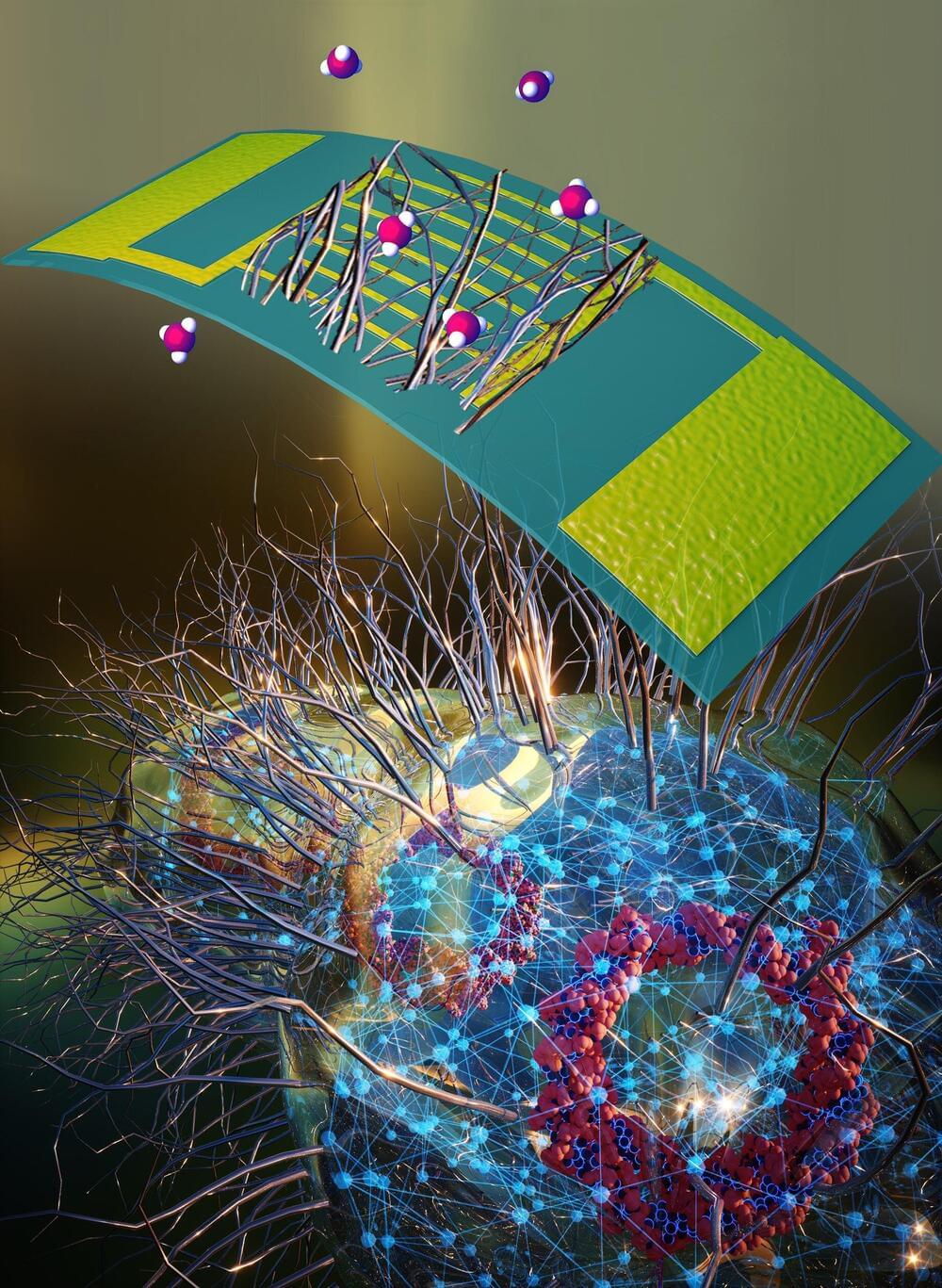
Scientists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently announced the invention of a nanowire, 10,000 times thinner than a human hair, which can be cheaply grown by common bacteria and can be tuned to “smell” a vast array of chemical tracers—including those given off by people afflicted with different medical conditions, such as asthma and kidney disease.
Thousands of these specially tuned wires, each sniffing out a different chemical, can be layered onto tiny, wearable sensors, allowing health-care providers an unprecedented tool for monitoring potential health complications. Since these wires are grown by bacteria, they are organic, biodegradable and far greener than any inorganic nanowire.
To make these breakthroughs, which were detailed in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectrics, senior authors Derek Lovley, Distinguished Professor of Microbiology at UMass Amherst, and Jun Yao, professor of electrical and computer engineering in the College of Engineering at UMass Amherst, needed to look no farther than their own noses.