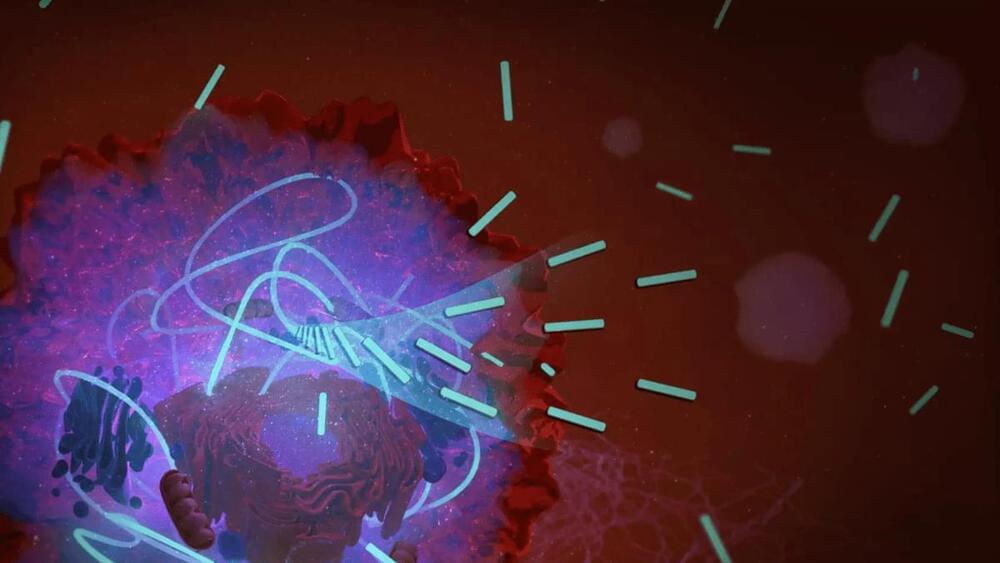
The technology at the heart of this research takes aim at one of the key metabolic functions of cells in all living things called ATP, or adenosine triphosphate. This molecule is the primary energy carrier in cells, capturing chemical energy from the breakdown of food molecules and distributing it to power other cellular processes.
Among those cellular processes is the proliferation of cancerous cells, and because of this we have seen ATP implicated in previous anti-cancer breakthroughs. The authors of the new study sought to cut off the supply of ATP, which is generated as mitochondria soak up oxygen and convert it into the molecule.