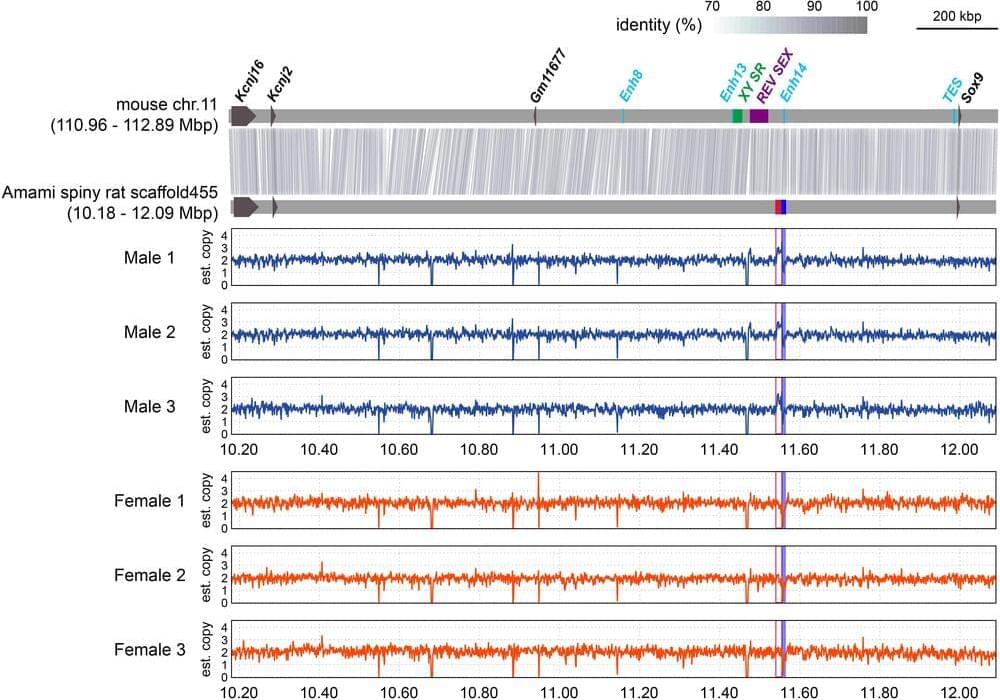
Mammalian sex chromosomes are highly conserved, and sex is determined by SRY on the Y chromosome. Two exceptional rodent groups in which some species lack a Y chromosome and Sry offer insights into how novel sex genes can arise and replace Sry, leading to sex chromosome turnover. However, intensive study over three decades has failed to reveal the identity of novel sex genes in either of these lineages. We here report our discovery of a male-specific duplication of an enhancer of Sox9 in the Amami spiny rat Tokudaia osimensis, in which males and females have only a single X chromosome (XO/XO) and the Y chromosome and Sry are completely lost. We performed a comprehensive survey to detect sex-specific genomic regions in the spiny rat. Sex-related genomic differences were limited to a male-specific duplication of a 17-kb unit located 430 kb upstream of Sox9 on an autosome. Hi-C analysis using male spiny rat cells showed the duplicated region has potential chromatin interaction with Sox9. The duplicated unit harbored a 1,262-bp element homologous to mouse enhancer 14 (Enh14), a candidate Sox9 enhancer that is functionally redundant in mice. Transgenic reporter mice showed that the spiny rat Enh14 can function as an embryonic testis enhancer in mice. Embryonic gonads of XX mice in which Enh14 was replaced by the duplicated spiny rat Enh14 showed increased Sox9 expression and decreased Foxl2 expression. We propose that male-specific duplication of this Sox9 enhancer substituted for Sry function, defining a novel Y chromosome in the spiny rat.
Menu
-
Sitemap
- Cool places
- Ark I
- Blue Beauty
- EM Launch
- GETAS
- Official Song
- Home
- About
- Blog
- Programs
- Reports
- A-PRIZE
- Donate
- Join Us
- Newsletter
- Quotes
- Store
- Press Releases

Tag cloud
aging AI Alzheimer's anti-aging Artificial Intelligence bioquantine bioquark biotech biotechnology bitcoin blockchain brain death cancer cryptocurrency culture Death existential risks extinction future futurism Google health healthspan humanity ideaxme immortality Interstellar Travel ira pastor Life extension lifespan longevity NASA Neuroscience politics reanima regenerage regeneration research risks singularity space sustainability technology transhumanism wellnessCategories
- 3D printing
- 4D printing
- Peter Diamandis
- DNA
- Ray Kurzweil
- Elon Musk
- Singularity University
- Skynet
- Mark Zuckerberg
- aging
- alien life
- anti-gravity
- architecture
- asteroid/comet impacts
- astronomy
- augmented reality
- automation
- bees
- big data
- bioengineering
- biological
- bionic
- bioprinting
- biotech/medical
- bitcoin
- blockchains
- business
- chemistry
- climatology
- complex systems
- computing
- cosmology
- counterterrorism
- cryonics
- cryptocurrencies
- cybercrime/malcode
- cyborgs
- defense
- disruptive technology
- driverless cars
- drones
- economics
- education
- electronics
- employment
- encryption
- energy
- engineering
- entertainment
- environmental
- ethics
- events
- evolution
- existential risks
- exoskeleton
- finance
- first contact
- food
- fun
- futurism
- general relativity
- genetics
- geoengineering
- geography
- geology
- geopolitics
- governance
- government
- gravity
- habitats
- hacking
- hardware
- health
- holograms
- homo sapiens
- human trajectories
- humor
- information science
- innovation
- internet
- journalism
- law
- law enforcement
- lifeboat
- life extension
- machine learning
- mapping
- materials
- mathematics
- media & arts
- military
- mobile phones
- moore's law
- nanotechnology
- neuroscience
- nuclear energy
- nuclear weapons
- open access
- open source
- particle physics
- philosophy
- physics
- policy
- polls
- posthumanism
- privacy
- quantum physics
- rants
- robotics/AI
- satellites
- science
- scientific freedom
- security
- sex
- singularity
- software
- solar power
- space
- space travel
- strategy
- supercomputing
- surveillance
- sustainability
- telepathy
- terrorism
- theory
- thought controlled
- time travel
- tractor beam
- transhumanism
- transparency
- transportation
- treaties
- virtual reality
- water
- weapons
- wearables
Top 30 Authors
- Genevieve Klien
- Quinn Sena
- Dan Breeden
- Shubham Ghosh Roy
- Saúl Morales Rodriguéz
- Shailesh Prasad
- Gemechu Taye
- Kelvin Dafiaghor
- Paul Battista
- Karen Hurst
- Dan Kummer
- Klaus Baldauf
- Jose Ruben Rodriguez Fuentes
- Omuterema Akhahenda
- Derick Lee
- Alberto Lao
- Shane Hinshaw
- Raphael Ramos
- Sean Brazell
- Steve Hill
- Seb
- Cecile G. Tamura
- Michael Lance
- Brent Ellman
- Jason Blain
- Atanas Atanasov
- Andreas Matt
- Montie Adkins
- Ira S. Pastor
- Nicholi Avery
All Authors
- 21st Century Tech Blog
- Maria Entraigues Abramson
- Mario Acosta
- Montie Adkins
- Andres Agostini
- Yugal Agrawal
- Tanvir Ahmed
- Omuterema Akhahenda
- Kemal Akman
- Liliana Alfair
- Greg Allison
- Jacob Anderson
- Lon Anderson
- Athena Andreadis
- Amara Angelica
- Michael Anissimov
- Elmar Arunov
- Dustin Ashley
- Atanas Atanasov
- Tracy R. Atkins
- Adriano Autino
- Nicholi Avery
- Yasemin B.
- Nicola Bagalà
- Gerard Bain
- Lawrence Baines
- Buddy Baker
- Klaus Baldauf
- Ankur Bargotra
- Joseph Barney
- Florence Pauline Gardose Basubas
- Jason Batt
- Jeremy Dylan Batterson
- Paul Battista
- Eric Baum
- Zola Balazs Bekasi
- Danny Belkin
- Joe Bennett
- Harry J. Bentham
- Daniel Berleant
- James Bickerton
- Alexandria Black
- Chuck Black
- Jason Blain
- Scott Bleackley
- Heather Blevins
- Phillipe Bojorquez
- Robert Bosnjak
- Johnny Boston
- Phil Bowermaster
- Sean Brazell
- Dan Breeden
- Julia Brodsky
- Chuck Brooks
- Arthur Brown
- Jim Brownfield
- Chris Browning
- Dirk Bruere
- Rachel Burger
- Bruce Burke
- Matthew Calero
- Ryan Calo
- Randy Campbell
- Alexandra Carmichael
- Alan Carsey
- Alessandro Carvalho
- Jamais Cascio
- John Cassel
- Peter Cawdron
- Juliian C'estMoi
- Rob Chamberlain
- Dennis Chamberland
- Natalie Chan
- Dmitrii Chekh
- Nicolas Chernavsky
- Chiara Chiesa
- Gary Michael Church
- Darnell Clayton
- Sidney Clouston
- Seth Cochran
- Logan Thrasher Collins
- José Cordeiro
- Nick Cordingly
- Franco Cortese
- Rebecca D. Costa
- Wei Cui
- Steven Curley
- Keith Curtis
- Sean Cusack
- Schwann Cybershaman
- Kelvin Dafiaghor
- Jayaprakash Damothran
- Dalton Daniel
- Richard Darienzo
- DataPacRat
- Jim Davidson
- John Davies
- Scott Davis
- Tahir Dawood
- Stan Daymond
- Alex Deadpool
- Yuri Deigin
- Peter DeKraker
- Alan DeRossett
- Ovie Desire
- Clyde DeSouza
- Leif DeVaney
- Michael Dickey
- Odette Bohr Dienel
- Lucas Dimoveo
- Mike Diverde
- Michael Dodd
- James Doehring
- Johnathan Doetry
- Bruce Dorminey
- James Dunn
- Ratnesh Dwivedi
- Bill D'Zio
- Dean Eaketts
- Amnon H. Eden
- Odd Edges
- Alexandros El
- Brent Ellman
- Dr Nick Engerer
- Joaquín Alvira Enríquez
- Blair Erickson
- Marcos Than Esponda
- Chris Evans
- Dylan Evans
- Woody Evans
- Eamon Everall
- Dan Faggella
- Alvaro Fernandez
- Christopher Field
- Adam Ford
- Durwin Foster
- Will Fox
- Bob Freeman
- Ron Friedman
- Magnus Frolov
- Jose Ruben Rodriguez Fuentes
- Steve Fuller
- Matt Funk
- Muhammad Furqan
- Future Timeline
- Edward Futurem
- Hiel Salming Gagarin
- Ole Peter Galaasen
- Colin Gallagher
- John Gallagher
- Julius Garcia
- Bryan Gatton
- Victoria Generao
- Joseph Anoop George
- Jennifer Gidley
- Paul Gonçalves
- Markus Goritschnig
- Ron Gowans-Savage
- Lily Graca
- Richard Graf
- Andrés Grases
- M. A. Greenstein
- Michael Greve
- Robert Grüning
- William E. Halal
- Ian Hale
- Chris K. Haley
- Tristan Hambling
- Stuart Hameroff
- James Hampton
- Jacob Haqq-Misra
- Narenda Har
- Stevan Harnad
- Matthew Harris
- Steven B. Harris
- Brady Hartman
- Mishari Al Hasawi
- Maciamo Hay
- Ciaran Healy
- Lola Heavey
- Andreas M. Hein
- Orenda Urbano Hernández
- Denise Herzing
- Martin Higgins
- Steve Hill
- Shane Hinshaw
- Karlyn Hixson
- Cherrie Ho
- Jeffrey Dean Hochderffer
- Dave Holt
- Matthew Holt
- David Houlding
- Kevin Huang
- Neurozo Huang
- John Hunt
- Nancie Hunter
- Eric Hunting
- Karen Hurst
- Krys Hyff
- Kelly Idehen
- Brett Gallie II
- Early Boykins III
- Robin Indeededo
- Peer Infinity
- Initiative for Interstellar Studies
- Zoltan Istvan
- Ruth Itzhaki
- Joseph Jackson
- Arav Jain
- Mary Jain
- Naveen Jain
- Vivek Jaiswal
- Chris Parbey Jnr
- Joseph John
- Summer Johnson
- Matt Johnstone
- Faith Jones
- Roderick Jones
- Steve Jordan
- Henrique Jorge
- Alan Jurisson
- Roman Kam
- Richard Kane
- Al Karaki
- Håkon Skaarud Karlsen
- Stu Kauffman
- James Felton Keith
- David J. Kelley
- Bill Kemp
- Chris J. Kent
- Samuel H. Kenyon
- Tom Kerwick
- Nare Khachatryan
- Farooq Khan
- Lawrence Klaes
- Bruce Klein
- Eric Klien
- Genevieve Klien
- Josef Koch
- Randal A. Koene
- Maria Konovalenko
- Oguzhan Kosar
- William Kraemer
- LHC Kritik
- Bob Krone
- Paulus Kudyak
- Dan Kummer
- Ray Kurzweil
- Marios Kyriazis
- Ósìnàkáchì Ákùmà Kálù
- Michael Lance
- Alberto Lao
- Mark Larkento
- Brandon Larson
- Cadell Last
- Michael LaTorra
- Manuel Canovas Lechuga
- Derick Lee
- Jeffrey L. Lee
- Michael Lee
- Valentina Lencautan
- Lilia Lens-Pechakova
- Gerd Leonhard
- Denisa Lepădatu
- Amberley Levine
- Jeremy Lichtman
- Teresa Lien
- Alan R. Light
- Malak Trabelsi Loeb
- Longevity
- Melvin Louis
- Ivan Lovric
- Dan Lovy
- JK Lund
- Mike Lustgarten
- Teresa Lynn
- Donald Maclean
- Alexander MacRae
- Pat Maechler
- Shahriar Mahmud
- Narendra Malewar
- Kiran Manam
- Jeremy Mancuso
- Jake Mann
- John Mardlin
- Thierry Marianne
- Lori Marino
- John Marlowe
- Kaiser Matin
- Andreas Matt
- Clark Matthews
- Frankie May
- Michael Walton McAnally
- Chris Mcaulay
- Tom McCabe
- Paul McGlothin
- Jamie McGuigan
- Matt McGuirl
- Joe McKinney
- Roman Mednitzer
- J.P. Medved
- Zack Miles
- Cathy Miller
- Elena Milova
- Josh Mitteldorf
- Alireza Mokri
- Marco Monfils
- Poopeh Morakkabati
- Peter Morgan
- Tatiana Moroz
- Paul Moscarella
- Victor V. Motti
- Thomas Munyon
- B.J. Murphy
- Jeff Myers
- Ramez Naam
- Mark Nall
- Unni Neel
- Caycee Dee Neely
- Sara Negar
- Steve Nerlich
- The Neuro-Network
- Steve Nichols
- Danko Nikolic
- David Nordfors
- Florence Nsiah
- Johan Nygren
- Nikki Olson
- Ours Ondine
- David Orban
- David Orrell
- Ken Otwell
- Jeffery Pacheco
- Steven Palter
- Mark Parkins
- Carla Parsons
- Eithen Pasta
- Ira S. Pastor
- Emanuel Yi Pastreich
- Michael Paton
- Ian D. Pearson
- Carse Peel
- Justin Penrose
- George Perry
- Jimmé Peters
- Michael Phillips
- Jim Pinkerton
- Federico Pistono
- Nicholas Play
- Thomas M. Powers
- Robert James Powles
- Shailesh Prasad
- Nonthapat “Brave” Pulsiri
- Walter Putnam
- Jimmy Quaresmini
- Vjekoslav Radišić
- Raphael Ramos
- Joseph Rampolla
- Yurii Rashkovskii
- Daniel W. Rasmus
- Mean Raven
- Philip Raymond
- Roderick Reilly
- Bill Retherford
- Michael Graham Richard
- Maico Rivero
- Germen Roding
- Alexander Rodionov
- Saúl Morales Rodriguéz
- Len Rosen
- Xavier Rosseel
- Martine Rothblatt
- Fyodor Rouge
- Asim Roy
- Roy
- Shubham Ghosh Roy
- Mike Ruban
- Pasha Rudenko
- Otto E. Rössler
- Mark Sackler
- Bob Sampson
- Laura Samsó
- Albert Sanchez
- Rosalind Sanders
- Magaly Santiago
- Maria Santos
- Julian Sapp
- Richard Christophr Saragoza
- Roland Schiefer
- Johan Scholtz
- Frank Schueler
- Eric Schulke
- Dirk Schulze-Makuch
- Seb
- Josh Seeherman
- Myra Sehar
- Brandon Seifert
- Quinn Sena
- Daniel Shafrir
- Arzu Al Siam
- Jamal Simpson
- Amalie Sinclair
- Eli Sklar
- Chris Smedley
- Andrew Smith
- James Christian Smith
- Rick Smyre
- Mike Snead
- Rx Sobolewski
- Tom Soetebier
- Benjamin T. Solomon
- Claudio Soprano
- Bruno Henrique de Souza
- Nova Spivack
- Chavis Srichan
- Oliver Starr
- Jason Stone
- Frank Sudia
- Takayuki Sugano
- Daniel Sunday
- Cecile G. Tamura
- Anderson Tan
- Sergio Tarrero
- Gemechu Taye
- Michael Taylor
- Wise Technology
- Reno J. Tibke
- Art Toegemann
- Laurence Tognetti
- Tihamer "Tee" Toth-Fejel
- Patrick Tucker
- Alexei Turchin
- Zachary Urbina
- Paul Velho
- Aaron Vesey
- Clément Vidal
- Prem Vijaywargi
- Alex Vikoulov
- Natasha Vita-More
- Paul M. Vittay
- Aleksandar Vukovic
- Glenn A. Walsh
- Frans van Wamel
- Brian Wang
- Simon Waslander
- TJ Wass
- Jaysen West
- Matthew White
- Alexandra Whittington
- Marcia Wiegand
- Keith Wiley
- J.R. Willett
- Samson Williams
- Chima Wisdom
- Müslüm Yildiz
- TJ Yoo
- Tomer Ze'ev








Comments are closed.