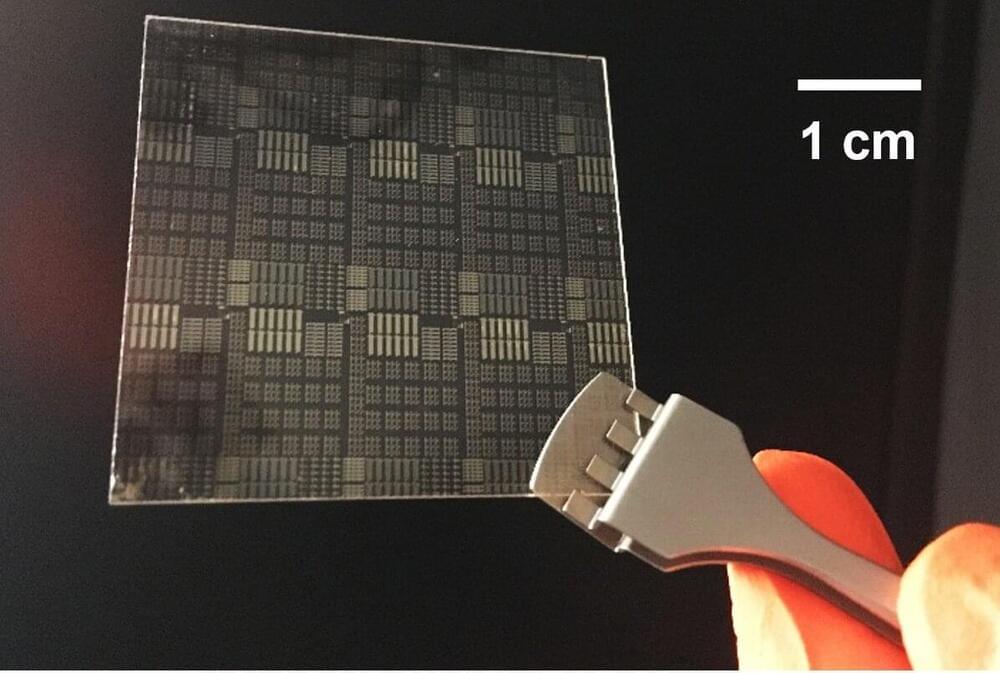
Low-cost, flexible displays that use very little energy could be a step closer, thanks to an innovation from the University of Surrey that solves a problem that has plagued source-gated transistors (SGT). The study has been published by IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices.
Dr. Radu Sporea, project lead from the University of Surrey, said, We used a rapidly emerging semiconductor material called IGZO or indium-gallium-zinc oxide to create the next generation of source-gated transistors. Through nanoscale contact engineering, we obtained transistors that are much more stable with temperature than previous attempts. Device simulations allowed us to understand this effect.
This new design adds temperature stability to SGTs and retains usual benefits like using low power, producing high signal amplification, and being more reliable under different conditions. While source-gated transistors are not mainstream because of a handful of performance limitations, we are steadily chipping away at their shortcomings.