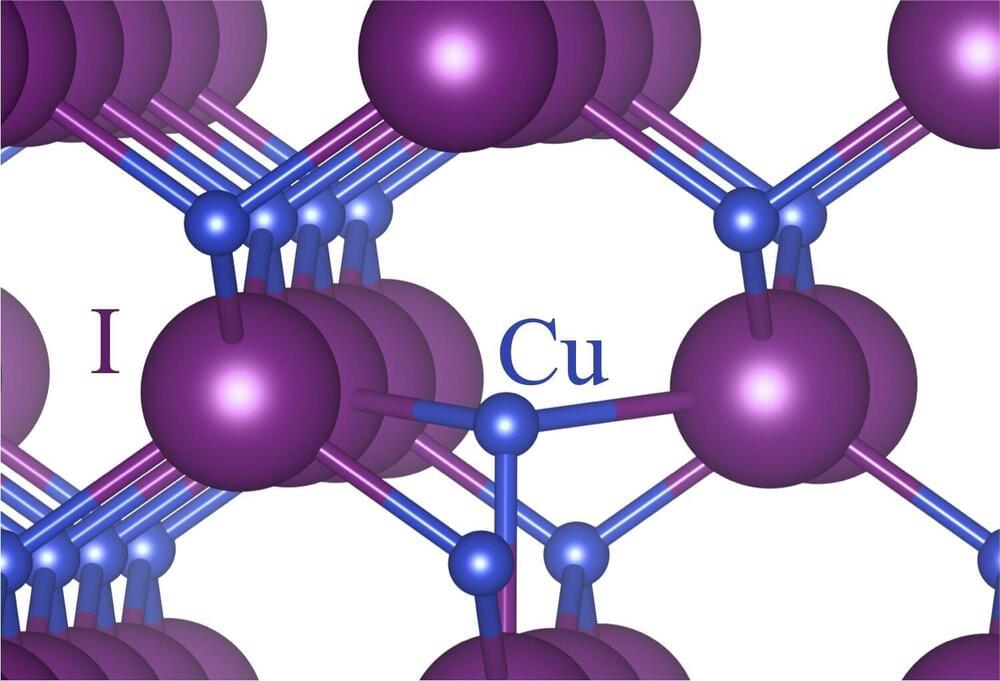
The NOMAD Laboratory researchers have recently shed light on fundamental microscopic mechanisms that can help with tailoring materials for heat insulation. This development advances the ongoing efforts to enhance energy efficiency and sustainability.
The role of heat transport is crucial in various scientific and industrial applications, such as catalysis, turbine technologies, and thermoelectric heat converters that convert waste heat into electricity.
Particularly in the context of energy conservation and the development of sustainable technologies, materials with high thermal insulation capabilities are of utmost importance. These materials make it possible to retain and utilize heat that would otherwise go to waste. Therefore, improving the design of highly insulating materials is a key research objective in enabling more energy-efficient applications.