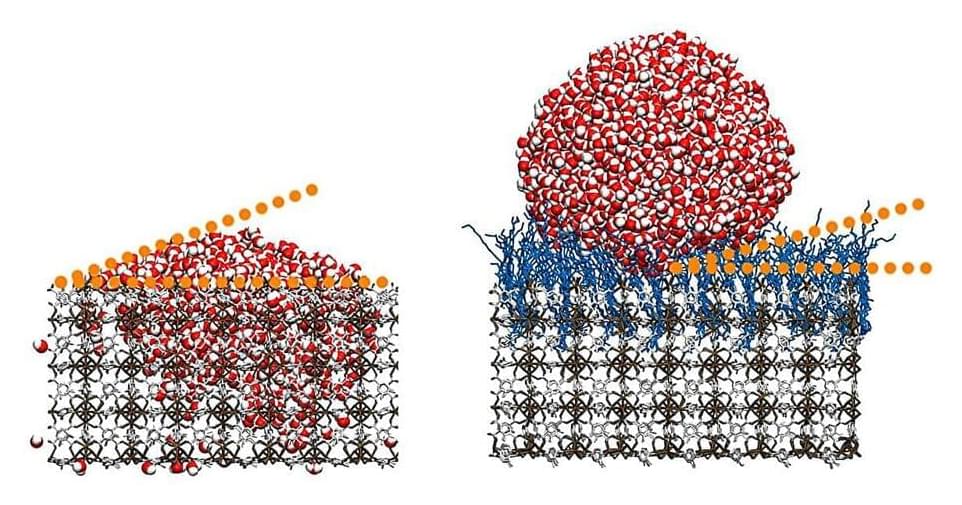
Scientists from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and the Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati (IITG) have developed a surface material that repels water droplets almost completely. Using an entirely innovative process, they changed metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)—artificially designed materials with novel properties—by grafting hydrocarbon chains.
The resulting superhydrophobic (extremely water-repellent) properties are interesting for use as self-cleaning surfaces that need to be robust against environmental influences, such as on automobiles or in architecture. The study was published in the journal Materials Horizons.
MOFs (metal-organic frameworks) are composed of metals and organic linkers that form a network with empty pores resembling a sponge. Their volumetric properties—unfolding two grams of this material would yield the area of a football pitch—make them an interesting material in applications such as gas storage, carbon dioxide separation, or novel medical technologies.