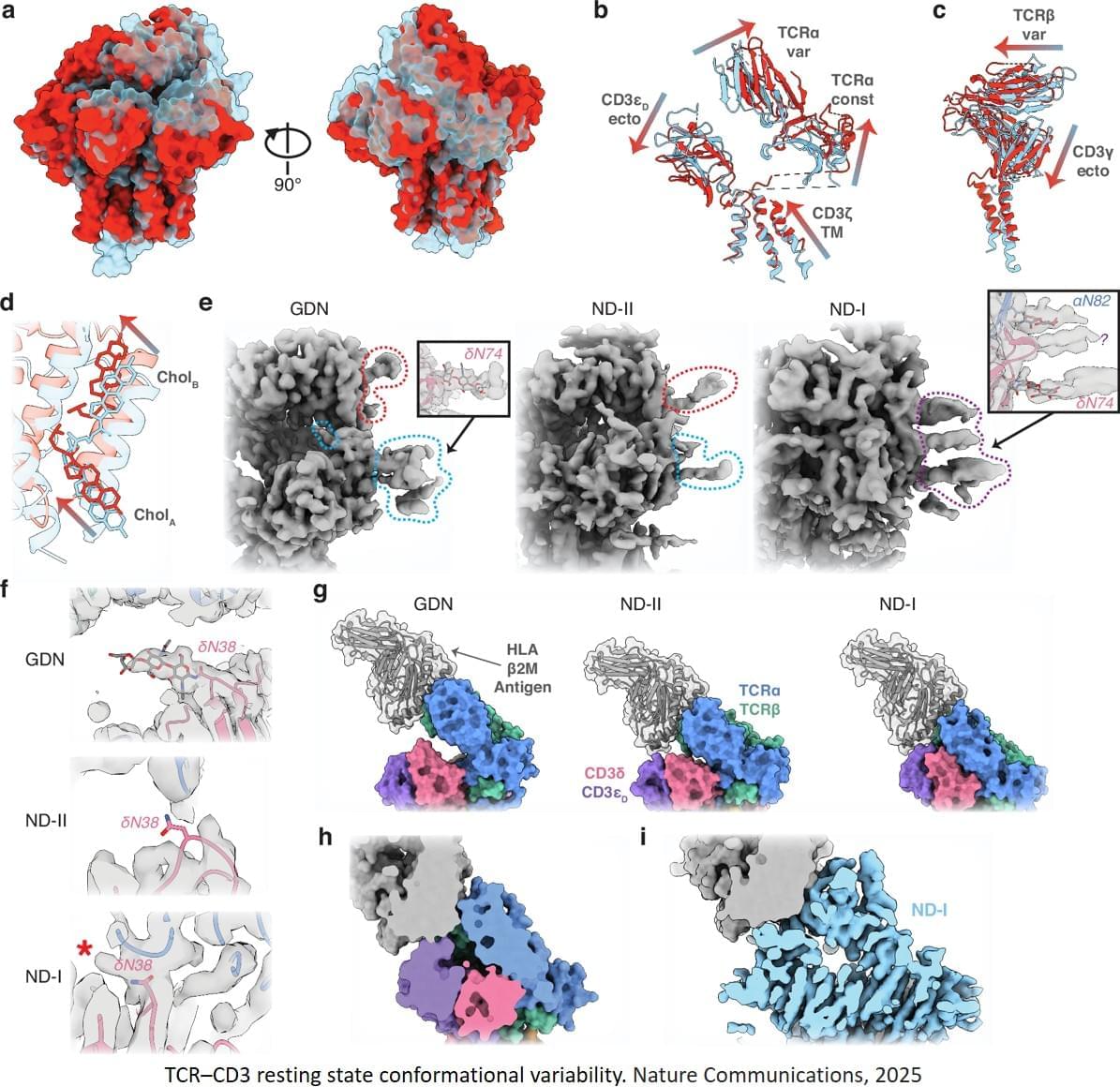
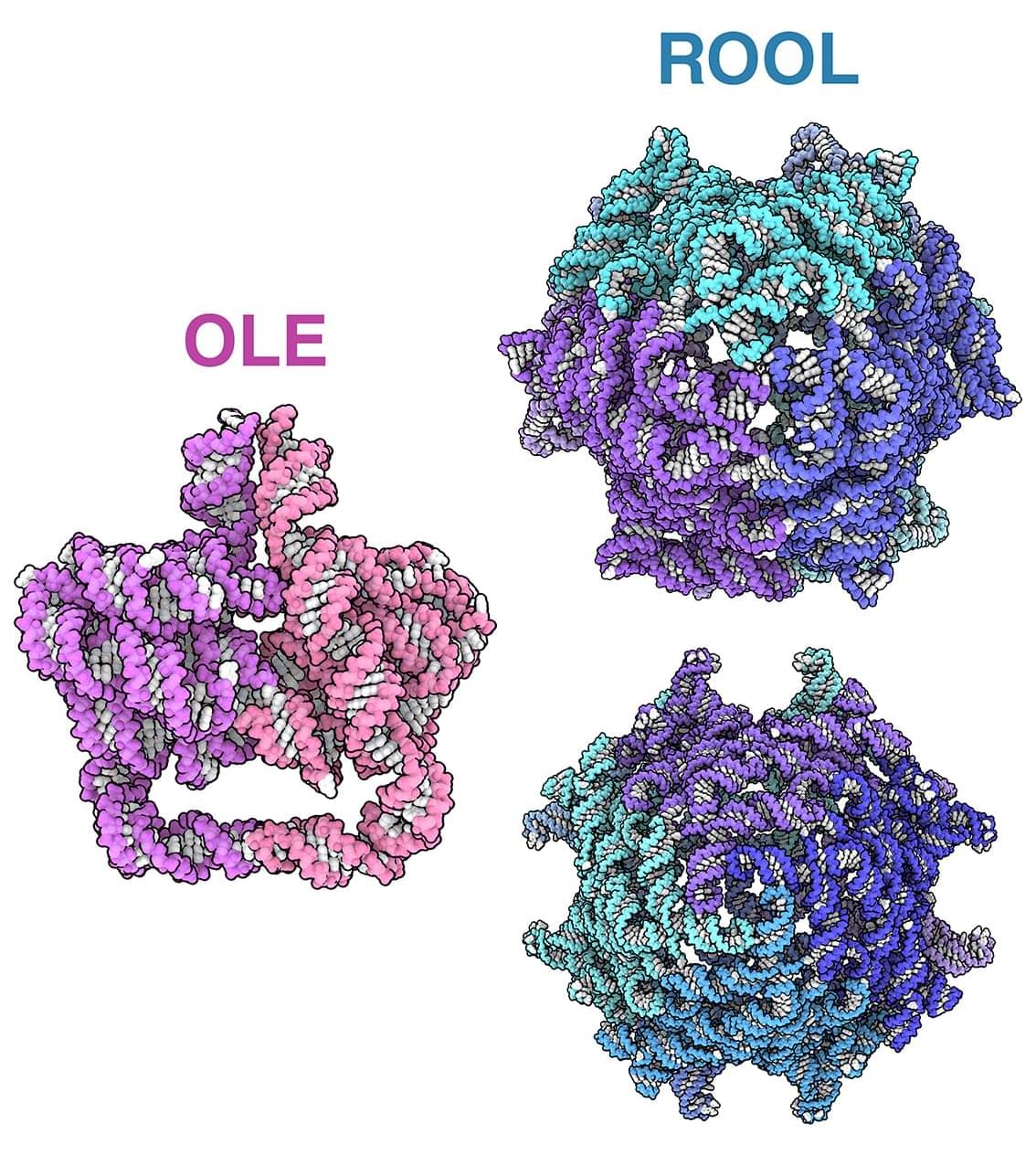
Naturally occurring enzymes, while powerful, catalyze only a fraction of the reactions chemists care about.
That’s why scientists are eager to design new-to-nature versions that could manufacture drugs more efficiently, break down pollutants, capture carbon, or carry out entirely new forms of chemistry that biology never evolved.
Read more.
RFdiffusion2, RFdiffusion3, and Riff-Diff each solve different structural problems in computational enzyme design by Elizabeth Walsh.