Human chromosomes are long polymer chains that store genetic information. The nucleus of each cell contains the entire human genome (DNA) encoded on 46 chromosomes with a total length of about 2 meters. To fit into the microscopic cell nucleus and at the same time provide constant access to genetic information, chromosomes are folded in the nucleus in a special, predetermined way. DNA folding is an urgent task at the intersection of polymer physics and systems biology.
A few years ago, as one of the mechanisms of chromosome folding, researchers put forward a hypothesis of active extrusion of loops on chromosomes by molecular motors. Although the ability of motors to extrude DNA in vitro has been demonstrated, observing loops in a living cell experimentally is a technically very difficult, almost impossible, task.
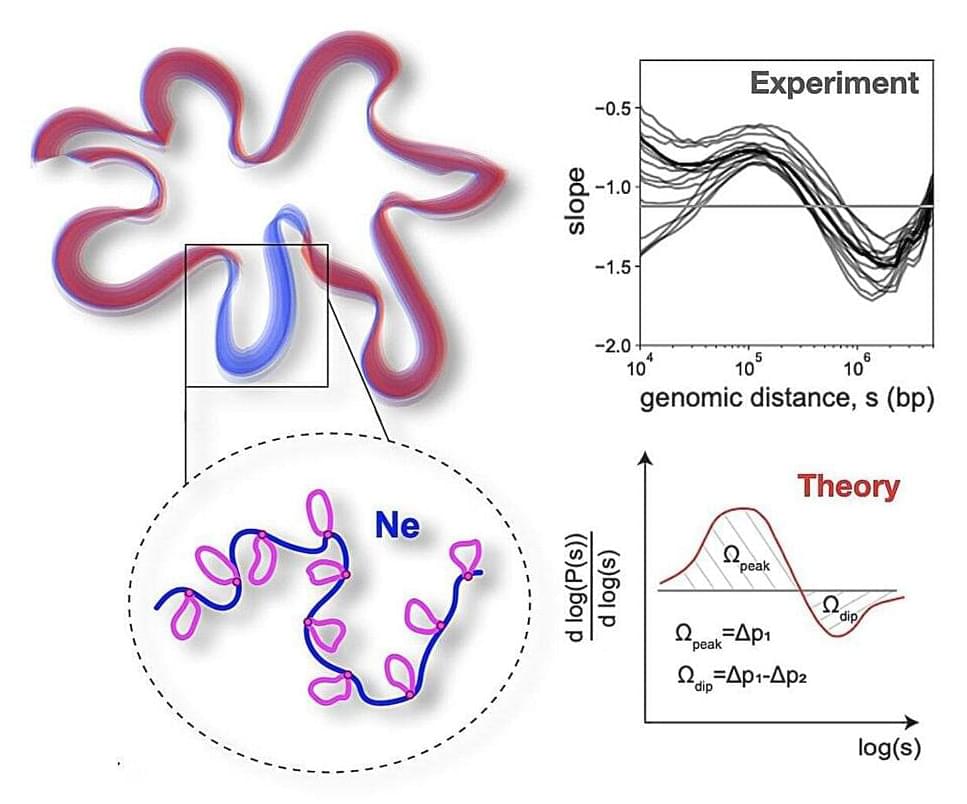
A team of scientists from Skoltech, MIT, and other leading scientific organizations in Russia and the U.S. have presented a physical model of a polymer folded into loops. The analytical solution of this model allowed scientists to reproduce the universal features of chromosome packing based on the experimental data—the image shows the peak-dip derivative curve of the contact probability.