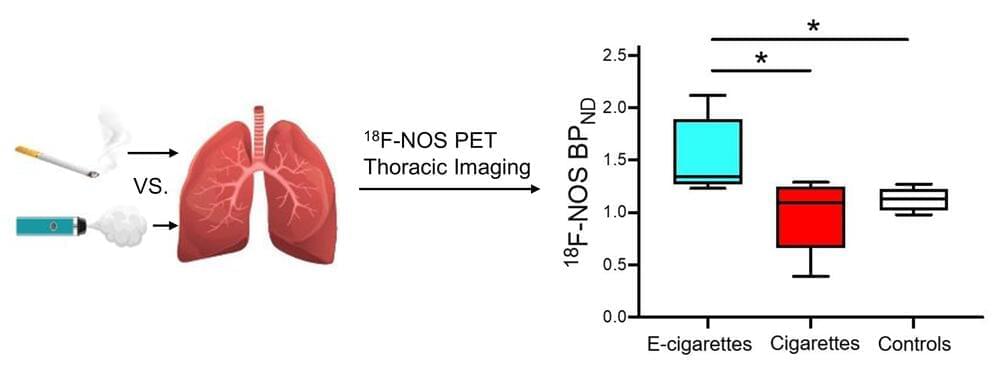
Electronic cigarette (e-cigarette) users have greater lung inflammation than cigarette smokers and non-smokers, according to a new study published online in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. This study is the first to provide evidence that vaping e-liquids with e-cigarettes creates a unique inflammatory response in the lungs that is different from cigarette smoking.
E-cigarette usage has increased dramatically in the past several years, particularly among adolescents and young adults. While many people assume that e-cigarettes are safer than conventional cigarettes, e-cigarettes can cause pulmonary inflammation and increase the risk of lung disease. In addition, their long-term safety has not been rigorously evaluated.
This is the first PET study to use a novel radiotracer, 18 F-NOS, to compare lung inflammation between cigarette and e-cigarette users in vivo. Although PET imaging with 18 F-FDG has been used in the past to investigate inflammation in smokers and vapers, its conclusions were limited.









Comments are closed.