Healthy cells work hard to maintain the integrity of our DNA, but occasionally, a chromosome can get separated from the others and break apart during cell division. The tiny fragments of DNA then get reassembled in random order in the new cell, sometimes producing cancerous gene mutations.
This chromosomal shattering and rearranging is called “chromothripsis” and occurs in the majority of human cancers, especially cancers of the bones, brain and fatty tissue. Chromothripsis was first described just over a decade ago, but scientists did not understand how the floating pieces of DNA were able to be put back together.
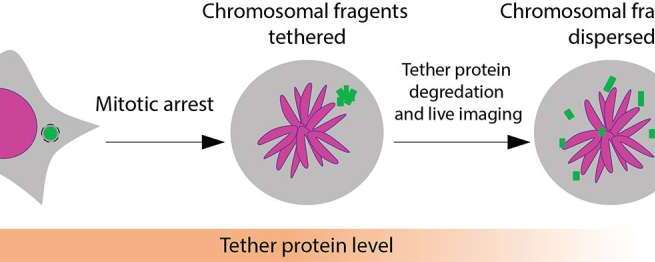
In a study published in Nature, researchers at University of California San Diego have answered this question, discovering that the shattered DNA fragments are actually tethered together. This allows them to travel as one during cell division and be re-encapsulated by one of the new daughter cells, where they are reassembled in a different order.