This year’s Nobel Prize in Physics celebrated the fundamental interest of quantum entanglement, and also envisioned the potential applications in “the second quantum revolution”—a new age when we are able to manipulate the weirdness of quantum mechanics, including quantum superposition and entanglement. A large-scale and fully functional quantum network is the holy grail of quantum information sciences. It will open a new frontier of physics, with new possibilities for quantum computation, communication, and metrology.
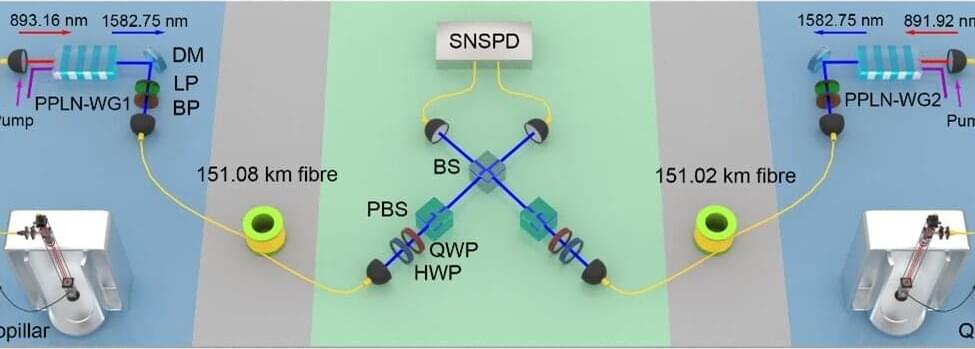
One of the most significant challenges is to extend the distance of quantum communication to a practically useful scale. Unlike classical signals that can be noiselessly amplified, quantum states in superposition cannot be amplified because they cannot be perfectly cloned. Therefore, a high-performance quantum network requires not only ultra-low-loss quantum channels and quantum memory, but also high-performance quantum light sources. There has been exciting recent progress in satellite-based quantum communications and quantum repeaters, but a lack of suitable single-photon sources has hampered further advances.
What is required of a single-photon source for quantum network applications? First, it should emit one (only one) photon at a time. Second, to attain brightness, the single-photon sources should have high system efficiency and a high repetition rate. Third, for applications such as in quantum teleportation that require interfering with independent photons, the single photons should be indistinguishable. Additional requirements include a scalable platform, tunable and narrowband linewidth (favorable for temporal synchronization), and interconnectivity with matter qubits.