Pagnini, Full Professor of Clinical Psychology at the Faculty of Psychology, Università Cattolica.
Prosocial behavior, or the act of helping others, is essential to social life, yet the spontaneous environmental factors that trigger such behavior remain little explored. This study tested the ability of an unexpected event, such as the presence of a person dressed as Batman, to increase prosocial behavior by interrupting routines and increasing people’s attention to the present moment.