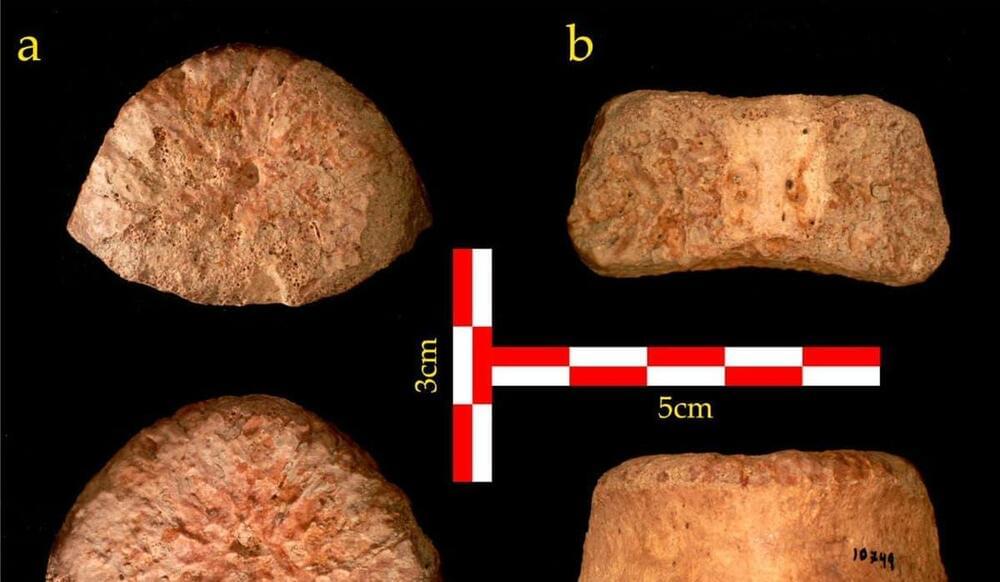
About 1.5 million years ago, a child died near the Sea of Galilee. All that remains of the youngster is a single bone, a vertebra. But that skeletal fragment, first unearthed in 1966 and only now recognized for what it actually is – the earliest large-bodied hominin found in the Levant – changes the story of human evolution.
Among other things, that one bone proves for the first time that there were multiple exits by archaic humans from Africa. At 1.5 million years of age, the bone is the second-oldest hominin fossil to be found outside Africa. The oldest date to 1.8 million years ago and were found in Dmanisi, Georgia, and that difference of about 300,000 years proves in and of itself that there was more than one exit.
More? This archaic child in the Jordan Valley and the hominins at Dmanisi were not the same species.